OpenStack (Provider View)
ZenPacks.zenoss.OpenStackInfrastructure
This ZenPack provides monitoring of OpenStack from a service provider perspective. In addition to the user-oriented components (instances, flavors, images), the underlying OpenStack servers and software are monitored.
The features added by this ZenPack can be summarized as follows. They are each detailed further below.
- Monitors overall OpenStack state, including all tenants.
- Monitors Nova, Neutron and Cinder health
- Models and monitors Nova Services and components
- Models and monitors Neutron Agents and components
- Models and monitors Cinder Services and components
- Impact and Root-Cause (Requires Zenoss Service Dynamics)
Open Source
This ZenPack is developed and supported by Zenoss Inc. Contact Zenoss to request more information regarding this or any other ZenPacks. Click here to view all available Zenoss Open Source ZenPacks.
License
GNU General Public License, Version 2, or later
Git Sources (For Cloning)
Support
This is an Open Source ZenPack developed by Zenoss, Inc. Enterprise support for this ZenPack is available to commercial customers with an active subscription.
OpenStackInfrstructure 4.0.0 Supports Queens, Rocky, Ussuri, Train, Victoria and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) version 13, 14 and 16
OpenStackInfrstructure 3.0.0 supports only Pike, Queens, and Rocky releases of OpenStack. OpenStack releases, prior to the Pike release, are not verified to work with the OpenStackInfrastrucure 3.0.0 ZenPack. Although the 3.0.0 ZenPack will work with the older AMQP based Ceilometer integration, those versions of Ceilometer are not supported by Zenoss.
Releases
Version 4.0.1-Download
- Released on 2024/08/06
- Requires PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.6.1), ZenPackLib ZenPack (>=2.1.0), OpenStack (Tenant View) ZenPack (>=1.2.3), LinuxMonitor ZenPack
- Compatible with Zenoss Cloud and Zenoss 6.7.0
Version 4.0.0-Download
- Released on 2021/08/05
- Requires PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.6.1), ZenPackLib ZenPack (>=2.1.0), OpenStack (Tenant View) ZenPack (>=1.2.3), LinuxMonitor ZenPack
- Compatible with Zenoss Cloud and Zenoss 6.7.0
Gallery
|
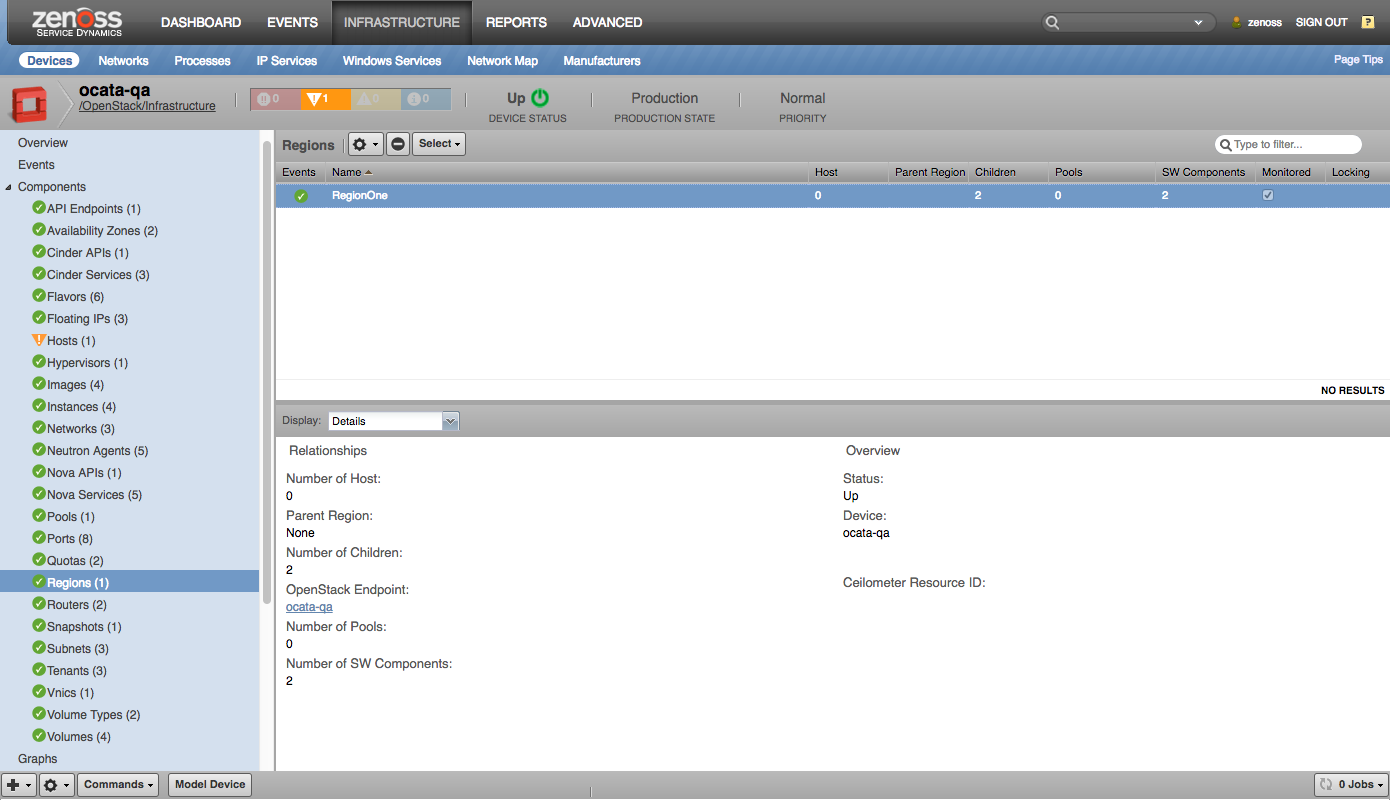
Region |
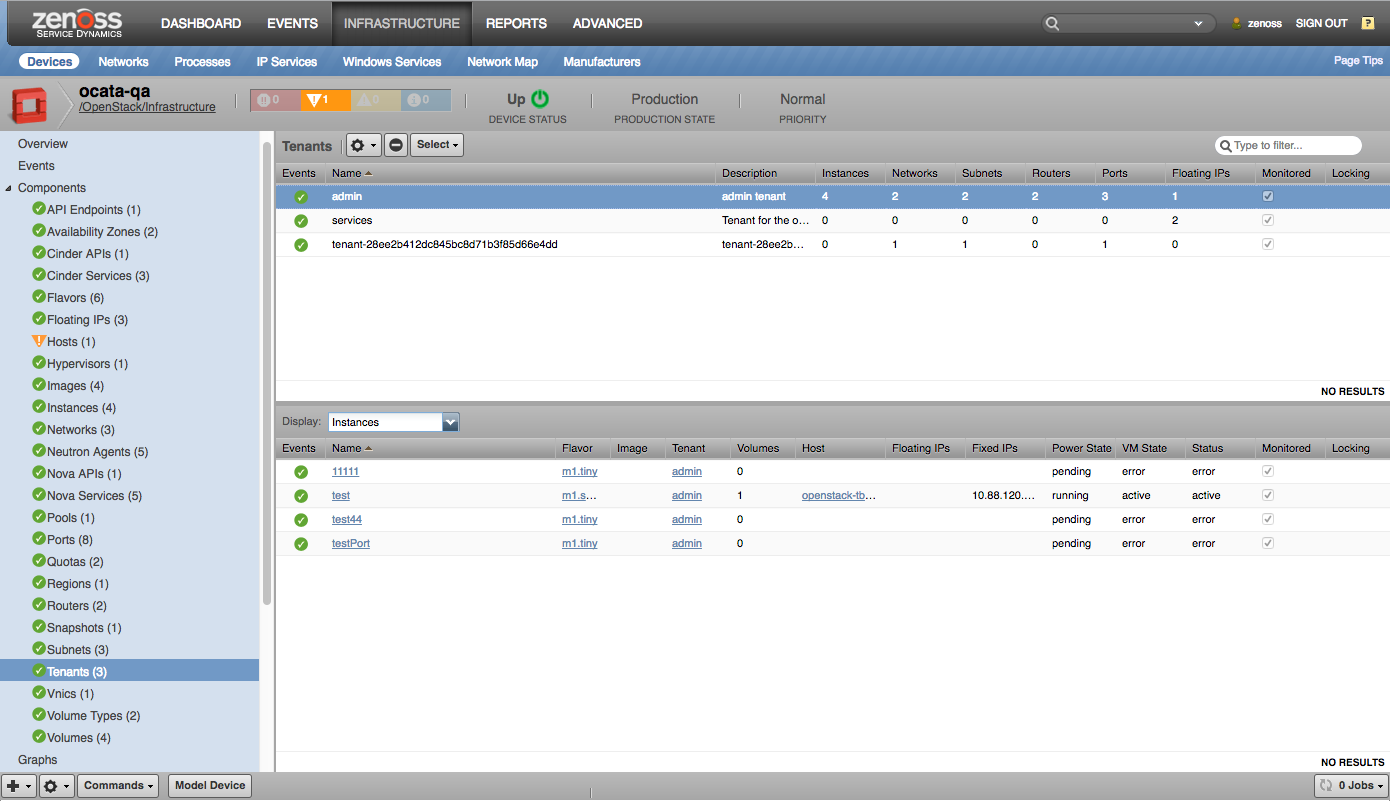
Tenants |
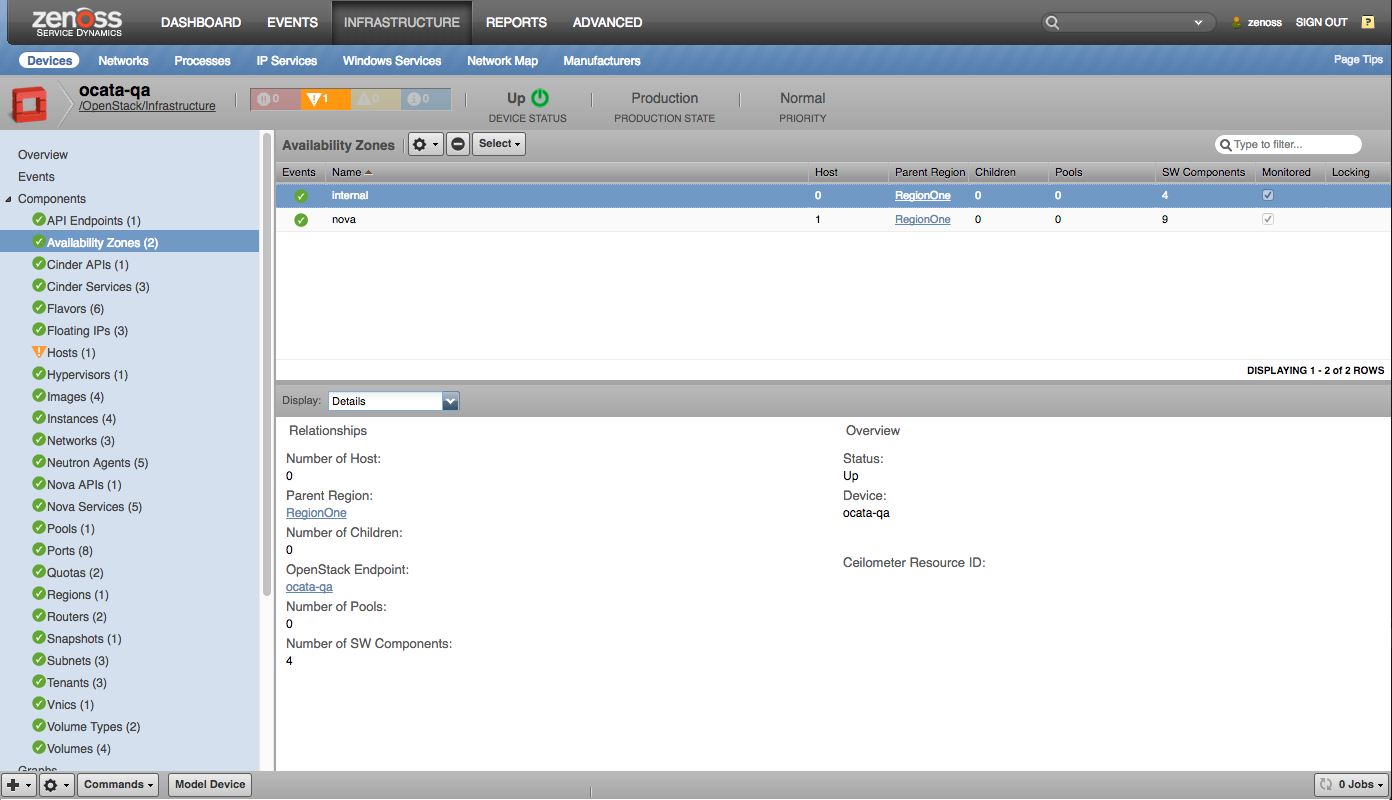
Availability Zones |
|
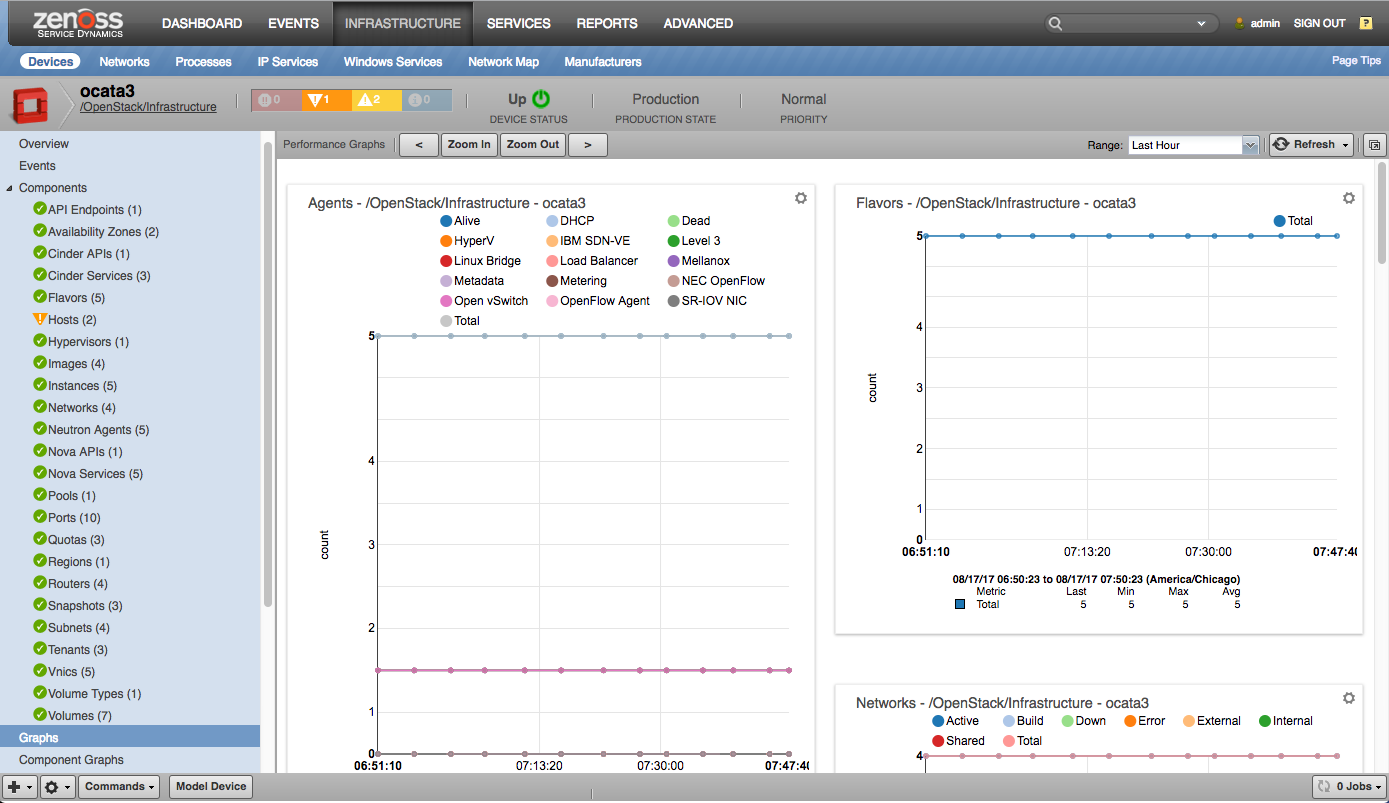
Device Graphs |
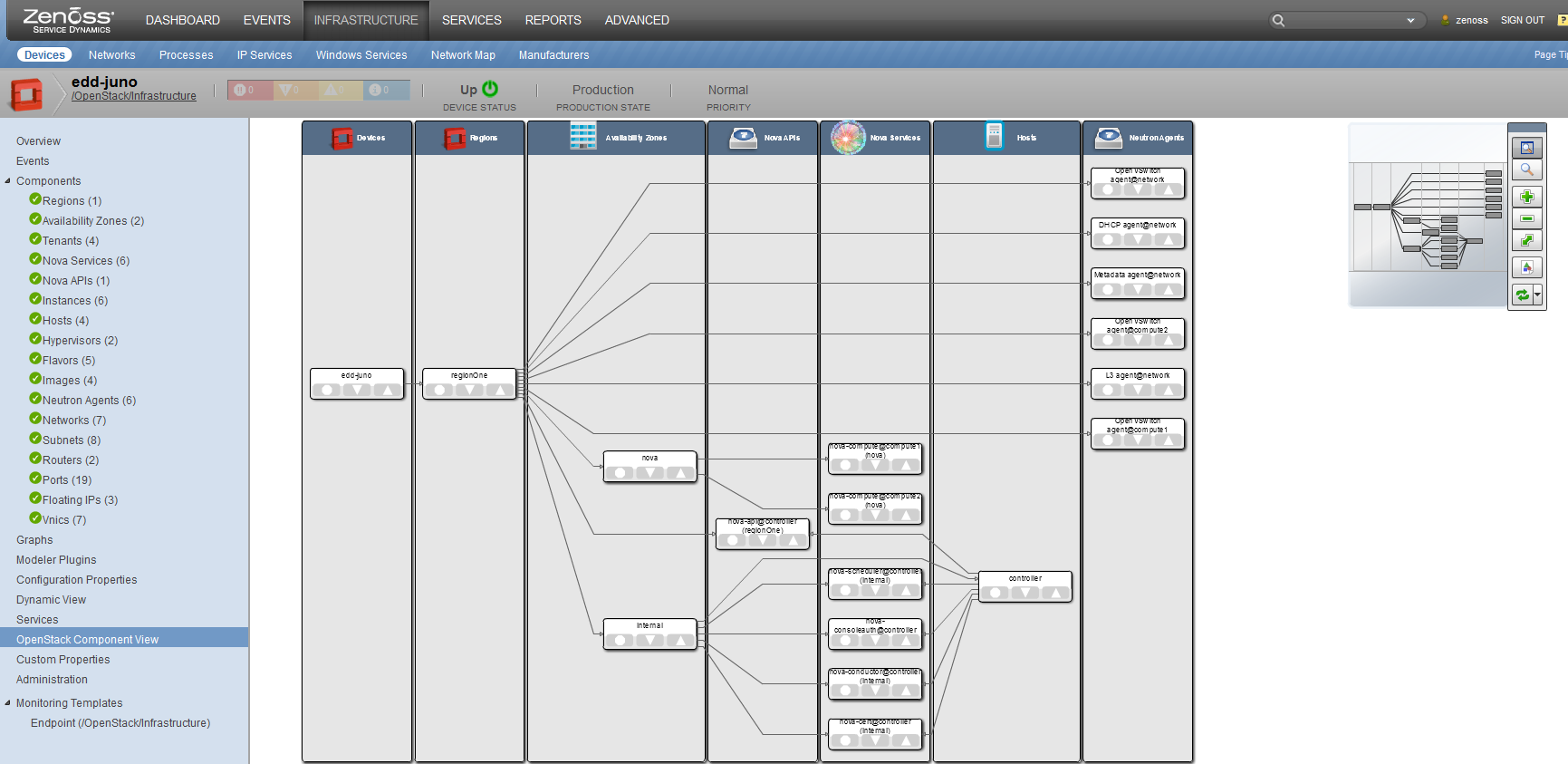
Component View |
|
|
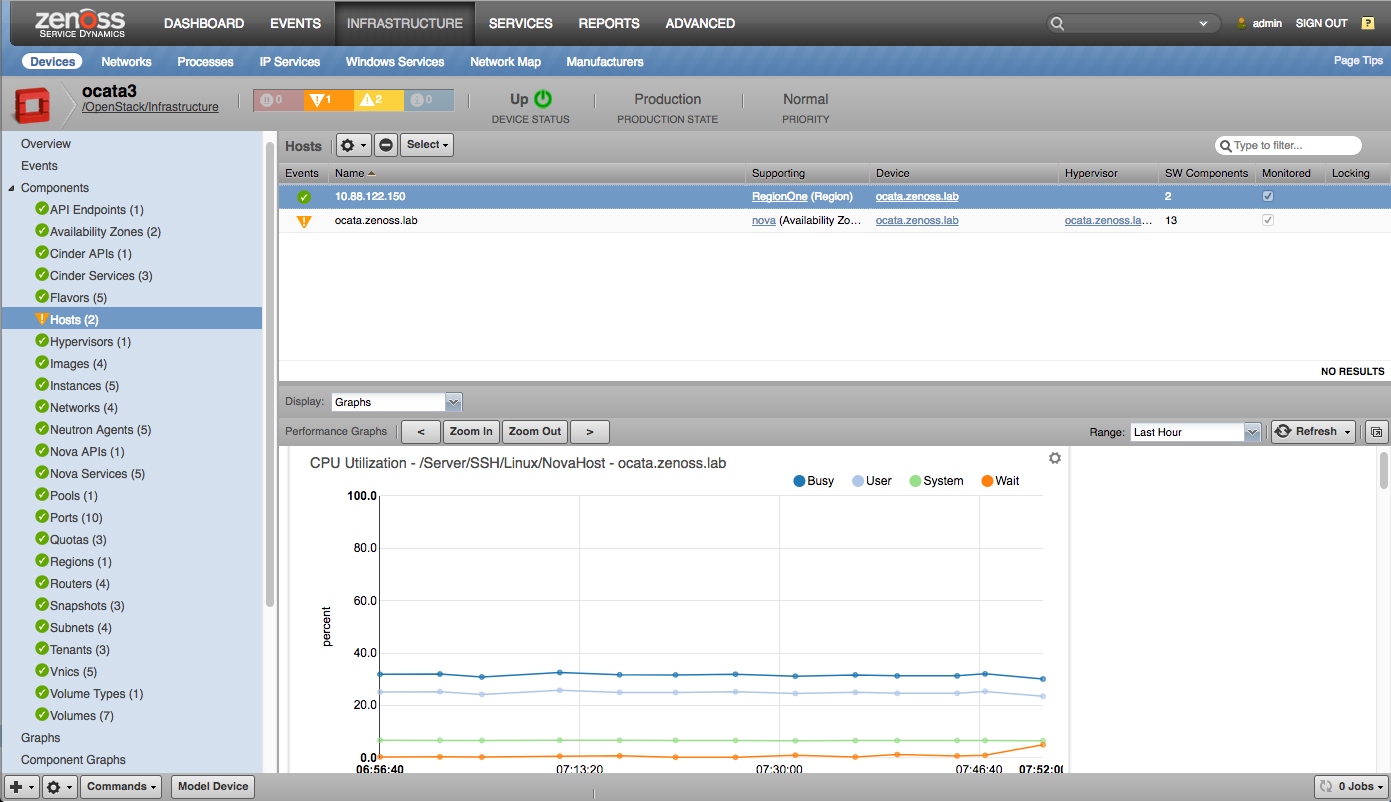
Hosts |
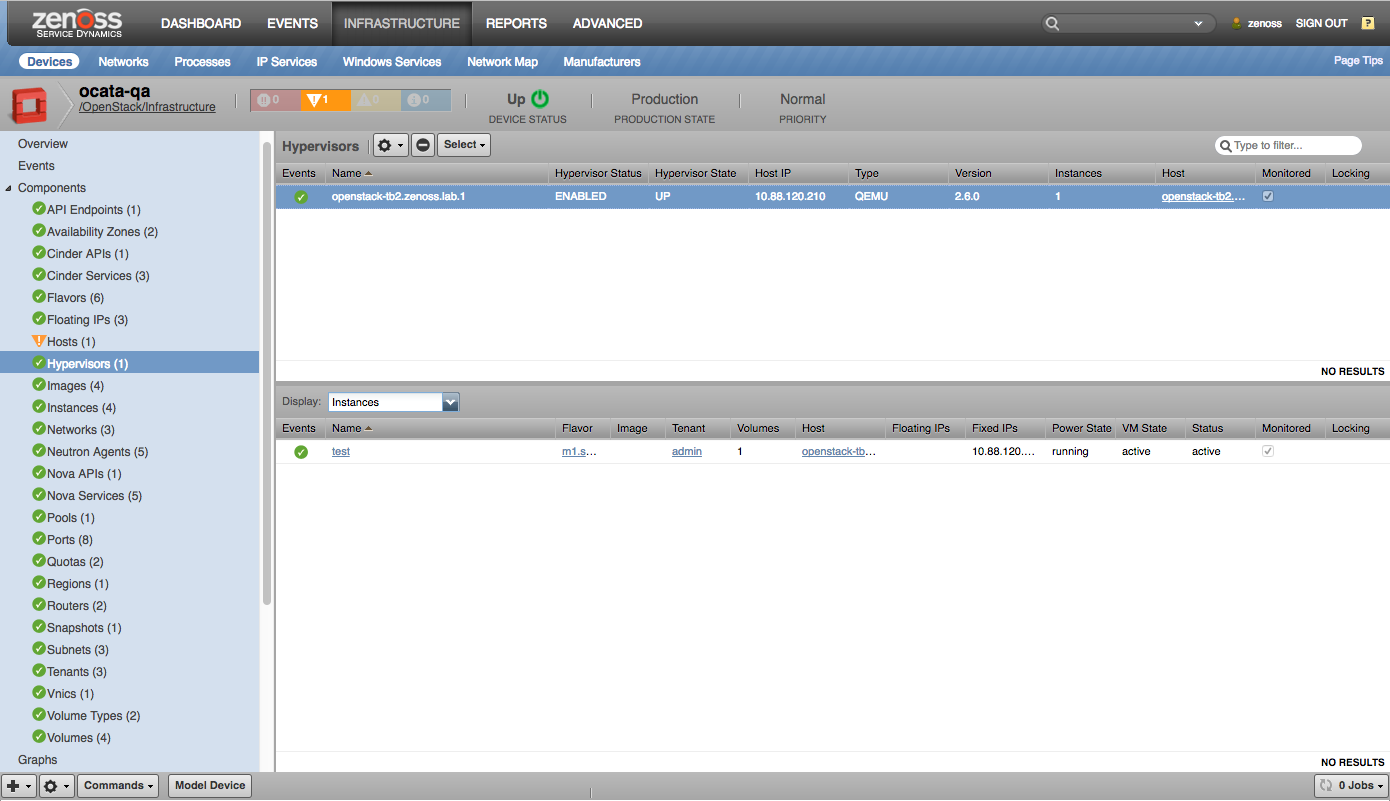
Hypervisors |
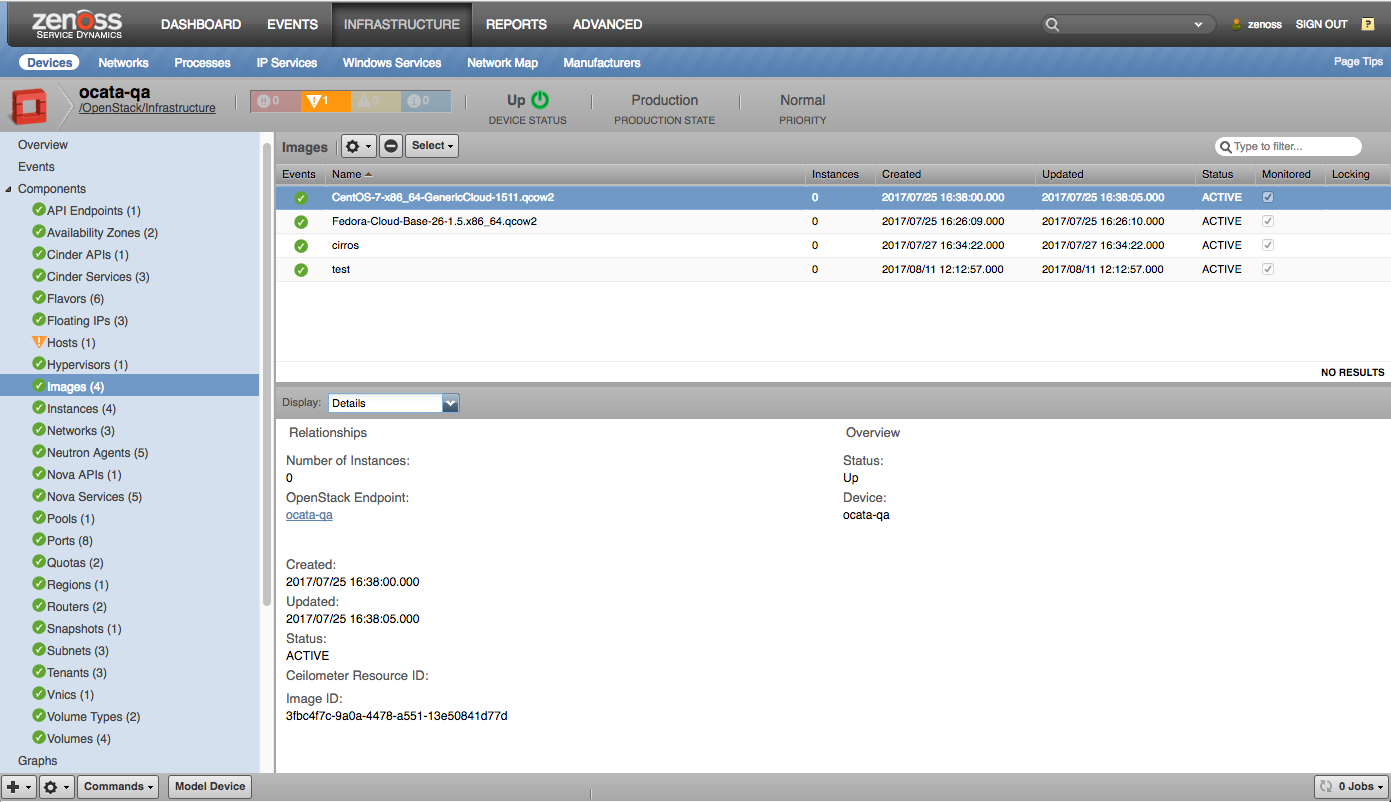
Images |
|
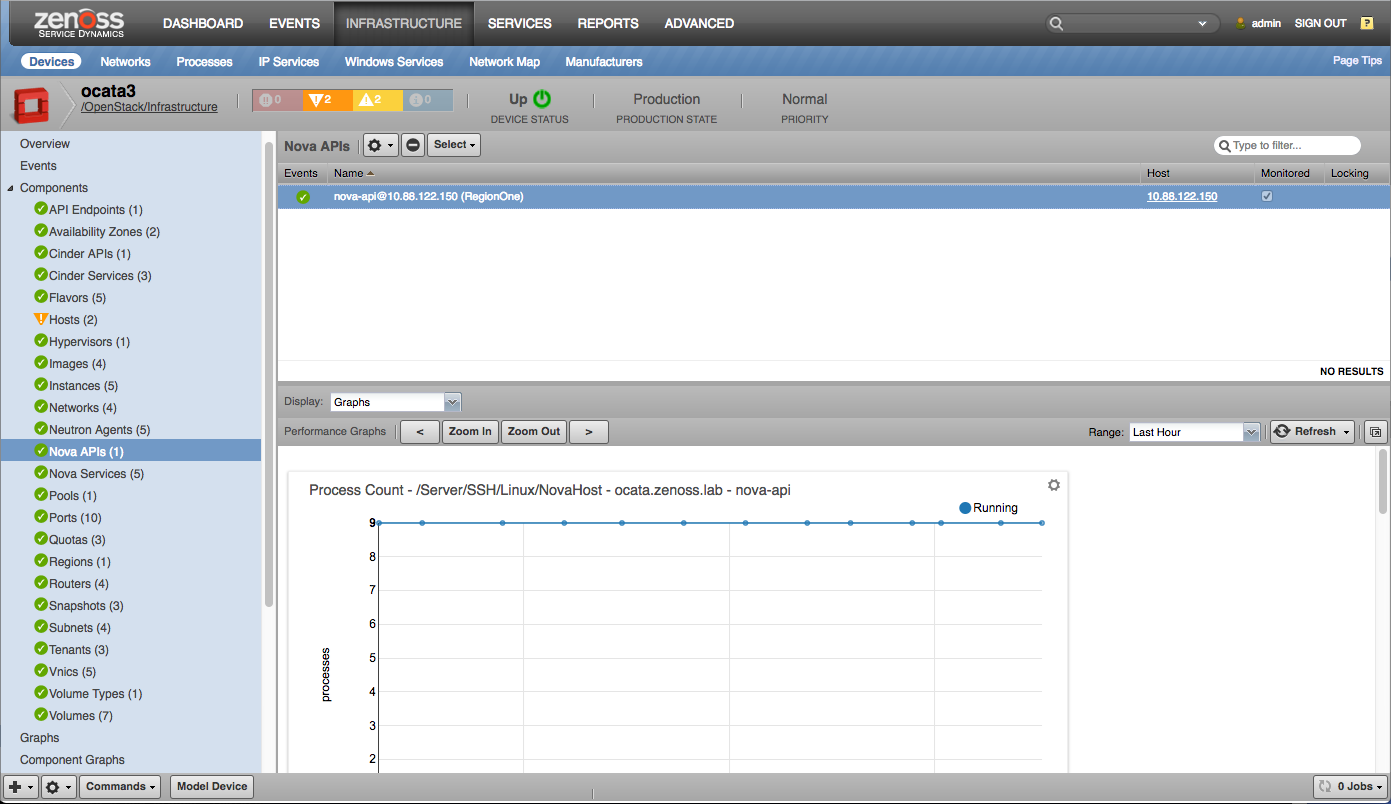
Nova APIs |
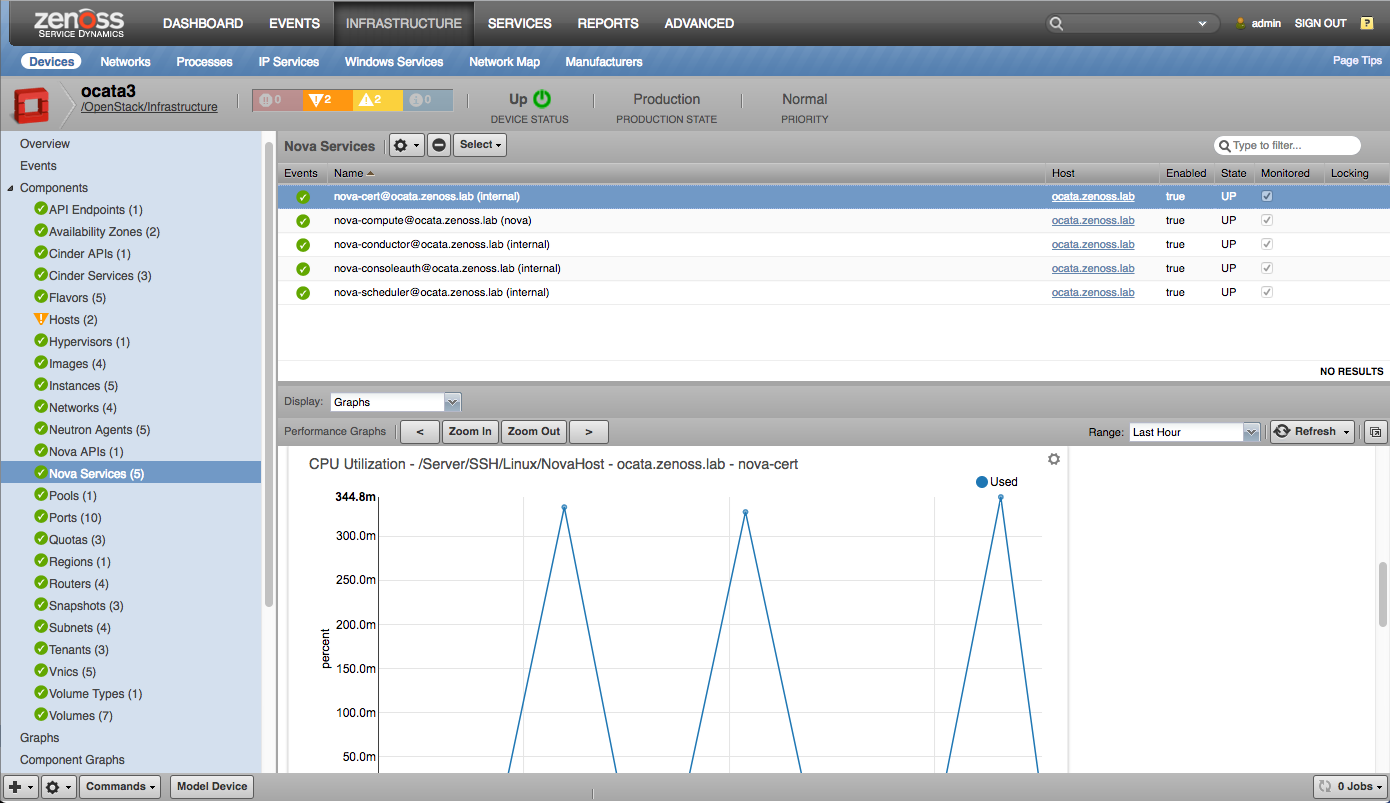
Nova Services |
Neutron Agents |
|
Instances |
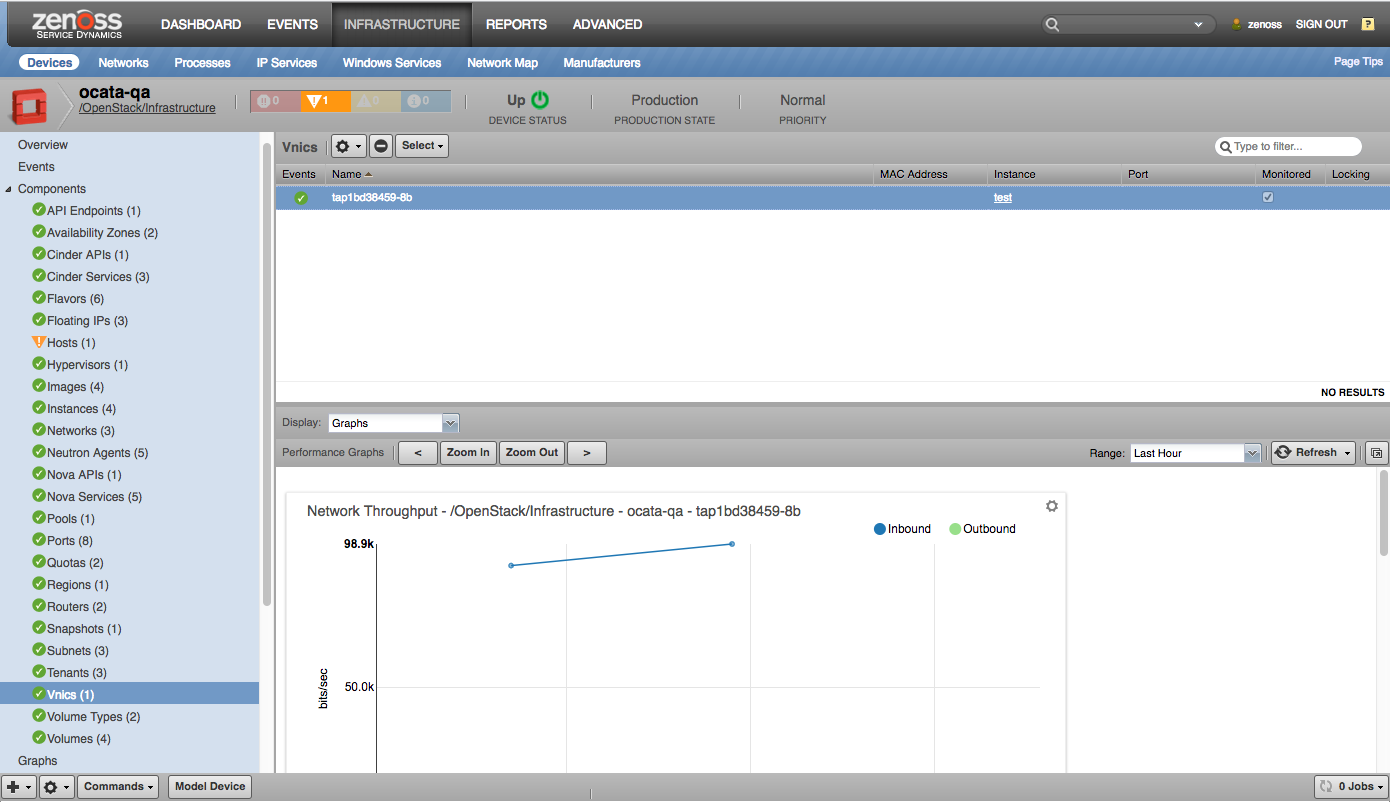
vNICs |
|
|
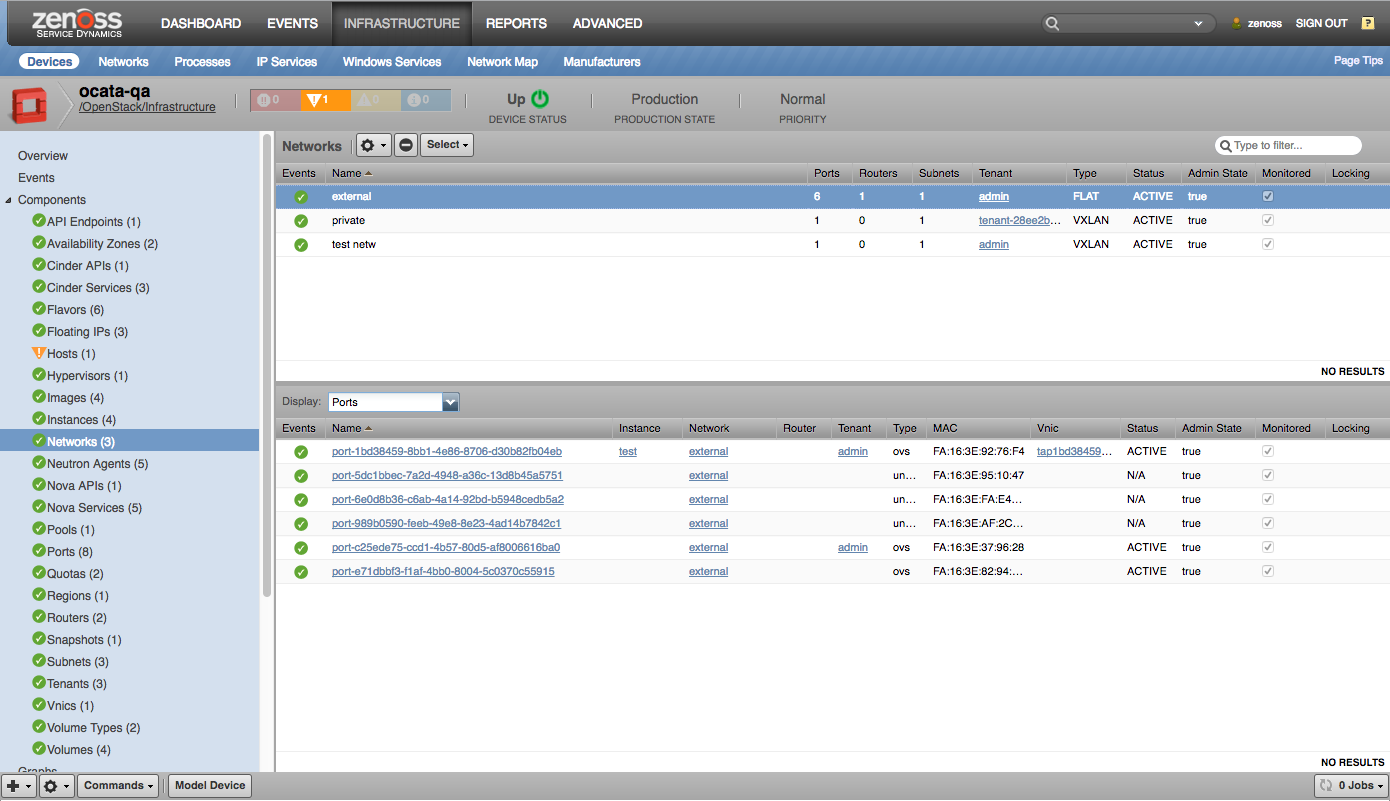
Networks |
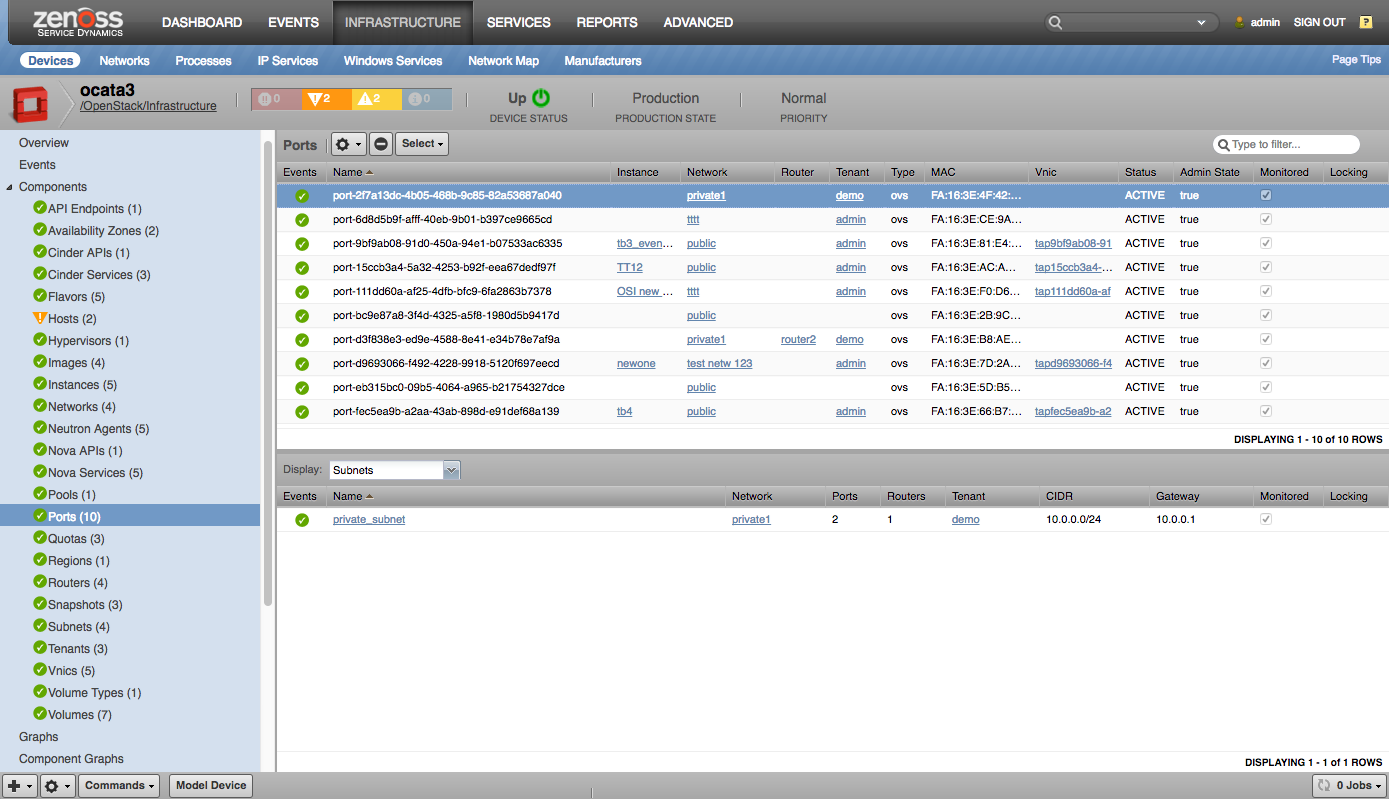
Ports |
|
|
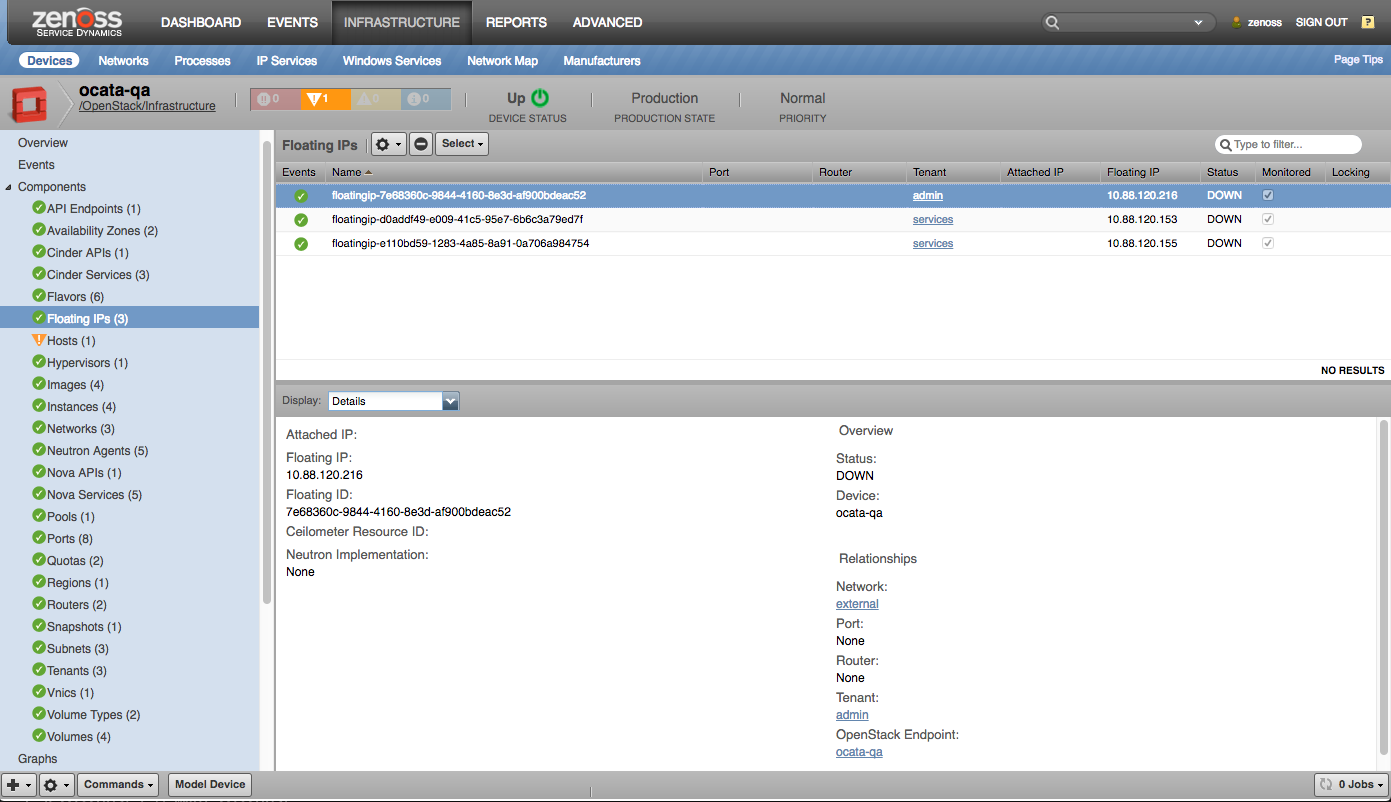
Floating IPs |
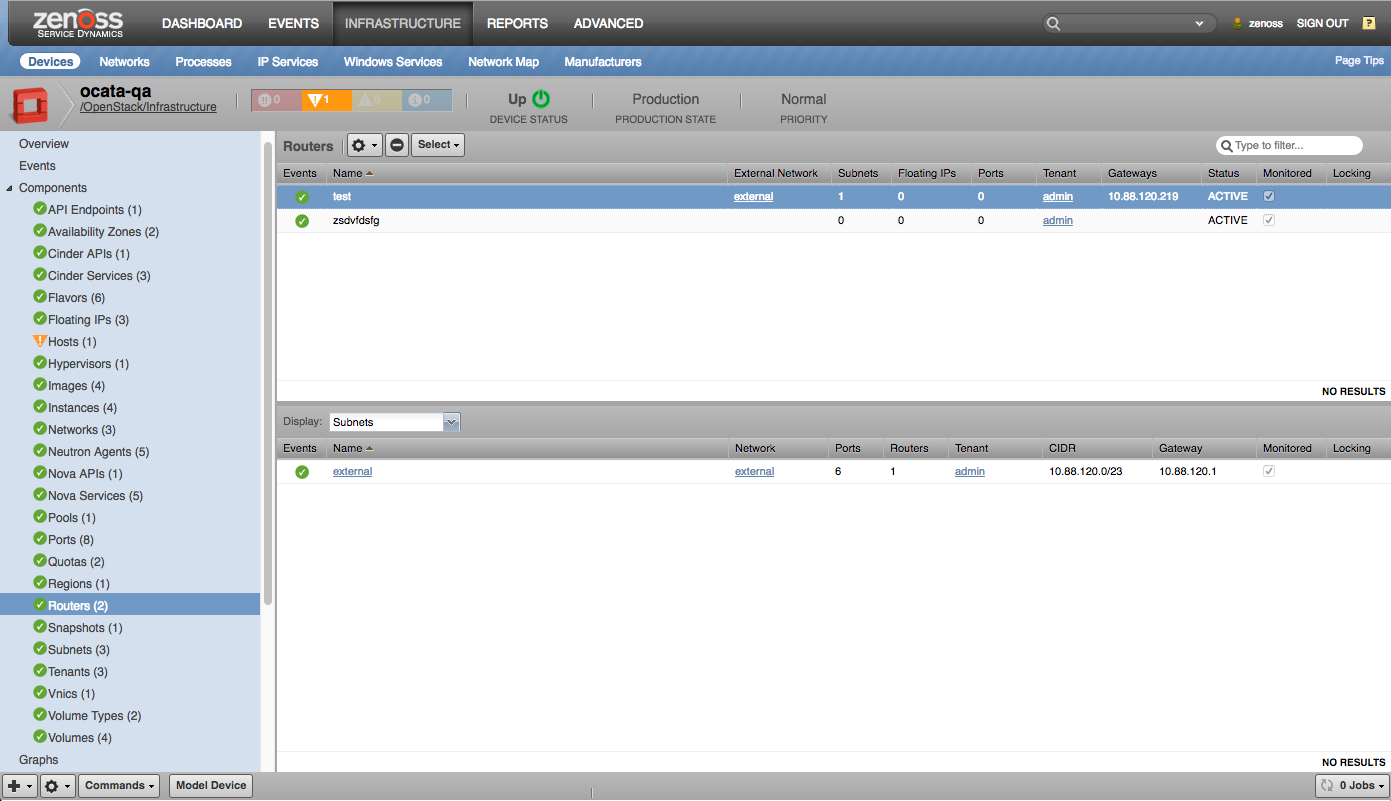
Routers |
Subnets |
|
Cinder Services |
Volumes |
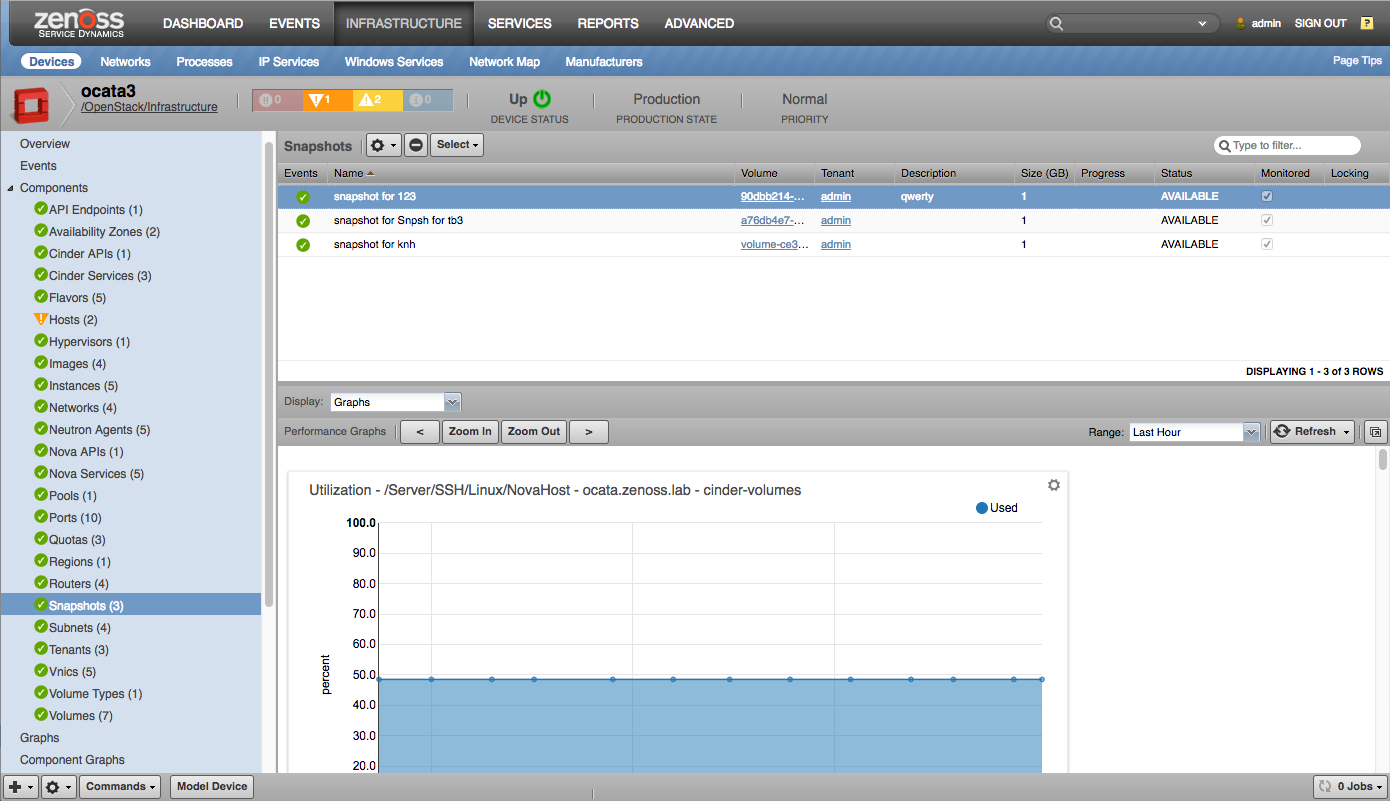
Volume Snapshots |
Prerequisites
- A supported OpenStack version (see below)
- Administrative credentials for your OpenStack environment
- Username, password, keystone URL, Region
- SSH access and credentials to the Linux devices in your OpenStack environment (See Post-ZenPack-Installation Notes)
Supported OpenStack Releases
- 2.3.x supports Mitaka
- 2.4.x supports Mitaka, Newton, and Ocata
- 3.0.0 supports Pike, Queens, Rocky, and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) version 13 and 14
Note: We denote Pike, Queens, and Rocky, RHOSP 13 and 14 as Pike+
Restricted Users
Restricted (non-administrator) users can also model and monitor OpenStack devices, with access to those devices consistent with that user's privileges. In other words, you should expect reduced visibility for restricted users.
A restricted should expect to see:
- Fewer modeled components
- Reduced monitored metrics
- Absent events for missing components
In particular, restricted users can see diminished components and metrics for:
- Cinder Pools
- Cinder Services
- Cinder Volumes
- Hypervisors
- Neutron Agents
- Nova Services
- Tenants
- Any API item that requires administrator access
If you believe a user should have more access to data, it is your responsibility to adjust the user's access level on OpenStack.
Organizational Elements
The following organizational elements are discovered:
- Regions
- Availability Zones
- Tenants
- API Endpoints
The following virtual-machine elements are discovered:
- Nova Services (processes supporting nova servers)
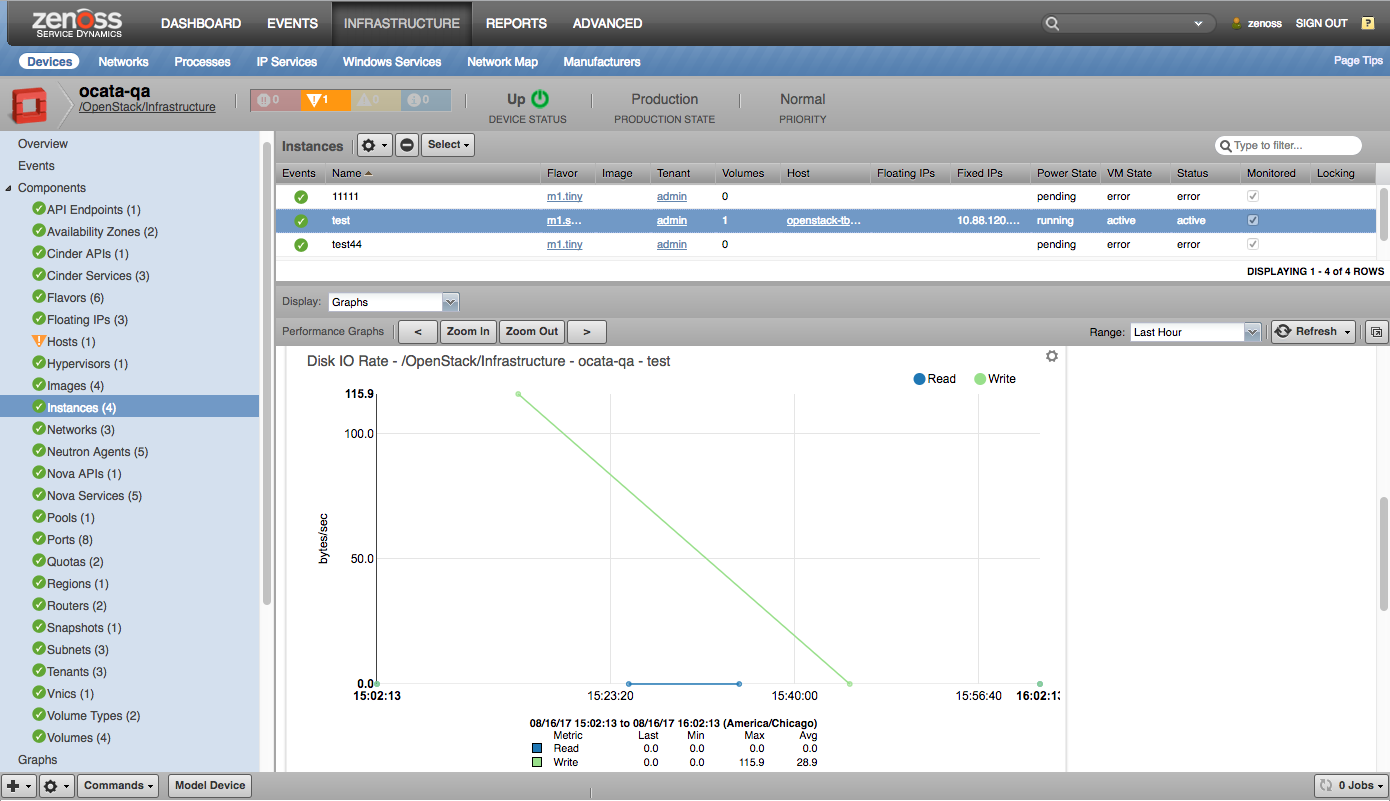
- Instances (Servers)
- Hosts
- Hypervisors
- Images
- Flavors
The following network elements are discovered:
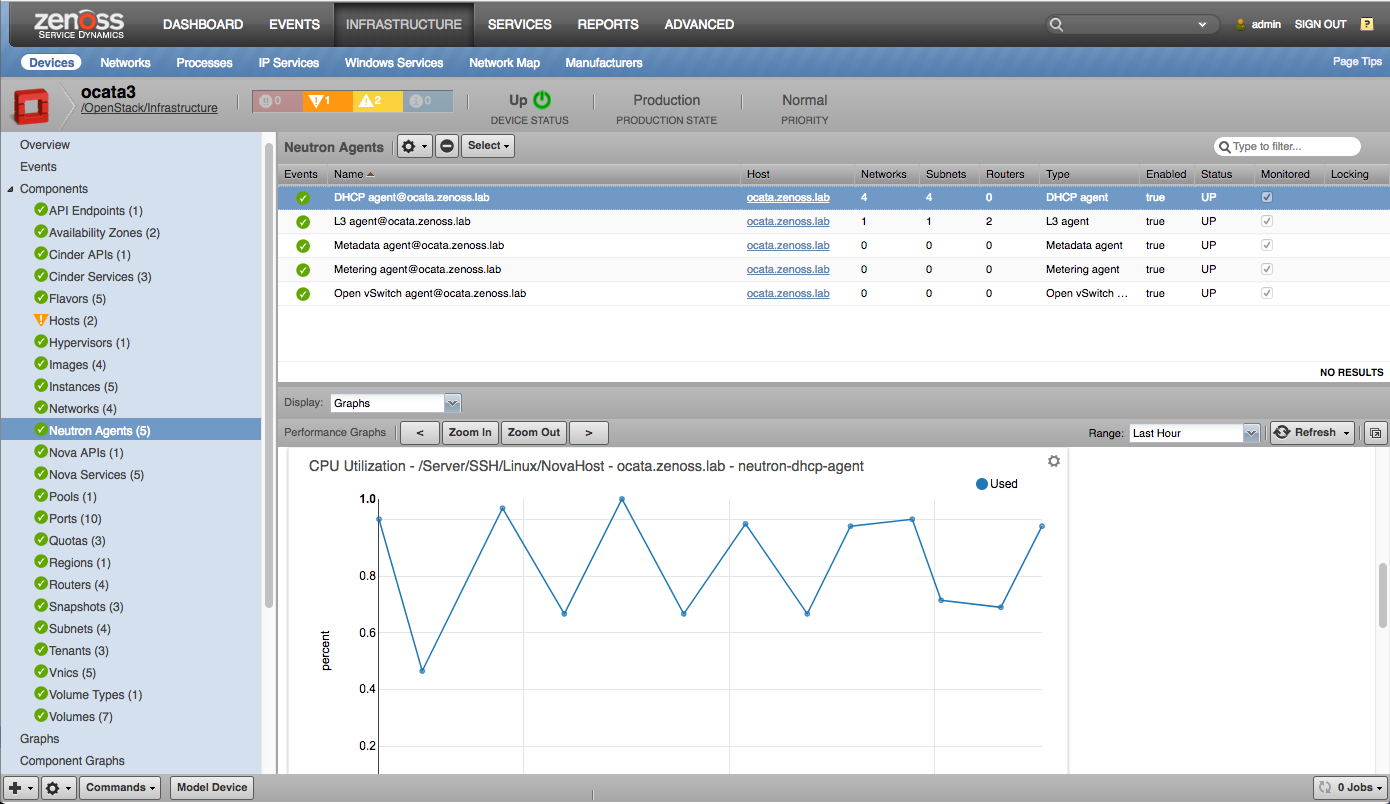
- Neutron Agents
- Networks
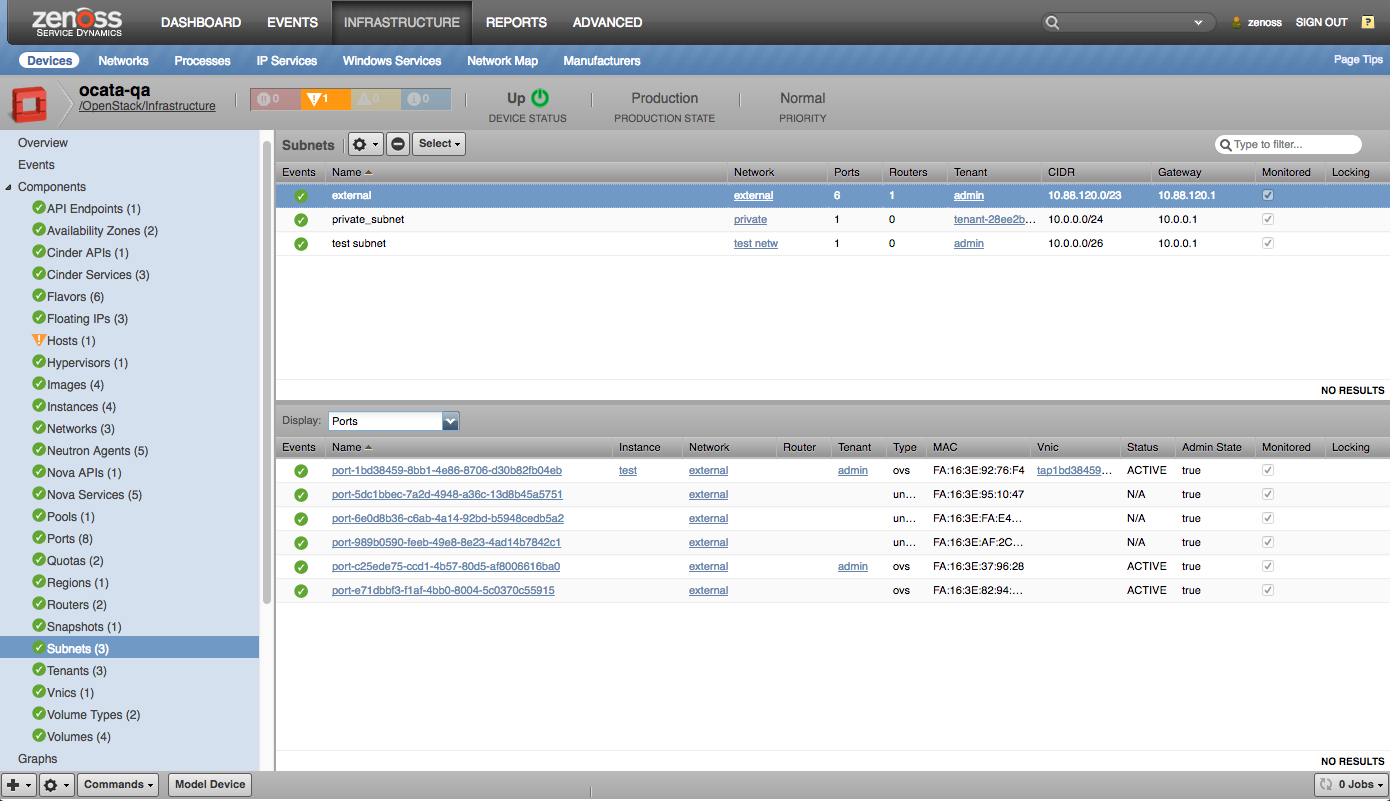
- Subnets
- Routers
- Ports
- Floating-Ips
- vNICs
The following block storage elements are discovered:
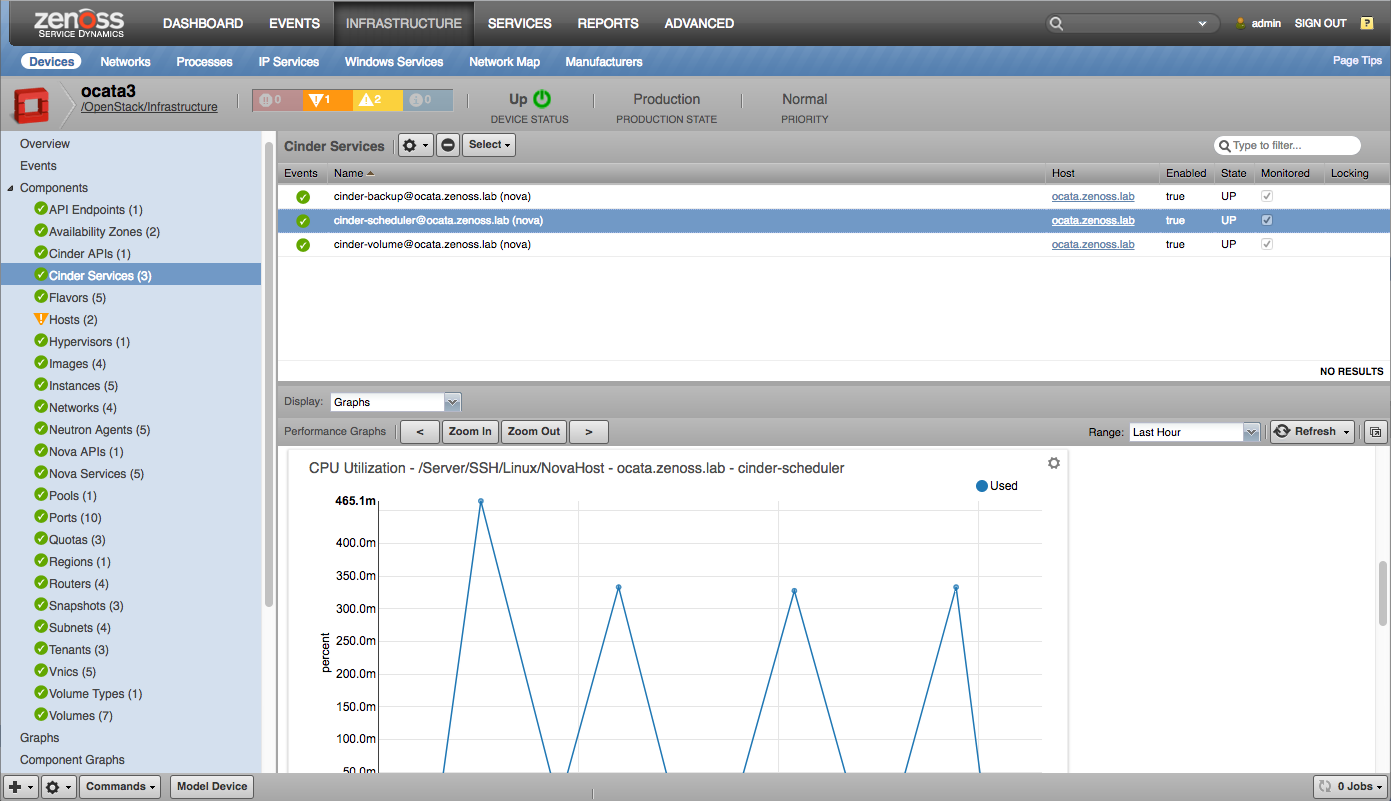
- Cinder Services (processes supporting block storage)
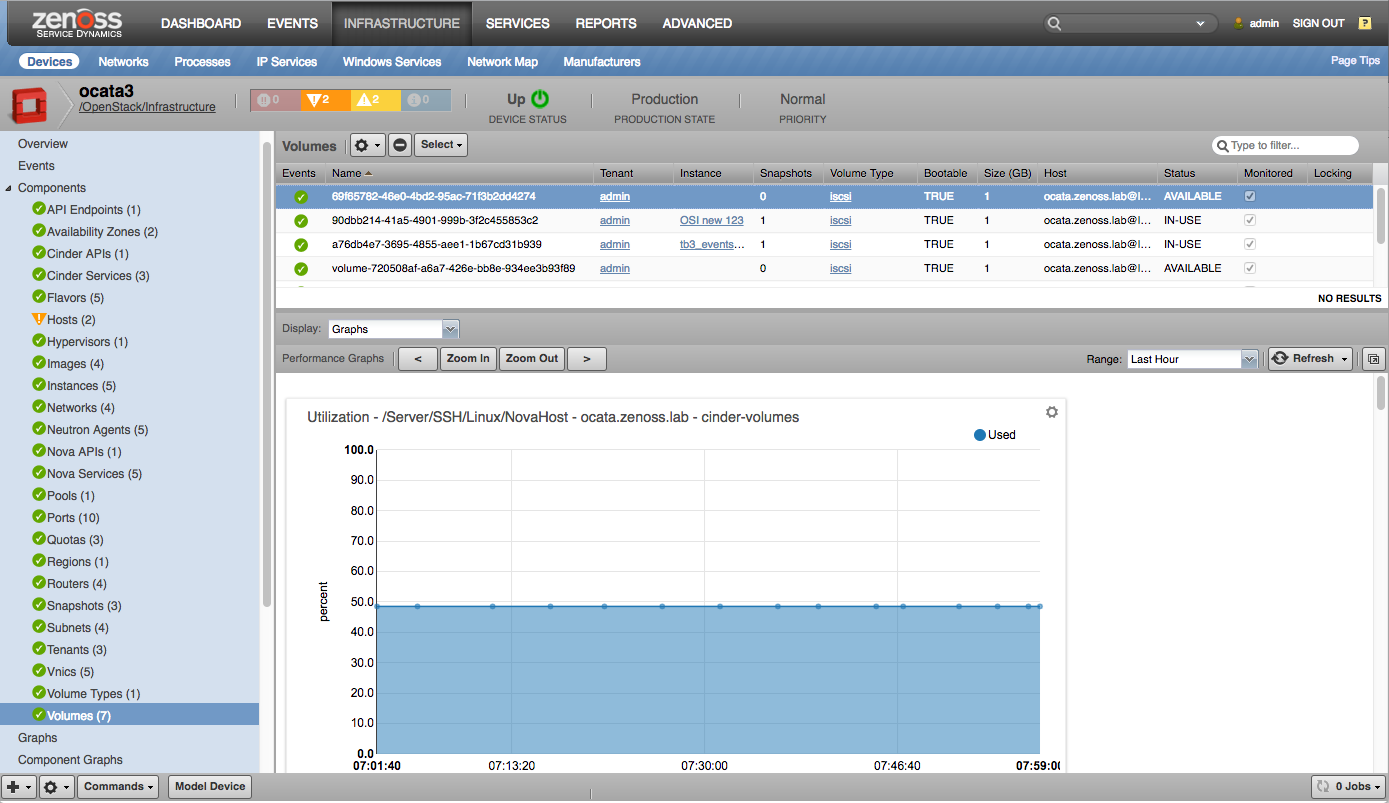
- Volumes
- Volume Snapshots
- Volume Types
- Storage Pools
- Cinder Quotas
Metrics
The following component level metrics are collected:
Instances
- CPU Utilization (percent)
- Disk Requests (requests/sec)
- Disk IO Rate (bytes/sec)
vNICs
- Network Packet Rate (packets/sec)
- Network Throughput (bytes/sec)
Hosts
- Load Average (processes)
- CPU Utilization (percent)
- Free Memory (bytes)
- Free Swap (bytes)
- IO (sectors/sec)
Nova Services
- CPU Utilization (percent)
- Memory Utilization (bytes)
- Process Count (processes)
Neutron Agents
- CPU Utilization (percent)
- Memory Utilization (bytes)
- Process Count (processes)
Cinder Services
- CPU Utilization (percent)
- Memory Utilization (bytes)
- Process Count (processes)
Volumes
- Storage Utilization (percent)
- Operation Throughput (operations/sec)
- Merge Rate (merged/sec)
- Sector Throughput (sectors/sec)
- IO Operations (operations)
- IO Utilization (percent)
- Weighted IO Utilization (weighted percent)
Volume Snapshots
- Storage Utilization (percent)
- Operation Throughput (operations/sec)
- Merge Rate (merged/sec)
- Sector Throughput (sectors/sec)
- IO Operations (operations)
- IO Utilization (percent)
- Weighted IO Utilization (weighted percent)
The following device level metrics are collected:
Flavors
- Total (count)
Images
- Total (count)
- Total count per image state
Servers
- Total (count)
- Total count per server state
Queues
- Event (count)
- Performance (count)
Agents
- Total (count)
- Total count per agent type
Networks
- Total (count)
- Total count per network state
Routers
- Total (count)
- Total count per router state
Volumes
- Total (count)
- Total count per volume state
Volume Snapshots
- Total (count)
- Total count per volume snapshot state
Volume Pool
- Total (count)
- Total count per volume pool state
Installed Items
Once installed, the ZenPack installs the following properties and components.
Daemons
The following daemons are installed:
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| Modeler | zenmodeler |
| Performance Collector | zencommand, zenpython, zenopenstack, proxy-zenopenstack |
Configuration Properties
- zOpenStackAuthUrl: The URL of the Identity endpoint.
- zOpenStackExtraHosts: The list of extra hosts that will be added to the system once OpenStack Infrastructure device is modeled.
- zOpenStackExtraApiEndpoints: A list of URLs to monitor for OpenStack APIs. Format is <service type>:<full URL> for each.
- zOpenStackHostDeviceClass: Used as a default device class for defined hosts in zOpenStackExtraHosts and zOpenStackNovaApiHosts properties. Default is /Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost.
- zOpenStackNovaApiHosts: The list of hosts upon which nova-api runs. This is required when the IP address in the nova API URL does not match any known host.
- zOpenStackCinderApiHosts: The list of hosts upon which cinder-api runs. This is required when the IP address in the cinder API URL does not match any known host.
- zOpenStackHostMapToId: A list of <name>=<id>, used to force a host referred to by OpenStack with the given name to be represented in Zenoss as a host component with the given ID. (this is not commonly used)
- zOpenStackHostMapSame: A list of <name1>=<name2>, used to inform the modeler that the same host may be referred to with an alternate name by some part of OpenStack. (this is not commonly used)
- zOpenStackNeutronConfigDir: Path to directory that contains Neutron configuration files. Default is /etc/neutron.
- zOpenStackProjectId: Corresponds to tenant name, project to work on.
- zOpenStackRegionName: The name of the OpenStack Region to use. Regions are autonomous OpenStack clouds joined together through shared Keystone identity server and managed through a common interface.
- zOpenStackRunNovaManageInContainer, zOpenStackRunVirshQemuInContainer, zOpenStackRunNeutronCommonInContainer: Used when OpenStack processes are running inside of docker containers. Provide the container names (or a pattern to match them) here, or leave blank in a non-containerized OpenStack environment.
- zOpenStackHostLocalDomain: When OpenStack hosts report names ending in .localdomain, replace domain with this value.
- zOpenStackAMQPUsername: Username for Ceilometer AMQP integration.
- zOpenStackAMQPPassword: Password for Ceilometer AMQP integration.
- zOpenStackProcessEventTypes: List of OpenStack event types to pass to Zenoss event system. (Other event types may be processed for model changes, but will not be stored as events in Zenoss)
- zOpenStackIncrementalShortLivedSeconds: Incremental Modeling - Delay component creation this period of time until no deletions are detected. (seconds)
- zOpenStackIncrementalBlackListSeconds: Incremental Modeling - Once a component is deleted, wait this interval between attempts to remodel same component to avoid flapping. (seconds)
- zOpenStackIncrementalConsolidateSeconds: Incremental Modeling - Wait this amount of time to aggregate components' properties before updating a component map. Ignored by deletions. (seconds)
- zOpenStackUserDomainName: Domain name containing opentstack user for authorization scope.
- zOpenStackProjectDomainName: Domain name containing opentstack project for authorization scope.
Device Classes
- /OpenStack: Root OpenStack device class. Typically, devices should not be put in this device class.
- /OpenStack/Infrastructure: Device class for OpenStack Infrastructure endpoints.
- /Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost: Device class for Nova host instances.
Modeler Plugins
- zenoss.OpenStackInfrastructure: Main modeler plugin- Queries the OpenStack APIs to populate the zenoss model.
- zenoss.cmd.linux.openstack.hostfqdn: Used to get OpenStack host FQDN.
- zenoss.cmd.linux.openstack.inifiles: Used to gather neutron.conf and ml2_conf.ini files.
- zenoss.cmd.linux.openstack.libvirt: Used to get OpenStack instance virtual NIC information using libvert.
- zenoss.cmd.linux.openstack.nova: Used to get installed OpenStack version.
Datasources
- ApiEndpointStatusDataSource: Checks that API endpoints are available.
- CinderServiceStatusDataSource: Checks the status of Cinder services via the Cinder API.
- EventsAMQPDataSource: Stores events received from OpenStack Ceilometer via AMQP.
- NeutronAgentStatusDataSource: Checks the status of Neutron agents via the Neutron API.
- NovaServiceStatusDataSource: Checks the status of Nova services via the Nova API.
- PerfAMQPDataSource: Stores performance data received from OpenStack Ceilometer.
- QueueSizeDataSource: Checks the number of unprocessed messages in Ceilometer AMQP queues.
Notes
-
As of the Pike+ (Late 2017) OpenStack release, the dispatcher mechanism previously used by this zenpack is no longer supported by Ceilometer. Because of this, the "heartbeat" mechanism that was previously used to verify connectivity between Ceilometer and Zenoss is no longer possible, and /Status/Heartbeat events will not be created if Zenoss stops receiving data from Ceilometer.
Connectivity problems between Ceilometer and Zenoss will still be reported in the Ceilometer agent-notification.log file on the OpenStack hosts.
-
All
OpenStack Ceilometer Perf AMQPdatasources' cycletime parameter will not work in Pike+ . Cycletime must be regulated in OpenStack itself. The cycletime setting is still present for backward compatibility with Ocata and prior versions, but has no effect.
Monitoring Templates
- /OpenStack/Infrastructure/
- Endpoint
- Instance
- vNIC
Event Classes and Mappings
- /OpenStack
- OpenStack Events Default
- /OpenStack/Cinder
- /OpenStack/Cinder/Snapshot
- Cinder Snapshot default mapping
- /OpenStack/Cinder/Volume
- cinder.volume default mapping
- /OpenStack/compute
- /OpenStack/compute/instance
- compute.instance default mapping
- compute.instance.create.error
- compute.instance.exists
- compute.instance.exists.verified.old
- /OpenStack/dhcp_agent
- dhcp_agent default mapping
- /OpenStack/firewall
- firewall default mapping
- /OpenStack/firewall_policy
- firewall_policy default mapping
- /OpenStack/firewall_rule
- firewall_rule default mapping
- /OpenStack/floatingip
- floatingip default mapping
- /OpenStack/network
- network default mapping
- /OpenStack/port
- port default mapping
- /OpenStack/router
- router default mapping
- /OpenStack/security_group
- security_group default mapping
- /OpenStack/security_group_rule
- security_group_rule default mapping
- /OpenStack/subnet
- subnet default mapping
- /Status
- openStackCinderServiceStatus
- openStackIniFileAccess
- openStackIniFileOptionParsing
- openStackNeutronAgentStatus
- openStackNovaServiceStatus
- openStackApiEndpointStatus
Processes
- /OpenStack
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-agent-central
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-agent-compute
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-agent-notification
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-alarm-evaluator
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-alarm-notifier
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-api
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-collector
- /OpenStack/ceilometer-polling
- /OpenStack/cinder-api
- /OpenStack/cinder-backup
- /OpenStack/cinder-scheduler
- /OpenStack/cinder-volume
- /OpenStack/glance-api
- /OpenStack/glance-registry
- /OpenStack/gnocchi-metricd
- /OpenStack/gnocchi-statsd
- /OpenStack/keystone-admin
- /OpenStack/keystone-all
- /OpenStack/keystone-main
- /OpenStack/neutron-dhcp-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-l3-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-lbaas-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-metadata-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-metering-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-openvswitch-agent
- /OpenStack/neutron-server
- /OpenStack/nova-api
- /OpenStack/nova-cert
- /OpenStack/nova-compute
- /OpenStack/nova-conductor
- /OpenStack/nova-consoleauth
- /OpenStack/nova-network
- /OpenStack/nova-scheduler
- /OpenStack/rabbitmq-server
Zenpack Installation
First-Time Installation
If you are installing the ZenPack for the first time, install as per usual ZenPack installation, and continue to Post-ZenPack Installation.
Upgrades from 2.4.x
If this is the first time you are upgrading to 3.0.0+ from a version of the zenpack 2.4.0 or earlier, there are no special steps required, nor any changes required on the OpenStack side.
When upgrading from 2.4.x on a system with multiple collectors, you may
see warnings such as ERRO\[0000\] Could not update proxy, as described
in ZPS-4689. These can be
safely ignored.
If you are using the ceilometer_zenoss dispatcher mechanism (with RabbitMQ) for integrating older versions of openstack with zenoss, this will still function with 3.0.0. Note that this is only supported as a bridge for old openstack environment which have not yet been upgraded to a supproted version of OpenStack. All currently supported versions use the http publisher mechanism to integrate with zenoss, rather than RabbitMQ.
Post-ZenPack Installation
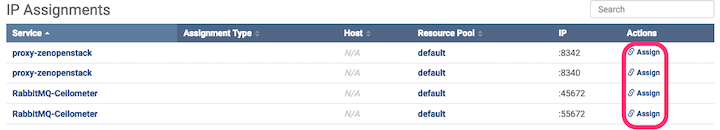
Because the zenopenstack and RabbitMQ-Ceilometer services run on each
collector, in order for openstack ceilometer to send messages to them,
they need to be assigned a specific IP address. These services will be
unable to start until IP assignment is completed. (The error service is
missing an address assignment will be displayed if you try to start the
service)
The IP assignment may be performed via the Control Center UI or command-line.
To use the UI:
- Log into the Control Center UI.
- Click the Zenoss.resmgr name to display the Applications/Zenoss.resmgr page.
- Scroll down the page to the IP Assignments section and click "Assign" next
- to each line for the proxy-openstack and RabbitMQ-Ceilometer services:
To use the command-line:
serviced service assign-ip RabbitMQ-Ceilometer serviced service assign-ip proxy-zenopenstack
If you have multiple collectors, specify the collector name for each service and repeat for each collector:
serviced service assign-ip collector1/RabbitMQ-Ceilometer serviced service assign-ip collector1/proxy-zenopenstack serviced service assign-ip collector2/RabbitMQ-Ceilometer serviced service assign-ip collector2/proxy-zenopenstack
Once the zenpack is installed, provide SSH credentials to the Linux devices in your OpenStack environment before adding any devices. * Configure the zCommandUsername/zCommandPassword/zKeyPath properties on the /Devices/Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost device class. * If your OpenStack nodes are already managed under Zenoss, move them into /Devices/Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost
Device Setup
Device Setup via UI
Once the OpenStack ZenPack is installed and you can begin monitoring by
going to the infrastructure screen and clicking the normal button for
adding devices. You'll find a new option labeled, Add OpenStack
Endpoint (Infrastructure).
Choose that option and you'll be presented with a dialog asking for the following inputs.
- Device To Create - non-empty, non-ip, non-dns, unique name to use for this device in Zenoss. See note below.
- Auth URL - A keystone URL. For Keystone's v3 API, it should look
like
http://<hostname>:5000/v3/. For Keystone's v2 API, it should look likehttp://<hostname>:5000/v2.0/. To have the ZenPack choose the newest supported API version, leave the path off, likehttp://<hostname>:5000/(sets zOpenStackAuthUrl). - Username: Enter your OS_USERNAME (sets zCommandUsername).
- Password: Enter your OS_PASSWORD (sets zCommandPassword).
- User Domain Name: Enter the user domain name per OS_USER_DOMAIN_NAME (sets zOpenStackUserDomainName).
- Project Domain Name: Enter the project domain name per OS_PROJECT_DOMAIN_NAME (sets zOpenStackDomainName).
- Region Name - choose the correct region from the drop-down. You may only choose one, so each region you wish to manage must be registered as a separate endpoint in Zenoss (sets zOpenStackRegionName).
Once you click Add, Zenoss will contact the OpenStack API and discover servers, images and flavors. Once it is complete you'll find a new device in the OpenStack device class with the same name as the hostname or IP you entered into the dialog. Click into this new device to see everything that was discovered.
NOTE: The "Device name" should be a non-empty, non-hostname, non-IP, since that name will be used when the host is registered as a Linux device. The name should be unique within the Zenoss environment. This is especially important if you are adding another device that share the same IP address or hostname that already exist on another device. Not doing this may result in devices with the same name conflicting with each other. (e.g. attempting to model device would show modeling results that belong to another device OR device would show relations that do not belong to that device)
Device Setup via Zenbatchload
You can setup the device using zenbatchload as follows:
zenbatchload <filename>
where <filename> should have the form:
/Devices/OpenStack/Infrastructure loader='openstackinfrastructure',\ loader_arg_keys=['deviceName', 'username', 'api_key', 'project_id, 'user_domain_name', 'project_domain_name', 'auth_url', 'region_name', 'collector'] <devicename> username='<username>', api_key='<password>', project_id='<tenant ID>', user_domain_name='default', \ project_domain_name='default', auth_url='http://<ip address>:5000/v2.0/', region_name='RegionOne' /Devices/Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost zCommandUsername='myusername', zCommandPassword='mypassword'
- As mentioned before, zCommandUsername and zCommandPassword properties must be set for /Devices/Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost devices (and vNICs) to be correctly modeled.
Host Identification
The OpenStack APIs do not contain an authoritative list of hosts with unique IDs. Instead, various APIs show hosts by name or IP. There zenpack does its best to identify IPs and names that refer to the same host, and represent them as a single host component. In some cases, though, it can't tell, and the same host may be modeled twice, or with an incorrect name.
Two zProperties are provided to override the default behavior of the zenpack when this happens.
-
zOpenStackHostMapSame
Specifies that two names refer to the same host. It is a list of entries of the form:
<name1>=<name2>For example,my.example.com=myothername.example.com my.example.com=10.1.1.1This means that any time the host
my.example.com,myothername.example.com, or10.1.1.1is encountered, they will be considered to be the same host, rather than separate ones. -
zOpenStackHostMapToId
It is also possible to specify not only that the devices are the same, but that they should be identified with one specific identifier (otherwise, one may be chosen at random). In this case, a list of entries of the form
<name>=<id>may be provided in the zOpenStackHostMapToId zProperty. For example,myothername.example.com=my.example.com 10.1.1.1=my.example.comThis would causemy.example.com,myothername.example.com, or10.1.1.1to all be definitely identified asmy.example.com, without the ambiguity that could exist if zOpenStackHostMapSame were used. -
zOpenStackHostLocalDomain
In some environments (in particular, the Red Hat OpenStack Platform), hosts are assigned names that end in
.localdomain. This would cause problems for Zenoss, because it is not possible to create a device in Zenoss with such a name, as they all resolve to 127.0.0.1, rather than their actual IP.The default value of zOpenStackHostLocalDomain is a blank string, meaning that the
.localdomainsuffix will be stripped from host names, and devices will be created in Zenoss with those shortened names. If those names do not resolve in DNS, they will be created without IPs, and will not be modeled. You would need to manually set their management IPs so that they can be modeled.Alternatively, if you already have these hostnames in dns, but just with a different domain name than
.localdomain, you may specify this domain name here, and it will be substituted for localdomain, and the devices will model automatically, based on the IPs returned from DNS.
Modeling Containerized Environments
If the target OpenStack environment runs processes inside of docker containers, it is necessary to configure several zProperties before modeling will succeed.
- zOpenStackRunNovaManageInContainer: Container to run
nova-managein - zOpenStackRunVirshQemuInContainer: Container to run
virshin - zOpenStackRunNeutronCommonInContainer: Container to access neutron configuration files in.
These should be set to container names or substrings of the container names. These can be set on the /Server/SSH/Linux/NovaHost device class or specific devices within it, as necessary.
NOTE: These zProperties must be set on the Linux devices, not the OpenStack (/OpenStack/Infrastructure) devices.
OpenStack Configuration
Before event and performance data can be collected, the following steps must be performed. That these steps are only tested with currently-supported versions of OpenStack (Pike and higher).
OpenStack Ceilometer Configuration
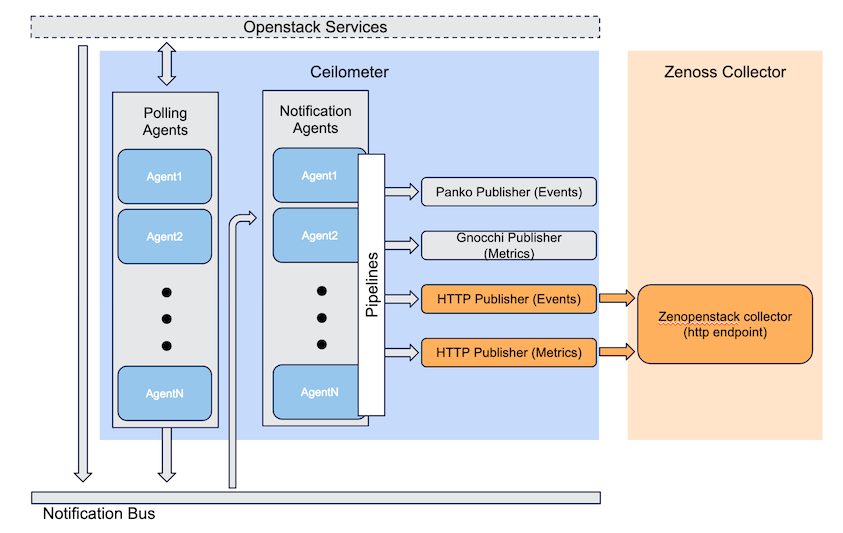
Ceilometer is a component of openstack which, through a combination of polling and notifications from the openstack message bus, collect a variety of metric and event data from the openstack environment and forwards it to external services, including Zenoss, for processing.
Ceilometer's polling agent and other openstack services (nova-api, for instance) send notifications through an internal notification bus, which are received by the ceilometer notification agent. It then passes these notifications through configurable "pipelines", which ultimately deliver the data through publishers.
In 2.4.x of this ZenPack, a custom ceilometer plugin called
ceilometer_zenoss was used to send the data to zenoss through the
RabbitMQ-Ceilometer service.
This approach was no longer practical with current versions of OpenStack, so the collection mechanism was changed to use ceilometer's built-in http publisher, rather than AMQP. Since the http publisher is part of ceilometer, there is no need to install additional software on the OpenStack environment to use this mechanism. It is only necessary to configure it correctly, as described below.
Ceilometer must be configured to send data to the correct Zenoss collector, using a device-specific URL.
The OpenStack environment will therefore need https access to the zenoss collector, and the Zenoss collector IP must be configured as described in the Post-ZenPack-Installation Notes.
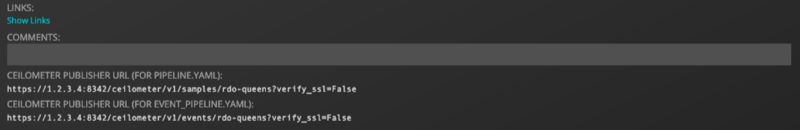
Once the device is added, and its collector's proxy-zenopenstack service has an assigned IP, the following two URLs will be displayed at the bottom of the device's overview page:
These URLs will be required to configure ceilometer on the OpenStack environment to send data to Zenoss. There are two ways to configure ceilometer:
RHOSP Configuration using TripleO (RedHat OpenStack Platform Director)
This is the best way to configure the Redhat OpenStack Platform.
-
Add the following to your environment template:
ManagePipeline: true PipelinePublishers: - *Zenoss Samples Publisher URL* - <other_pipeline_publishers> ManageEventPipeline: true EventPipelinePublishers: - *Zenoss Events Publisher URL* - <other_event_pipeline_publishers>Where the publisher URLs are device-specific, and copied from the device overview page shown above. For example:
ManagePipeline: true PipelinePublishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False ManageEventPipeline: true EventPipelinePublishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/events/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False
If desired, multiple publisher URLs may be specified, for instance to publish to more than one zenoss instance, or to other openstack systems such as gnocchi or panko. Note, however, that ceilometer will publish data to every publisher sequentially, so if one of the URLs is timing out, it will block ceilometer and slow down the publishing of data to Zenoss. Therefore, it is advisable to make sure that the URLs specified are valid and functioning.
-
This template must be rendered into your templates before you initiate a deployment from Undercloud. For more information on RHOSP template management, see RedHat's Including Environment Files in Overcloud Creation.
-
After deployment is complete, go to the undercloud, SSH into controller and go to
/etc/ceilometerin ceilometer_agent_notification container to check ifpipeline.yamlandevent_pipeline.yamlfile is updated:ssh heat-admin@<controller ip> sudo su - sudo docker exec --user 0 -it ceilometer_agent_notification /bin/bash # Ensure your configuration had the right publishers -
Add Zenoss specific extensions to the Ceilometer event definitions:
Edit
/etc/ceilometer/event_definitions.yamland add the contents of zenoss_additions.yaml to the bottom of the file. -
Restart the ceilometer-notification service on all controller nodes.
Manual Configuration
When RedHat OpenStack Platform is not being used, you will need to update the affected configuration files directly. The following modifications are required on every controller node where ceilometer is running:
-
Add Zenoss specific extensions to the Ceilometer event definitions:
Edit
/etc/ceilometer/event_definitions.yamland add the contents of zenoss_additions.yaml to the bottom of the file. -
The
/etc/ceilometer/event_pipeline.yamlfile contains one sink, namedevent_sink. In its publishers section, add the event URL from above:For example:
--- sources: - name: event_source events: - "*" sinks: - event_sink sinks: - name: event_sink transformers: triggers: publishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/events/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False - <some_other_publisher> -
The
/etc/ceilometer/pipeline.yamladd the samples URL to the publish sections for the three sinks, cpu_sink, disk_sink, and network_sink:For example:
--- sources: - name: meter_source meters: - "*" sinks: - meter_sink ... etc ... sinks: - name: meter_sink transformers: publishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False - <some_other_publisher> - name: cpu_sink transformers: - name: "rate_of_change" parameters: target: name: "cpu_util" unit: "%" type: "gauge" max: 100 scale: "100.0 / (10**9 * (resource_metadata.cpu_number or 1))" publishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False - <some_other_publisher> - name: disk_sink transformers: - name: "rate_of_change" parameters: source: map_from: name: "(disk\\.device|disk)\\.(read|write)\\.(bytes|requests)" unit: "(B|request)" target: map_to: name: "\\1.\\2.\\3.rate" unit: "\\1/s" type: "gauge" publishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False - <some_other_publisher> - name: network_sink transformers: - name: "rate_of_change" parameters: source: map_from: name: "network\\.(incoming|outgoing)\\.(bytes|packets)" unit: "(B|packet)" target: map_to: name: "network.\\1.\\2.rate" unit: "\\1/s" type: "gauge" publishers: - https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack?verify_ssl=False - <some_other_publisher> -
Make sure you restart ceilometer-notification service whenever you change
pipeline.yamlorevent_pipeline.yaml. -
Configure nova to send events to ceilometer when instance state changes occur. (This step is optional, but recommended.) Add the following settings to
/etc/nova/nova.confon all compute nodes:[notifications] notify_on_state_change=vm_and_task_state [oslo_messaging_notifications] driver = messagingv2 -
Configure neutron to send events for ceilometer to forward to zenoss. Add the following settings to
/etc/neutron/neutron.conf:[oslo_messaging_notifications] driver = messagingv2 topics = notifications
Ceilometer Troubleshooting
A variety of errors can be returned by zenopenstack to ceilometer. Here are the most common ones.
The errors would be found in
/var/log/ceilometer/agent-notification.log on the OpenStack controller
nodes.
-
Connection Refused
ERROR ceilometer.pipeline.sample ConnectionError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='1.2.3.4', port=8342): Max retries exceeded with url: /ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstack (Caused by NewConnectionError('<requests.packages.urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7f80d1e89590>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 111] Connection refused',))Verify that the IP address is correct and that the proxy-zenopenstack service is running.
-
Network Connectivity
ERROR ceilometer.pipeline.event ConnectTimeout: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='1.2.3.4', port=8342): Max retries exceeded with url: /ceilometer/v1/events/myopenstack (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<requests.packages.urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7f4307dc94d0>, 'Connection to 1.2.3.4 timed out. (connect timeout=5)')) ERROR ceilometer.pipeline.event ConnectionError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='1.2.3.4', port=8342): Max retries exceeded with url: /ceilometer/v1/events/myopenstack (Caused by NewConnectionError('<requests.packages.urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7f0b78e686d0>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 113] No route to host',))Ensure that the correct IP was specified and that it is reachable from the OpenStack hosts.
-
Bad Gateway
ERROR ceilometer.publisher.http HTTPError: 502 Server Error: Bad Gateway for url: https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstackIn general, this indicates that proxy-zenopenstack is running, but zenopenstack is not. This can be normal during a zenoss restart, but if it does not resolve, check the status of the zenopenstack service.
-
404 Errors (Not Found)
ERROR ceilometer.publisher.http HTTPError: 404 Client Error: Not Found for url: https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstackThis usually indicates that the device ID found in the url is not recognized. Check the URL and make sure the device ID is correct.
This can be normal during zenopenstack restarts, since it will not know about devices to be monitored until it lots the configuration from zenhub. If this is the case, it will resolve in a few minutes.
It is also possible to get a 404 error because of a typo in the URL unrelated to the device ID.
-
422 Errors (Unprocessable Entity)
ERROR ceilometer.publisher.http HTTPError: 422 Client Error: Unknown Status for url: https://1.2.3.4:8342/ceilometer/v1/samples/myopenstackThis error indicates that the payload of the http request sent to zenoss was not in the expected format. The most common cause for this is putting the samples url in event_pipeline.json, or the events url in pipeline.json. Ensure that the correct URL was put in the right file.
Additional zenopenstack debugging is possible through the zenopenstack
diagnostics link under show links on the device's detail page. This
link connects your browser directly to zenopensatck and provides
detailed debugging information, including request rates and a log of all
recently received http messages. Note that this option requires that
your browser have https connectivity to the Zenoss collector.
General Notes
-
In prior versions of this zenpack, all events from ceilometer were forwarded to zenoss under /OpenStack. Since most events were not actionable, they were used to update the model (for instance, a new instance is created), but were immedaitely archived. In version 3.0.0, these events are still used for incremental model updates, but are not stored in zenoss as events any more (since they placed additional load on zenoss for no benefit).
If there is a ceilometer event type which is actually useful to track in zenoss as an event, that capability still exists, however. The list of event types to be exposed to zenoss are configurable in
zOpenStackProcessEventTypes.By default, this only contains
compute.instance.create.error, but other types may be added if desired. -
The Instance metrics for Disk IO Rate are deprecated in OpenStack version Queens and later. Collection for those metrics will be missing. Future OpenStack releases will remove these metrics and graphs completely.
In the meantime, if you still require these metrics, you can edit the OpenStack Ceilometer configuration
/etc/ceilometer/polling.yamland add the following to the meters section:- disk.read.bytes - disk.read.requests - disk.write.bytes - disk.write.requestsAfter editing this file, ensure the resulting YAML syntax is valid and restart the ceilometer-polling service.
Finally, note that these metrics ARE deprecated and will be removed in future releases of OpenStack itself.
-
The OpenStack ZenPack relies upon standard zenoss Linux Monitoring for some functions, including process monitoring and the modeling of vNICs. This means that the Zenoss collectors require SSH access to the NovaHost devices. In some OpenStack deployments (including RHOSP's overcloud), external SSH access may not be available by default, and additional configuration may be required to achieve it.
-
Starting from OpenStackInfrastructure version 4.0.1, the RabbitMQ-ceilometer service has been removed from the ZenPack. As a result, events and performance data are no longer collected from OpenStack Ceilometer via AMQP. OpenStack Ceilometer collection has been fully migrated to the zenopenstack service. The following OpenStackInfrastructure AMQP data source types are deleted during the upgrade:
- OpenStack Ceilometer AMQP; - OpenStack Ceilometer Events AMQP; - OpenStack Ceilometer Heartbeats AMQP; - OpenStack AMQP Queue Size.
Zenoss Analytics
This ZenPack provides additional support for Zenoss Analytics. Perform the following steps to install extra reporting resources into Zenoss Analytics after installing the ZenPack.
- Copy vsphere-analytics.zip from
$ZENHOME/ZenPacks/ZenPacks.zenoss.OpenStackInfrastructure*/ZenPacks/zenoss/OpenStackInfrastructure/analytics/on your Zenoss server. - Navigate to Zenoss Analytics in your browser.
- Login as superuser.
- Remove any existing OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack folder.
- Choose Repository from the View menu at the top of the page.
- Expand Public in the list of folders.
- Right-click on OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack folder and choose Delete.
- Confirm deletion by clicking OK.
- Add the new OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack folder.
- Choose Server Settings from the Manage menu at the top of the page.
- Choose Import in the left page.
- Remove checks from all check boxes.
- Click Choose File to import a data file.
- Choose the OpenStackInfrastructure-analytics.zip file copied from your Zenoss server.
- Click Import.
You can now navigate back to the "OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack" folder in the repository to see the following resources added by the bundle.
- Domains
- OpenStackInfrastructure Domain
- Ad Hoc Views
- OpenStack Instance List
The OpenStackInfrastructure Domain can be used to create ad hoc views using the following steps.
- Choose Ad Hoc View from the Create menu.
- Click Domains at the top of the data chooser dialog.
- Expand Public then OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack.
- Choose the OpenStackInfrastructure Domain domain
Service Impact and Root Cause Analysis
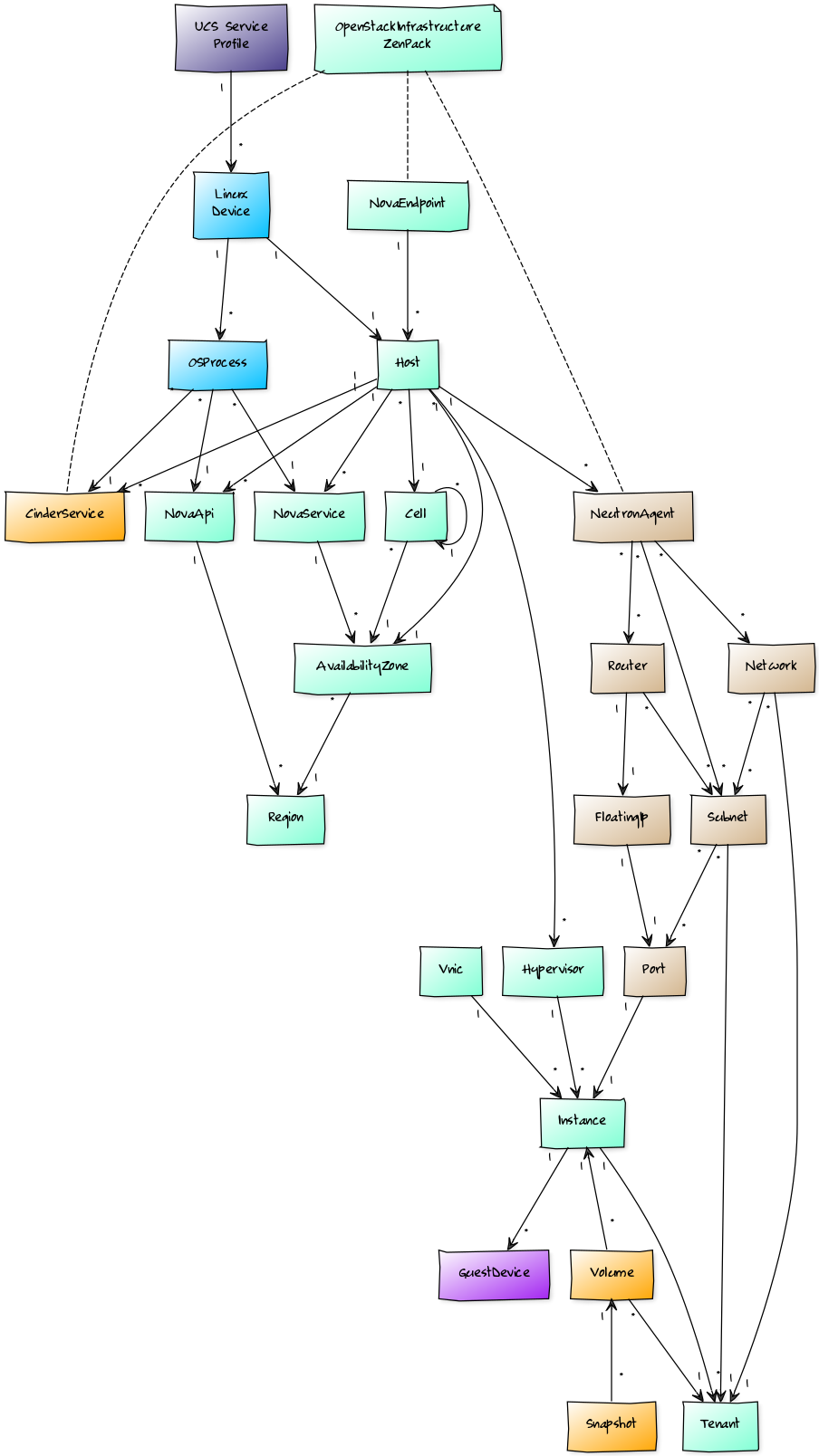
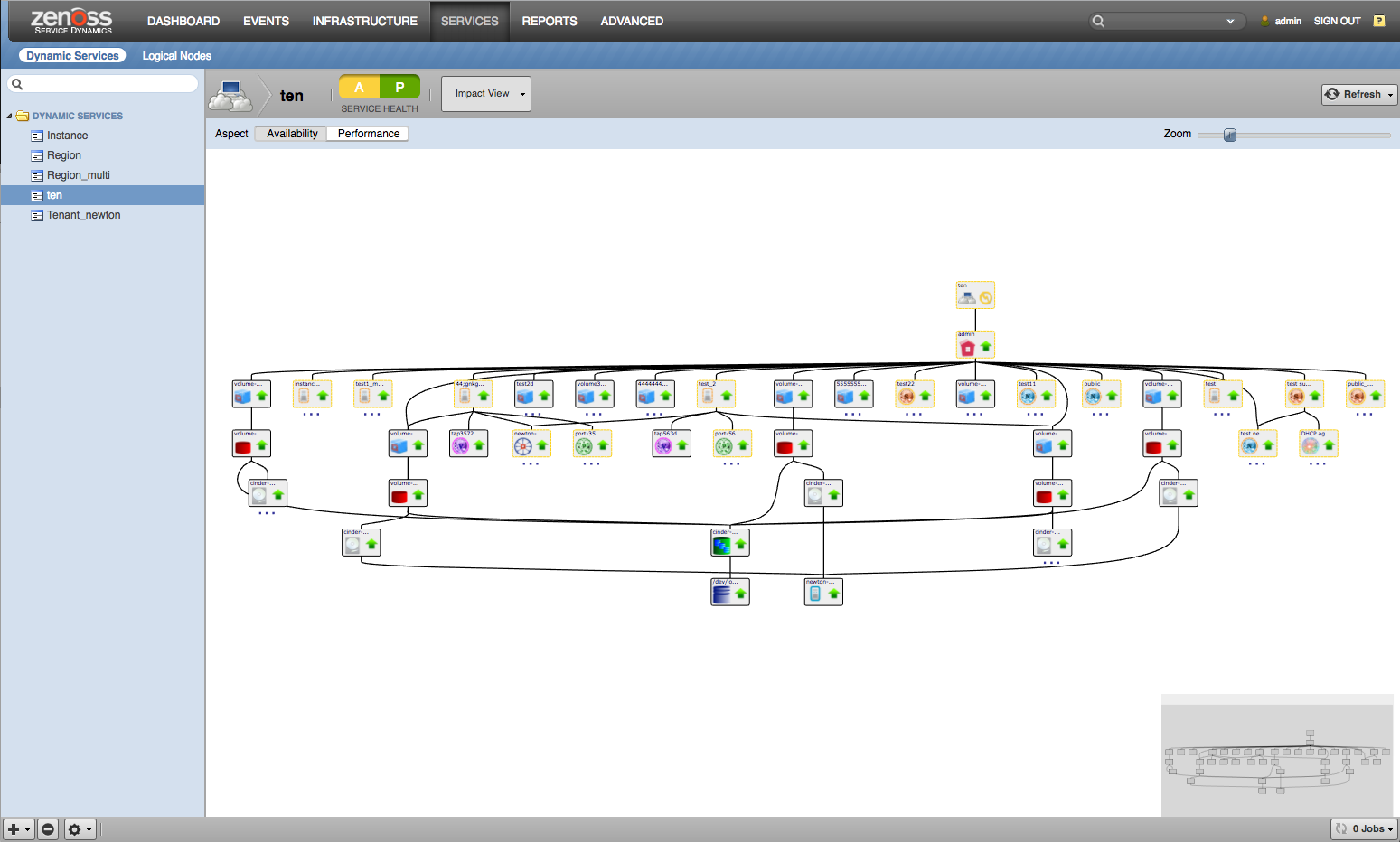
When combined with the Zenoss Service Dynamics product, this ZenPack adds built-in service impact and root cause analysis capabilities for OpenStack infrastructure and instances. The service impact relationships shown in the diagram and described below are automatically added. These will be included in any services that contain one or more of the explicitly mentioned components.
Recommended Impact Setup
Since most components will be related to Tenants and Region we recommend:
- Navigate to Services (Impact)
- Add a Dynamic Service to your Services tab
- Add all Tenants to the Dynamic Service
- Add all Regions to the Dynamic Service
Impact Relations
Component failures will affect Impact as follows:
Internal Impact Relationships
- OpenStack API endpoint impacts all Hosts
- Availability zone impacts associated Region
- Host impacts associated Hypervisors, Nova Services, Cells, Nova Apis, Neutron Agents, and Cinder Services
- Hypervisor impacts the resident Instances (VMs)
- Nova Service affects the Availability Zone or Region that it supports
- Instance impacts the associated Tenant
- vNIC impacts the related Instance.
- Port impacts associated Instance
- Subnet impacts associated Ports and Tenants
- Floating-IP impacts associated Port
- Network impacts associated Subnets and Tenants
- Router impacts associated Subnets and Floating-ips
- Neutron Agent impacts associated Networks, Subnets and Routers
- volume impacts Instances (VMs), Volume Snapshots
External Impact Relationships
- Instance impacts guest operating system device.
- Cisco UCS vNIC impacts related host's underlying Linux device NIC.
- Cisco UCS service profile impacts host's underlying Linux device.
- Host impacted by associated Linux device.
- OS Processes on an underlying Linux device impact corresponding Nova APIs, Nova Services, Neutron Agents and Cinder Services on Host.
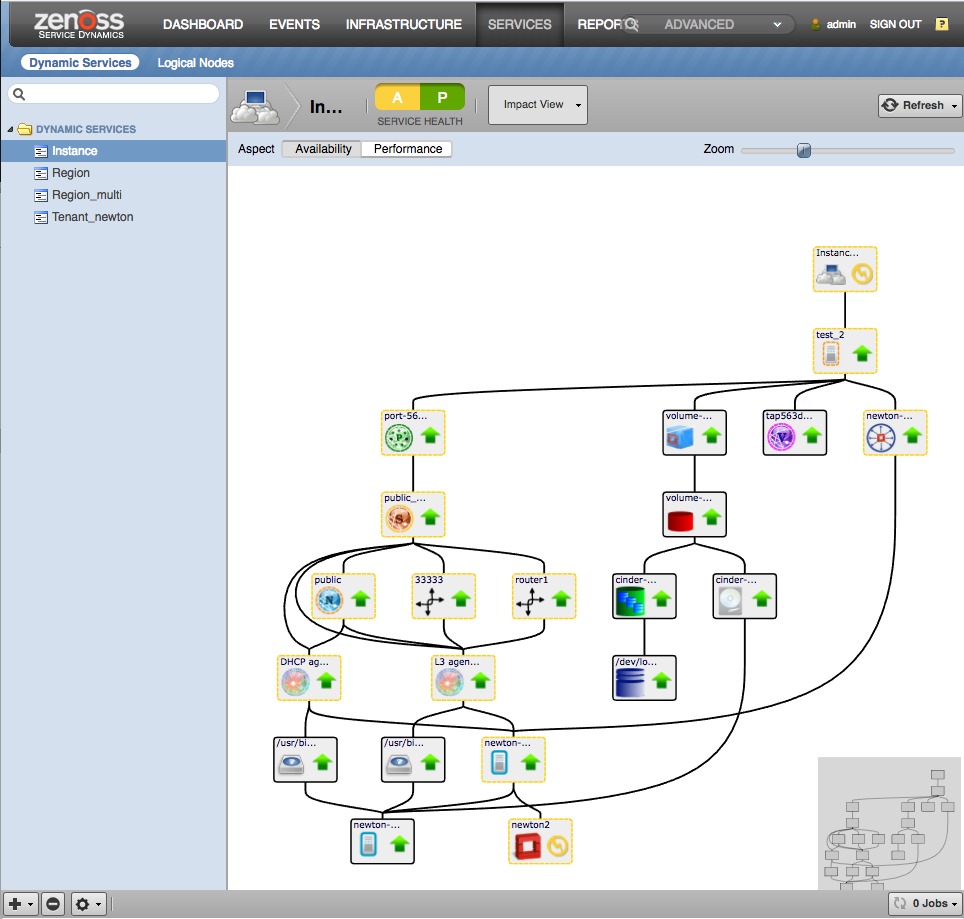
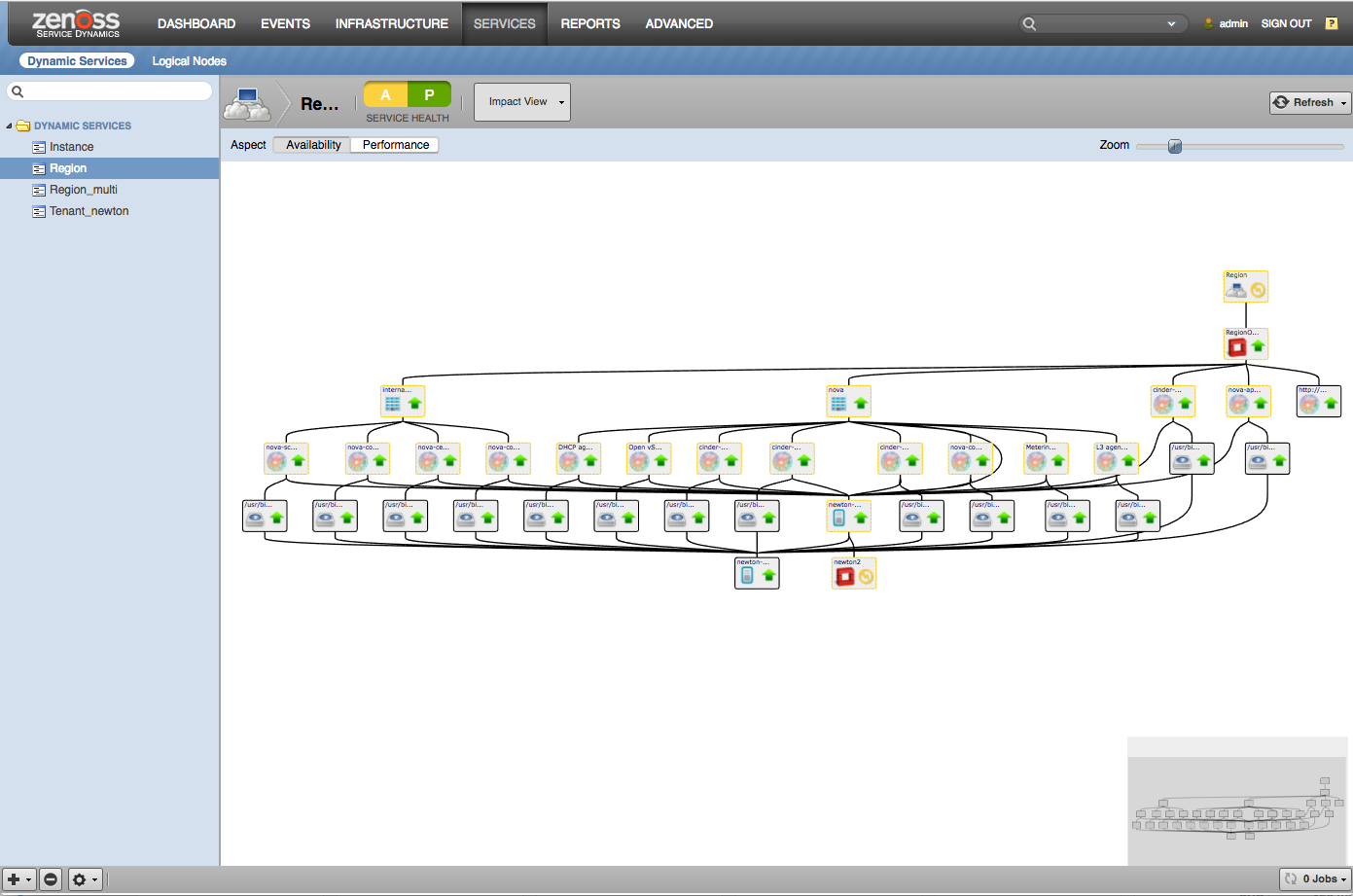
Examples
|
Impact (Instance) |
Impact (Network) |
|
Impact (Region) |
Impact (Tenant) |
Integration with other ZenPacks
In some cases, the underlying network or storage technology is monitored by a different zenpack. The OpenStackInfrastructure zenpack is able to integrate with the following ZenPacks to provide component-level linkage and impact model integration:
- Neutron OpenvSwitch ml2 plugin <-> OpenvSwitch ZenPack
- Neutron APIC ml2 plugin <-> Cisco APIC ZenPack
- Neutron NSX ml2 plugin <-> VMWare NSX ZenPack
- Cinder LVM logical volumes <-> Linux Monitor ZenPack (>= 2.0.0)
- Ceph RBD volumes <-> Ceph ZenPack
Known Issues
-
ZEN-17905: Nova APIs component: Grey icons for Enabled and State after model/monitor.
-
OpenStack nova service API does not provide information about Nova-API, so its status is, in fact, unknown.
-
ZPS-1762: When using OpenvSwitch integration, the Linux devices must be added to the system first (normally through automatic discovery by the OpenStackInfrastructure ZenPack) before the corresponding OpenvSwitch devices are registered. This is because the two devices use the same management IP address, and a special exclusion is in place for OpenvSwitch devices, allowing them to be added after the Linux device, but not the other way around.
-
ZPS-2004: When adding an OSI device, if the same host is already added as a generic device (such as /SSH/Linux), the host device's device class will be changed, and an error generated, preventing modeling. As a workaround, remove the Linux device before adding the OSI device.
-
ZPS-4742: Networking functions through SR-IOV and OVS-DPDK used in NFV like setups are not supported. Ceilometer is not able to collect monitoring data for these interfaces and hence Zenoss doesn't have any insight into these interfaces. This is because legacy Ceilometer only supports traditional OpenvSwitch networking, where a TAP interface is created through libvirt.
-
ZPS-5468: Newly deployed RabbitMQ-Ceilometer service can fail to start, with an error
badmatch,{error,{no_such_vhost,<<"/">>}}. When this occurs, all health checks for the service will fail.If this error is encountered, the simplest fix seems to be to attach to the affected container, then run:
rm -rf /var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia*/rabbit@rbt-ceil0and restart the service.
-
ZPS-4689: During upgrades you can see an error like:
ERRO[0000] Could not update proxyYou can safely ignore this error, which should stop after the upgrade is completed.
Changes
4.0.1
- Removed RabbitMQ-ceilometer service from the ZenPack (ZPS-8941)
- Fixed execute permission for OSI devices (ZPS-8939)
- Tested with Zenoss Resource Manager 6.7.0, Zenoss Cloud and Service Impact 5.7.0
4.0.0
- Add support for OSP 16.x
- Increased Read timeout (ZPS-7352)
- Modeling needs to succeed when cinder service is not available. (ZPS-7362)
- Host name is constructed with informative string unique to the endpoint and host combination (ZPS-7318)
- Supports Queens, Rocky, Ussuri, Train, Victoria and Red Hat OpenStack Platform (RHOSP) version 13, 14 and 16
- Tested with Zenoss Resource Manager 6.5.0, 6.6.0, Zenoss Cloud and Service Impact 5.5.3
3.0.1
- Add support for Twisted library update (ZPS-6975)
- Tested with Zenoss Resource Manager 6.4.1, Zenoss Cloud and Service Impact 5.5.1
3.0.0
- Add support for Keystone Domains (ZPS-3850)
- Add support for Pike, Rocky, Queens, RHOSP 13-14 versions of OpenStack
- Add support for multiple Zenoss instances (ZPS-1598)
- Add support for restricted (non-administrator) users (ZPS-3851, ZPS-5043)
- Exclude erroneous "hostgroup" host components (ZPS-4914)
- Fix KeyError in PerfAMQPDataSource vNIC discovery (ZPS-4661)
- Guard against missing tenant quota. (ZPS-4627)
- Refactor Ceilometer introducing zenopenstack service to simplify collection
- Allow temporary legacy metrics for
Disk IO RateandDisk Requests(ZPS-5205) - The HeartBeat datasource was removed as heartbeats are no longer supported by OpenStack (ZPS-1984)
2.4.2
- Avoid nameconfict for proxy devices and be more flexible in linking to existing devices when appropriate (ZPS-3991)
- Prevent modeling invalid host components for Ceph storage backend and API endpoints (ZPS-3751, ZPS-3971, ZPS-4183)
- When mapping hostnames, treat all host references in case-insensitive manner (ZPS-3989)
- Fix hostfqdn modeler plugin for systems where the
dnsdomainnamecommand is not available (ZPS-4083) - expected_ceilometer_heartbeats includes additional possible names for a host, based on hostmap, proxy device, and the host's local hostname (ZPS-4082)
- Fix for
OpenStack Component Viewoption missing in left-hand nav (ZPS-3927) - Corrected URL escaping in modeler plugin to avoid receiving 400 error when a proxy is in front of nova-api services (ZPS-3894)
- Tested with Zenoss Resource Manager 6.2.0, Zenoss Resource Manager 5.3.3 and Service Impact 5.3.1
2.4.1
- Disallow spaces in device IDs in the "Add OpenStack Endpoint" dialog (ZPS-2583)
- Remove certain warnings related to port update events (ZPS-2606)
- Eliminate warnings when running tests under 6.x (ZPS-2574)
- Support for self-signed certificates which include an IP address as a subjectAltName (ZPS-2056)
- Fix situation where certain errors are reported as TimeoutError instead of the actual error message (ZPS-2039)
- Fix for errors when modeling when the hosts already exist in a different device class (ZPS-2004)
2.4.0
- Added support for Newton and Ocata
- Added support for Keystone v3 authentication
- Model API endpoints (currently only the public keystone API endpoint). Allow user to specify additional ones via zOpenStackExtraApiEndpoints. Supported API services are included in the provided ApiEndpoint monitoring template.
- Removed zOpenStackCeilometerUrl zProperty, which was unused
- Added descriptions for OpenStack configuration properties (ZPS-1590)
- Tested with Zenoss Resource Manager 5.2.6, Zenoss Resource Manager 4.2.5 RPS 743 and Service Impact 5.1.5
2.3.3
- Fix error in modeler when neutron agent extension is not available (ZPS-1243)
- Fix certain problems modeling OpenStack environments where hosts have .localdomain names (ZPS-1244)
2.3.2
- Wrap brain.getObject() into try/except block (ZPS-442)
2.3.1
- Upgrade txsshclient to fix critical change in twisted.conch (ZEN-25870)
2.3.0
- Added support for Mitaka.
- Provide various host-checking fixes: (ZEN-24803, ZEN-25262)
- Prevent queues from being deleted when device is removed/re-added (ZEN-24803)
- Use publicURL if adminURL not working: (ZEN-24546)
- Upgrade ZenPackLib to 1.1.0 to fix Liberty/Mitaka status: (ZEN-24464)
2.2.0
- Added Cinder block storage components.
- Added LVM, Ceph block storage integration via LinuxMonitor and Ceph ZenPacks.
- Various bug fixes
2.1.3
- Fix malformed hostnames in the F5 LBAAS plugin (ZEN-22126)
2.1.2
- Remove deprecated ceilometer-agent-notification heartbeats
2.1.1
- Various bug fixes
- Add meta.zcml feature tags for Neutron Integration
2.1.0
- Added Neutron network components
- Update Impact models for Neutron
- Update multiple UI interfaces
- Upgrade to ZenPackLib 1.0.1
- Add ML2 Plugin Capability
2.0.0
- Initial Release