Cisco APIC
ZenPacks.zenoss.CiscoAPIC
This ZenPack provides support for monitoring the Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) via the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC).
Commercial
This ZenPack is developed and supported by Zenoss Inc. Commercial ZenPacks are available to Zenoss commercial customers only. Contact Zenoss to request more information regarding this or any other ZenPacks. Click here to view all available Zenoss Commercial ZenPacks.
Releases
Version 1.3.0 Download
- Released: 2020-07-02
- Compatible with Zenoss 4.2.5 - 6.5.0, Zenoss Cloud
- Requires: PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.3)
Version 1.2.3 Download
- Released: 2017-12-08
- Compatible with Zenoss 4.2.5 - 6.0.
- Requires: PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.3)
Version 1.1.0 Download
- Released: 2015-08-21
- Compatible with Zenoss 4.2.5 - 5.1.
- Requires: PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.3)
Version 1.0.5 Download
- Released: 2015-08-21
- Compatible with Zenoss 4.2.5 - 5.1.
- Requires: PythonCollector ZenPack (>=1.3)
Features
This ZenPack adds the following features to Zenoss.
- Initial discovery and continual update of relevant components.
- Performance monitoring. Both of statistics and health scores.
- Event management. Integration of APIC faults into Zenoss event system.
- Service impact and root cause analysis. (Requires Zenoss Service Dynamics)
Discovery
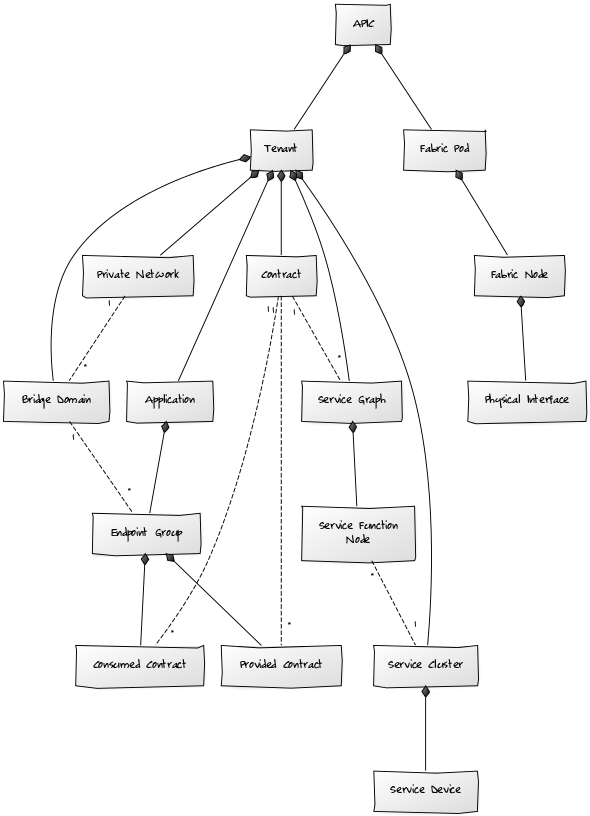
The following components will be automatically discovered through a controller (APIC).
APICs
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Fabric Pods, Tenants
Tenants
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: APIC, Private Networks, Bridge Domains, Contracts, Applications, Service Graphs, Service Clusters
Applications
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Tenant, Endpoint Groups
Endpoint Groups
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Application, Bridge Domain, Provided Contracts, Consumed Contracts
Client Endpoints
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class, MAC Address, IP Address, Learning Source, Encapsulation
- Relationships: Endpoint Group
Contracts
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class, Subjects
- Relationships: Tenant, Provided Contracts, Consumed Contracts, Service Graphs
Provided Contract
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Endpoint Group, Contract
Consumed Contract
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Endpoint Group, Contract
Private Networks
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Tenant, Bridge Domains
Bridge Domains
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Tenant, Private Network, Endpoint Groups
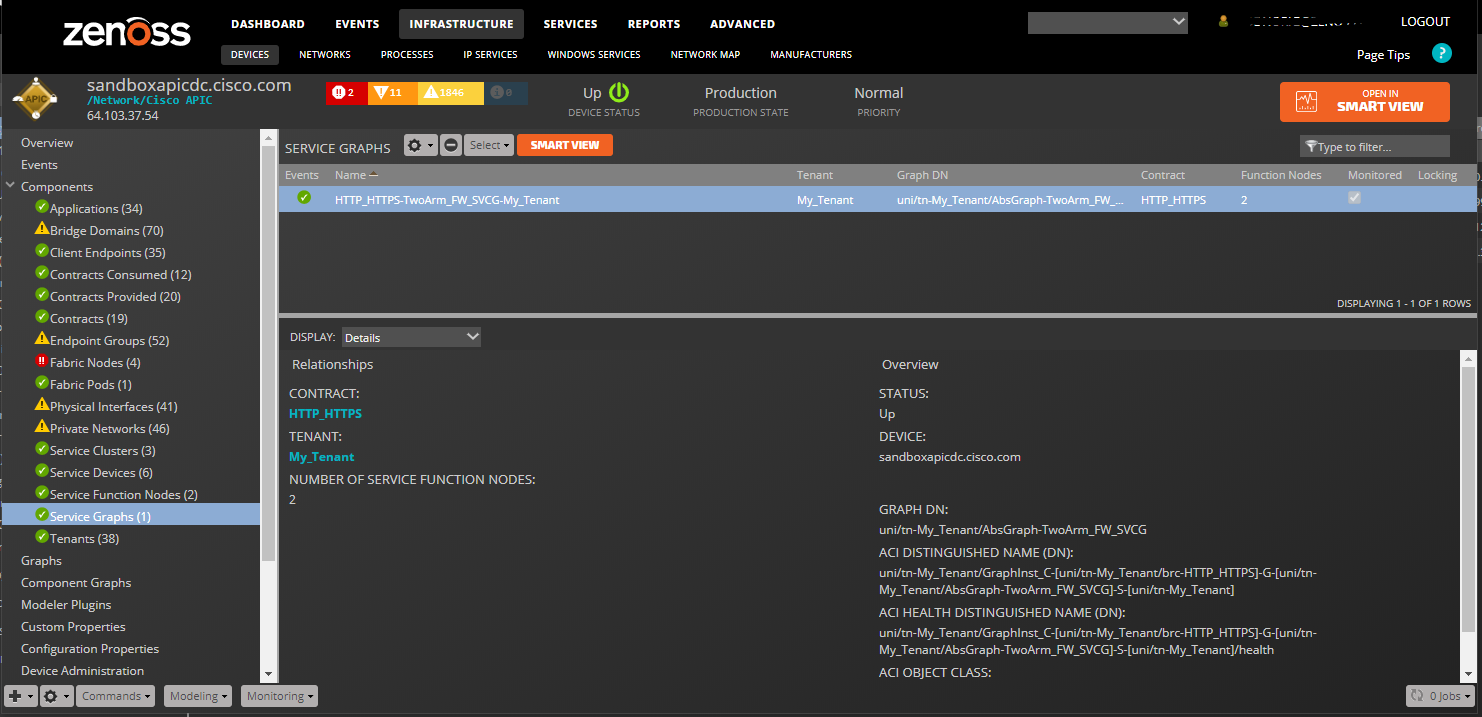
Service Graphs
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Tenant, Service Function Nodes, Contract
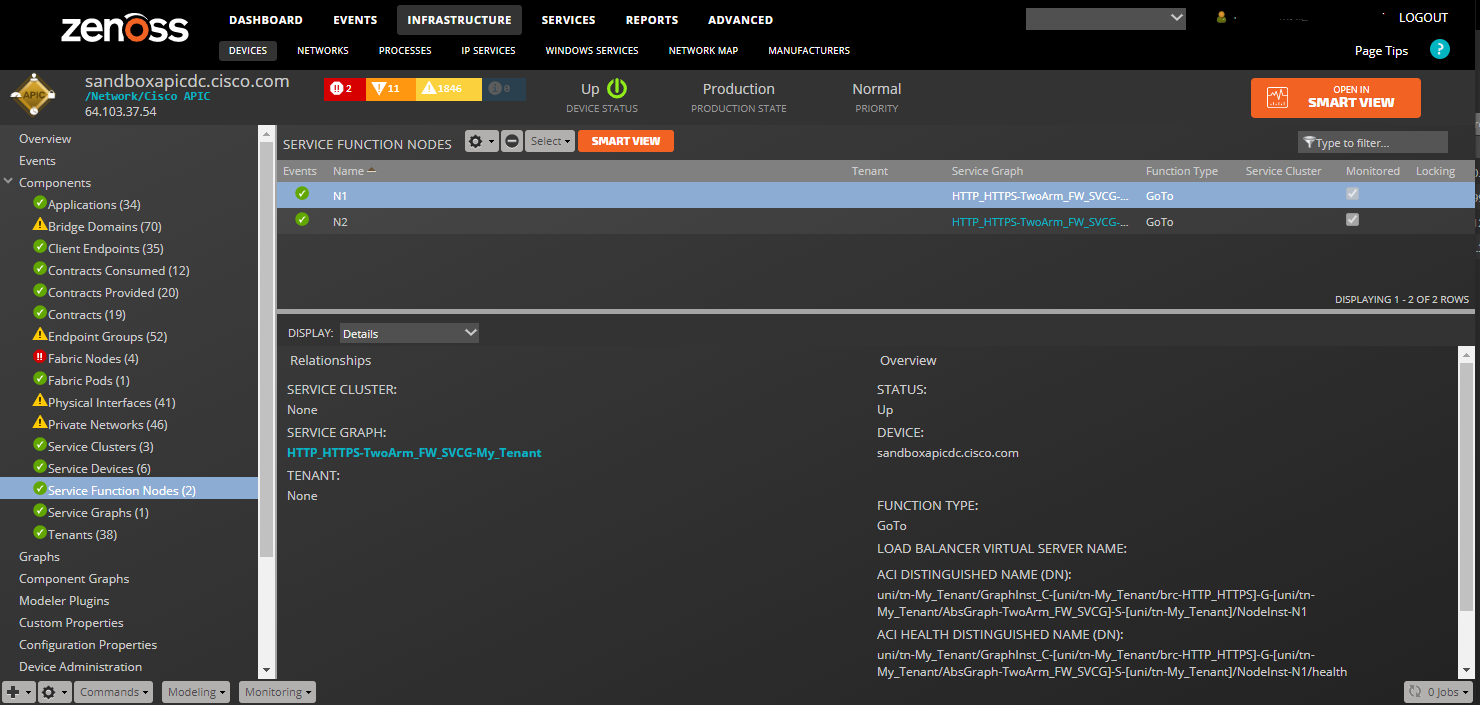
Service Function Nodes:
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Service Graph, Service Cluster
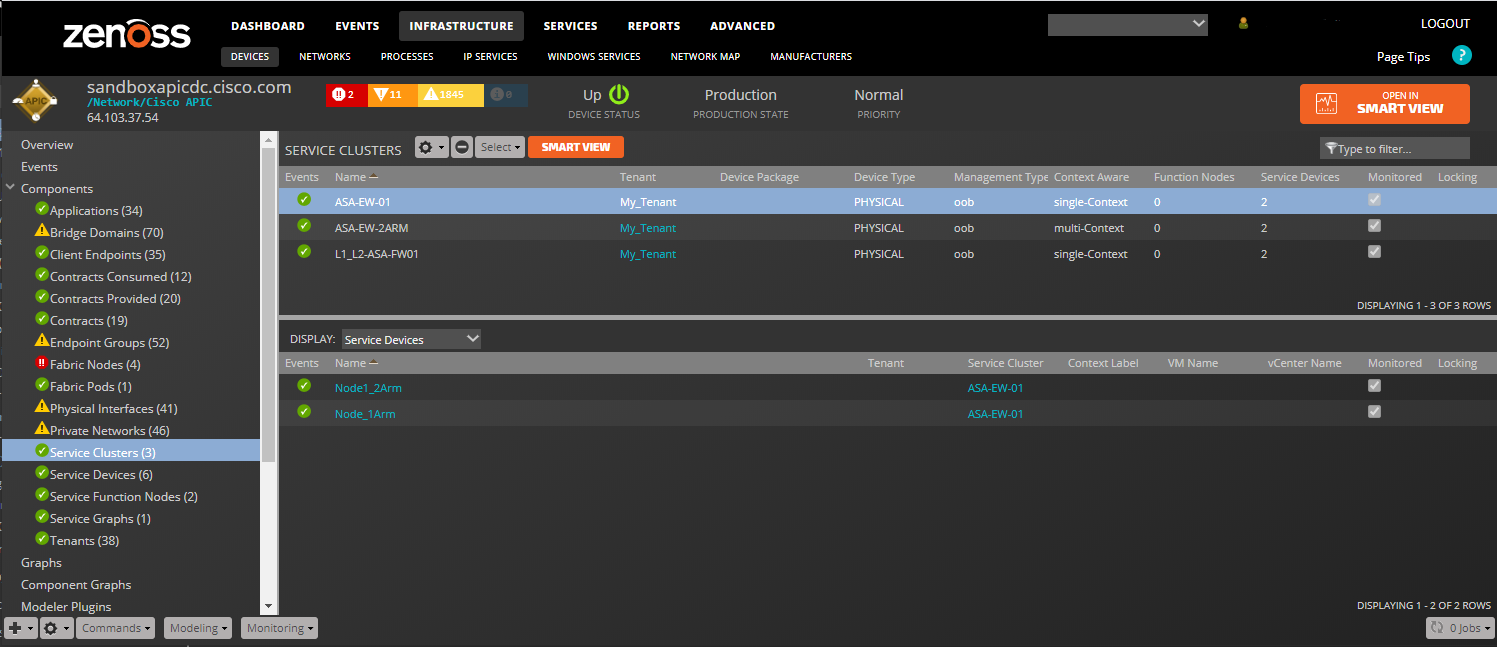
Service Clusters
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class, Device Package, Vendor, Model, Version:
- Relationships: Tenant, Service Devices, Service Function Nodes
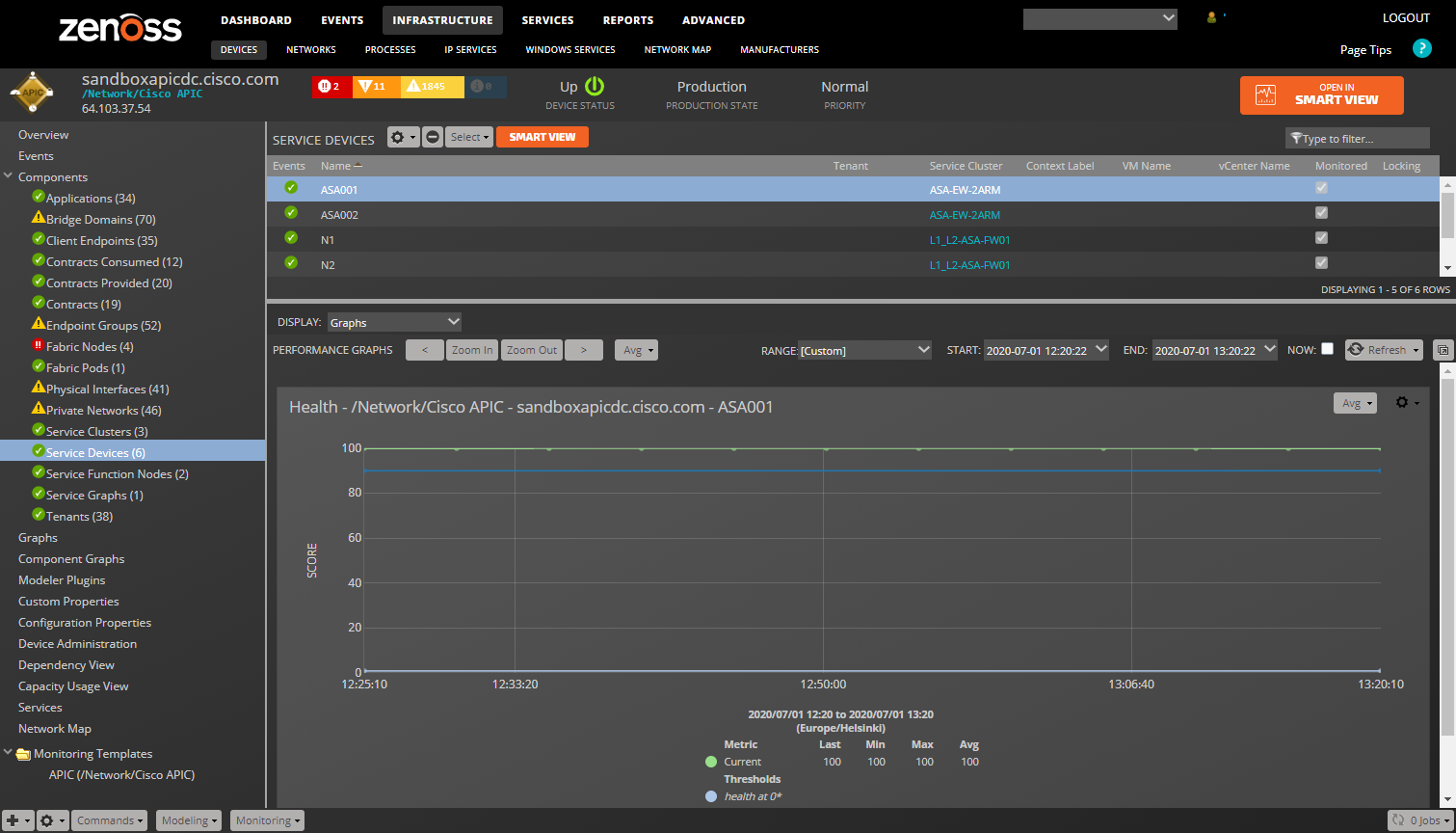
Service Devices
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: Service Cluster
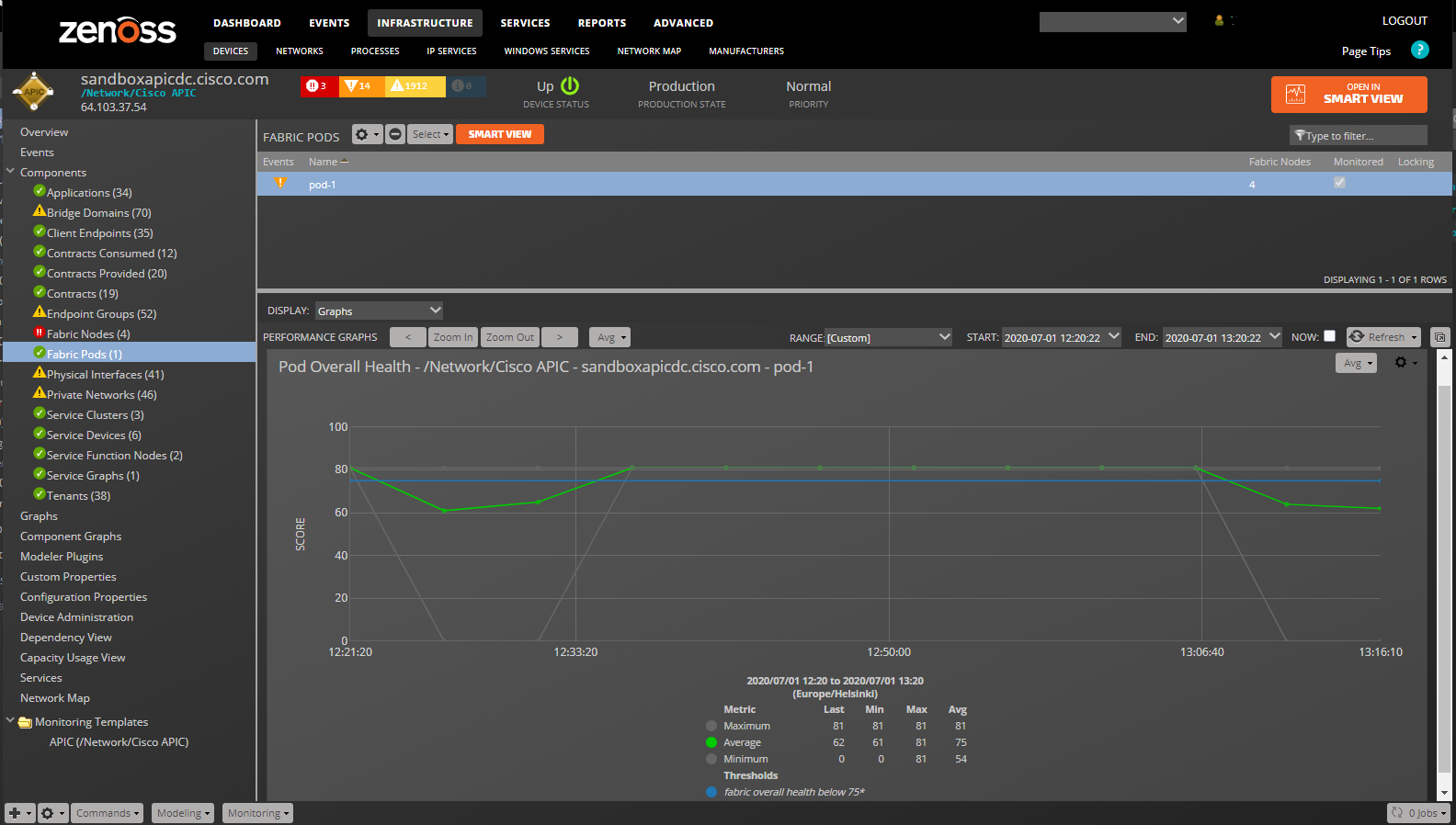
Fabric Pods
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class
- Relationships: APIC, Fabric Nodes
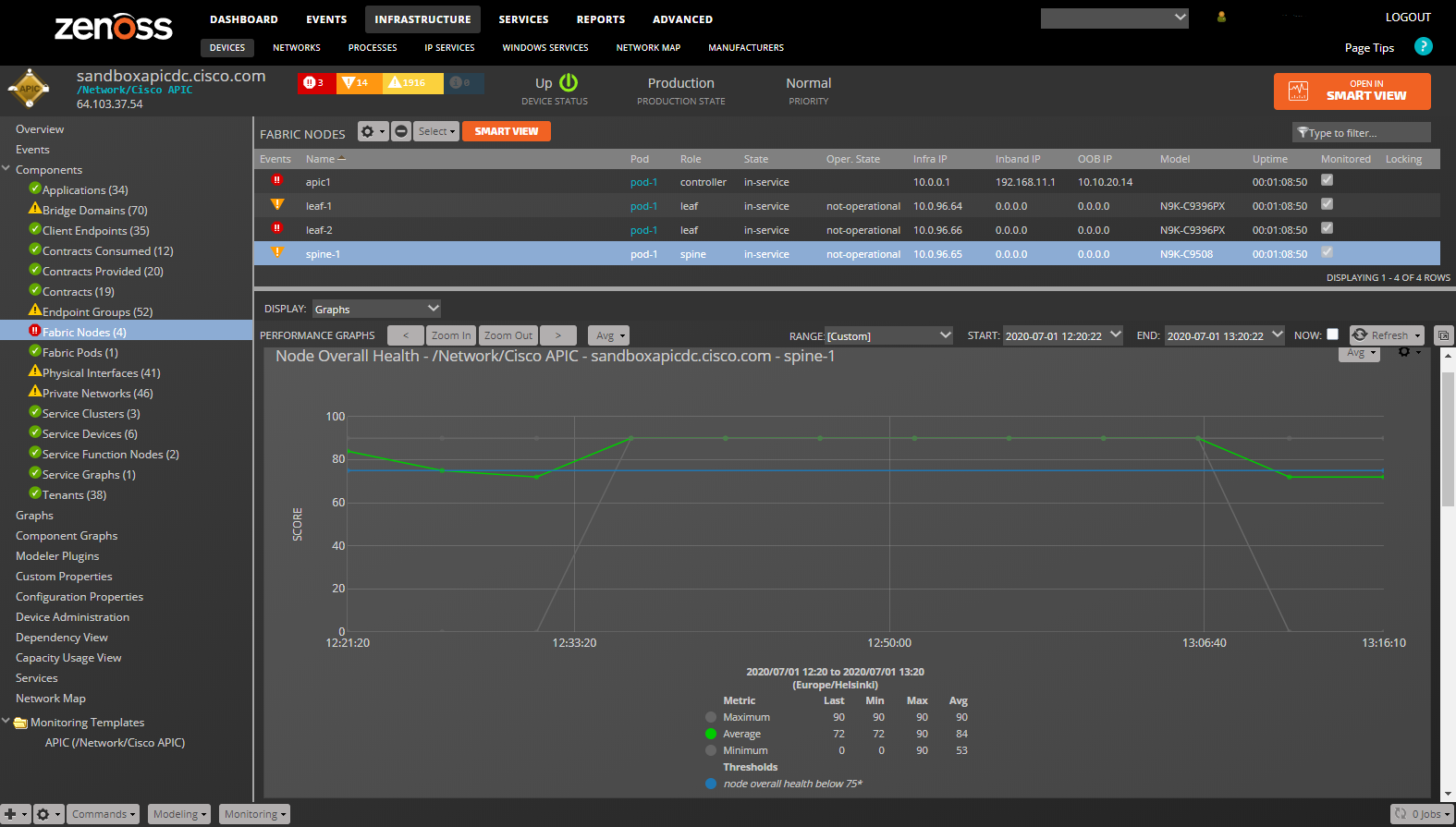
Fabric Nodes
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class, Node ID, Role, State, Operational State, Uptime, Infrastructure IP, In-Band Management IP, Out-of-Band Management IP, Fabric ID, Pod ID, Model, Revision, Serial Number, Firmware Version
- Relationships: Fabric Pod, Physical Interfaces
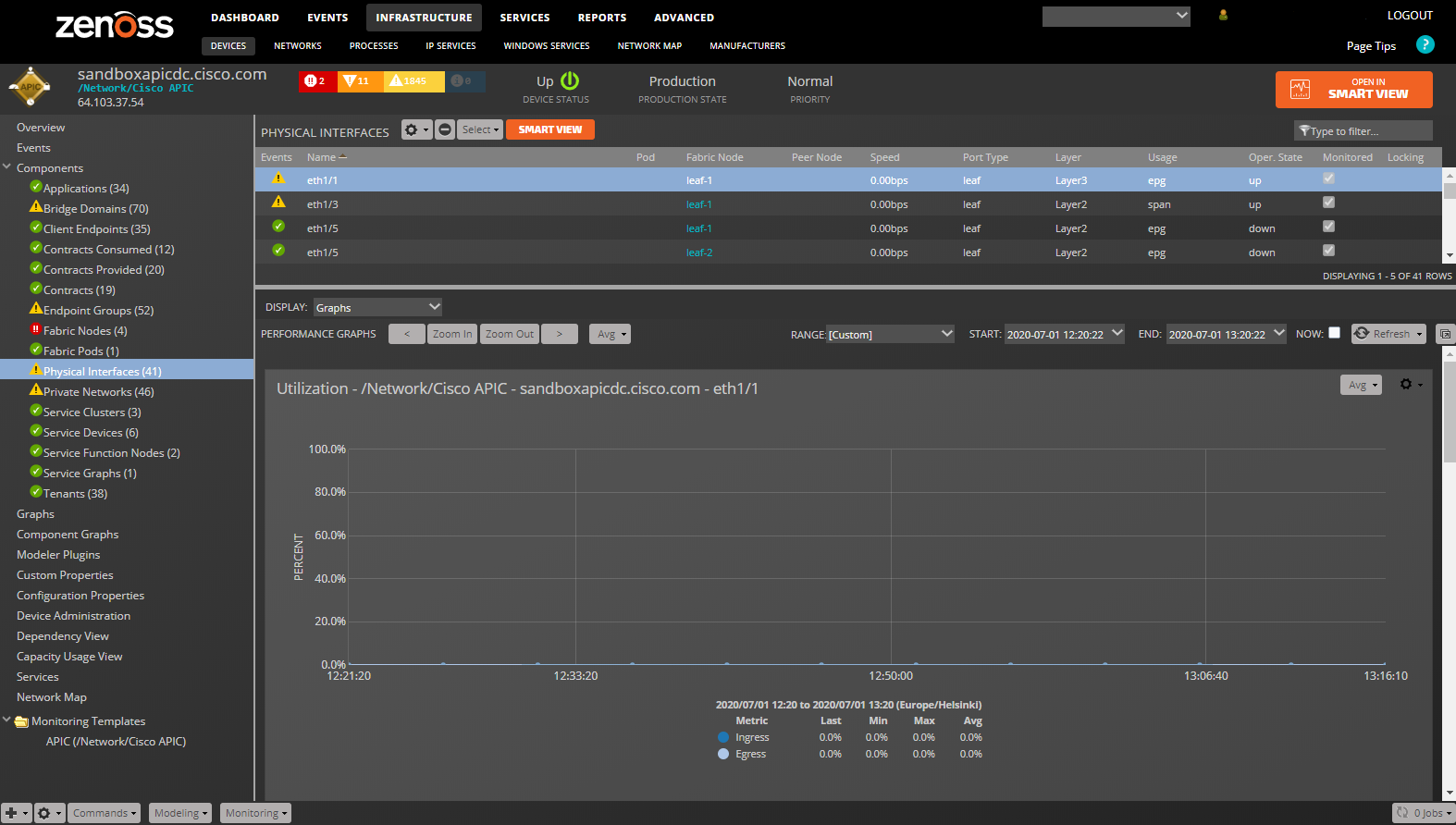
Physical Interfaces
- Properties: Title, ACI Distinguished Name (DN), ACI Object Class, Operational State
- Relationships: Fabric Node
Performance Monitoring
The following datapoints will be collected every 5 minutes by default. The individual health scores can be configured to collect at a different interval using the zCiscoAPICHealthInterval configuration property. All other statistics are pre-aggregated to 5 minute intervals by the APIC, so collecting on a different interval would lead to inaccurate results. For this reason the collection interval for all other statistics cannot be changed in Zenoss.
Tenants (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Applications (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Endpoint Groups (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Private Networks (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Bridge Domains (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Service Devices (Health Monitoring Template): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Fabric Pods (FabricPod Monitoring Template): fabricOverallHealth_healthAvg: Fabric Overall Health (5 minute average). (percent): fabricOverallHealth_healthMax: Fabric Overall Health (5 minute maximum). (percent): fabricOverallHealth_healthMin: Fabric Overall Health (5 minute minimum). (percent)
All Fabric Nodes (FabricNode Monitoring Template): topSystem_systemUpTime: Seconds since the node booted. (seconds)
Spine and Leaf Fabric Nodes (FabricSwitch and Health Monitoring Templates): fabricNodeHealth_healthAvg: Node Overall Health (5 minute average). (percent): fabricNodeHealth_healthMax: Node Overall Health (5 minute maximum). (percent): fabricNodeHealth_healthMin: Node Overall Health (5 minute minimum). (percent): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Physical Interfaces (L1PhysIf and Health Monitoring Templates): eqptIngrTotal_utilAvg: Ingress utilization. (percent): eqptIngrTotal_bytesRate: Ingress bytes rate. (bytes/sec): eqptIngrTotal_pktsRate: Ingress packets rate. (packets/sec): eqptEgrTotal_utilAvg: Egress utilization. (percent): eqptEgrTotal_bytesRate: Egress bytes rate. (bytes/sec): eqptEgrTotal_pktsRate: Egress packets rate. (packets/sec): health_cur: Current Health Score. (percent)
Event Management
Zenoss periodically polls the APIC for faults and creates Zenoss events when they occur. The APIC fault life-cycle closely matches that of a Zenoss event. This means that corresponding Zenoss events will automatically clear when their APIC fault counterparts clear.
Note: APIC fault events may reoccur in Zenoss if they're close in Zenoss, but not cleared on the APIC. For this reason it is recommended that the APIC fault events be acknowledged in Zenoss instead of closed until they are actually resolved on the APIC.
Note: Zenoss attempts to set the timestamp on fault events to the timestamp the APIC reported their occurrence instead of the time that Zenoss collected them. For this reason it is recommended that both your APICs and Zenoss servers keep accurate time. Zenoss will attempt to determine any time difference between the Zenoss collector server and the APIC and adjust event timestamps accordingly.
The following fields will be populated for each event.
Standard Zenoss Event Fields
- device: APIC device in the /Network/Cisco APIC device class.
- component: Zenoss component related to the fault.
- eventKey: APIC distinguished name (DN) for the fault.
- eventClassKey: cisco-apic-code where code is the APIC fault code.
- eventGroup: cisco-apic-faultInst.
- summary: Description or descr for the APIC fault.
- severity: Mapped from the APIC severity for the fault using the
following table.
- APIC cleared = Zenoss Clear
- APIC info = Zenoss Info
- APIC warning = Zenoss Warning
- APIC minor = Zenoss Warning
- APIC major = Zenoss Error
- APIC critical = Zenoss Critical
- count: Occurrences or occur for the APIC fault.
The following additional fields and potentially more will also be populated for each event. These are the fields native to an APIC fault. If a fault occurs that has other fields, those fields will be added with the same cisco.apic prefix.
Additional APIC Fault Event Details
- cisco.apic.ack
- cisco.apic.cause
- cisco.apic.changeSet
- cisco.apic.code
- cisco.apic.created
- cisco.apic.descr
- cisco.apic.dn
- cisco.apic.domain
- cisco.apic.highestSeverity
- cisco.apic.lastTransition
- cisco.apic.lc
- cisco.apic.occur
- cisco.apic.origSeverity
- cisco.apic.prevSeverity
- cisco.apic.rule
- cisco.apic.severity
- cisco.apic.subject
- cisco.apic.type
Impact and Root Cause Analysis
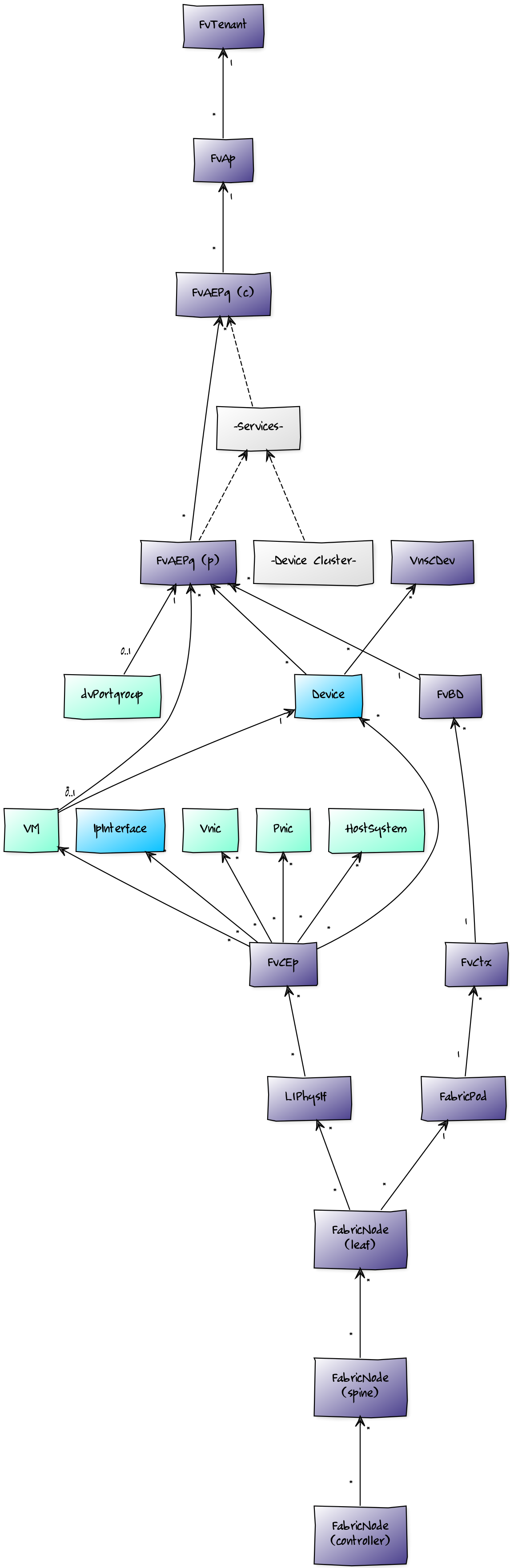
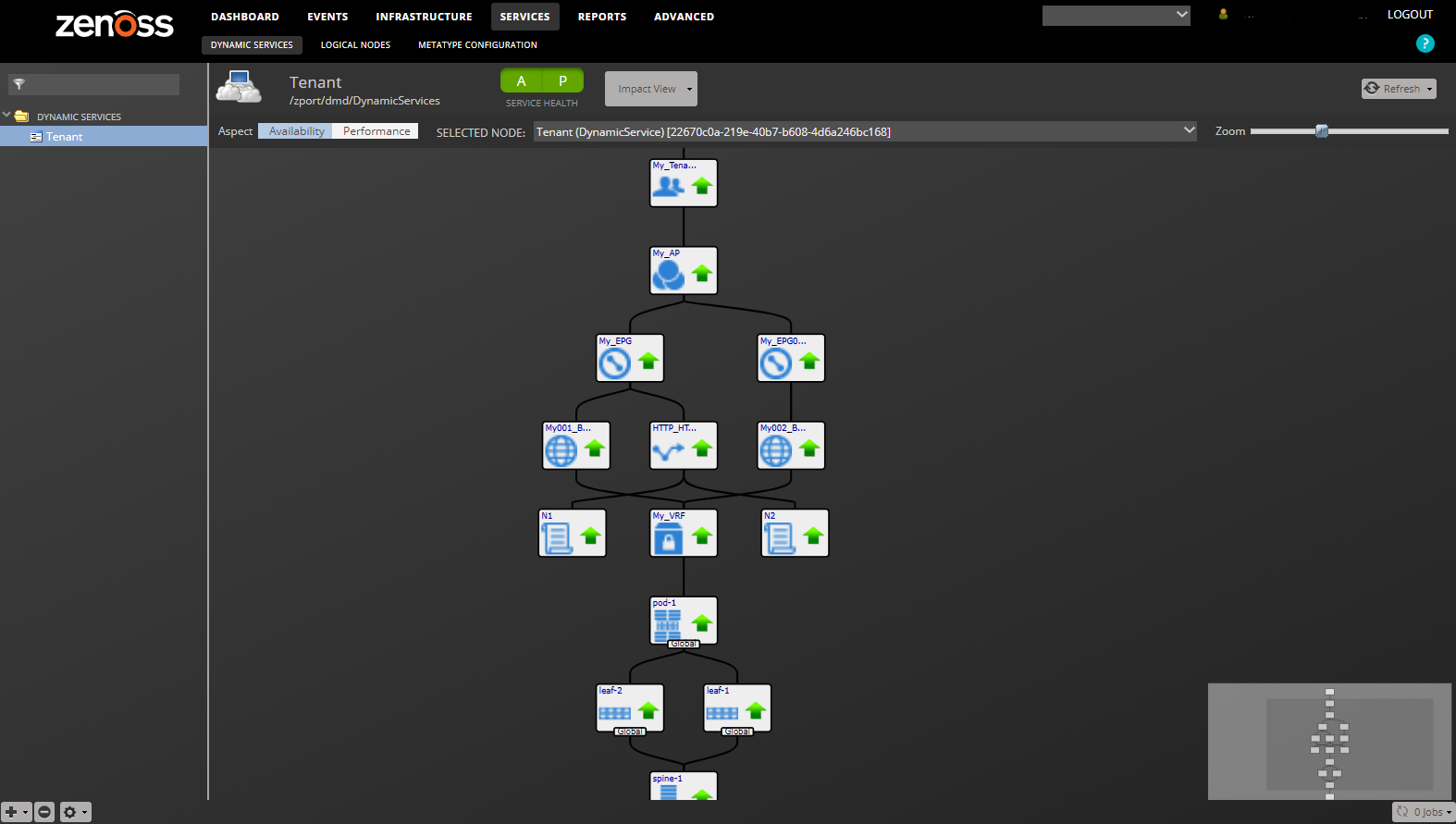
When combined with Zenoss Service Dynamics, this ZenPack adds built-in service impact and root cause analysis capabilities for services running on the ACI fabric. The service impact relationships shown in the diagram and described below are automatically added and maintained. These will be included in any services that contain one or more of the discovered components listed above.
Impact Relationships between APIC Components
- Controller fabric nodes impact controlled spine fabric nodes.
- Spine fabric nodes impact connected leaf fabric nodes.
- Leaf fabric nodes impact their fabric pod.
- Fabric pods impact private networks on the fabric.
- Private networks impact associated bridge domains.
- Bridge domains impact associated endpoint groups.
- Endpoint groups impact their application.
- Service graphs impact endpoint groups that consume their associated contract.
- Service function nodes impact their service graph.
- Service clusters impact their service function node.
- Service devices impact their service cluster.
- Applications impact their tenant.
- Physical interfaces impact connected client endpoints
Impact Relationships with non-APIC Components
- Underlying network service devices impact associated APIC service devices.
- NetScaler virtual servers impact associated APIC service function nodes.
- Server devices impact connected APIC endpoint groups.
- Client endpoints impact server devices.
- Client endpoints impact network interfaces.
- Client endpoints impact vSphere host systems.
- Client endpoints impact vSphere virtual machines.
- Client endpoints impact physical NICs.
- Client endpoints impact virtual NICs.
- vSphere dvPortgroups impact associated APIC endpoint groups.
- vSphere VMs impact connected APIC endpoint groups.
Most of the impacts described above follow the default policy of a node being in the worst state of the nodes that impact it. For example, a single controller fabric node failure will imply that all controlled switches are failed. In cases like these the default policy is not appropriate and a custom policy will be used instead.
Custom Impact Policies
- A fabric pod will be DOWN if 100% of its leaf nodes are DOWN. It will be DEGRADED if 50% or more of the leaf nodes are down, and ATRISK if 2 or more leafs are down.
- A leaf node will be DOWN if 100% of its spine nodes are DOWN. It will be DEGRADED if 50% or more of the spine nodes are down, and ATRISK if 2 or more spines are down.
- A spine node will be ATRISK if 2 or more controllers are down.
Usage
Adding an APIC
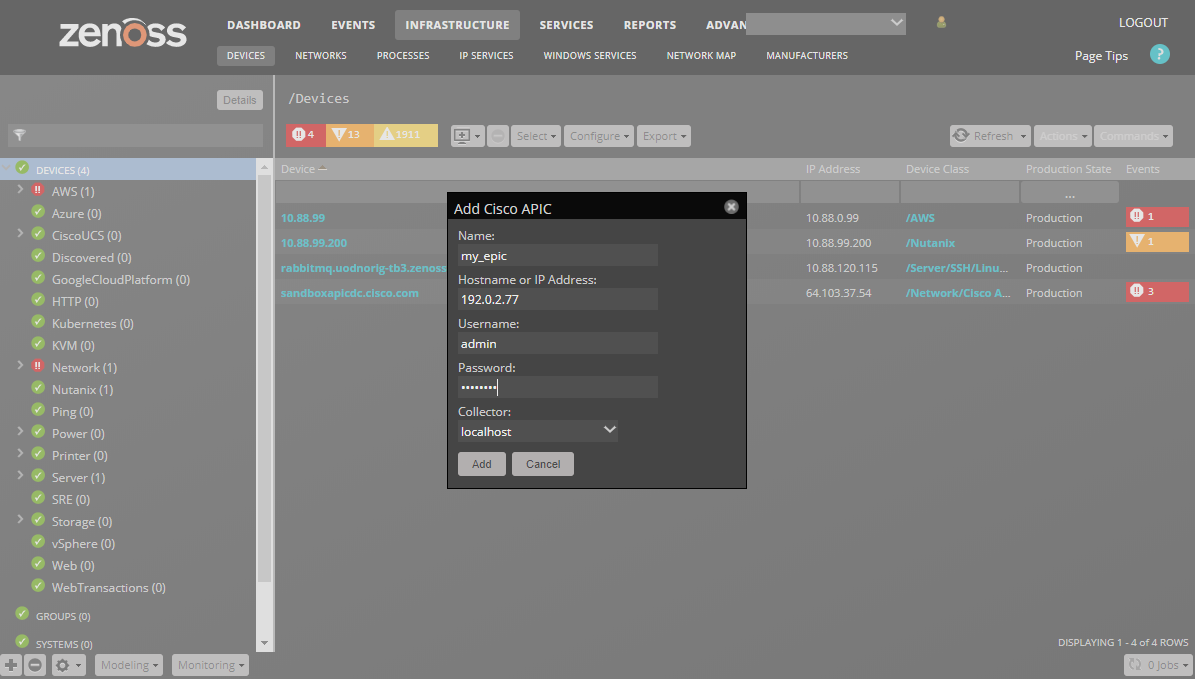
Use the following steps to start monitoring an APIC using the Zenoss web interface.
- Navigate to the Infrastructure page.
- Choose Add Cisco APIC from the add device button.
- Fill out the form.
- Name can be anything you want.
- Hostname or IP Address must be resolvable and accessible from the collector server chosen in the Collector field. See Configuring Management Addresses for more information on what address should be specified.
- Username and Password are the same as what you'd use to login the the APIC's web interface. See Minimum Permissions for more information on the minimum permissions the provided APIC username must have.
- Click ADD.
Alternatively you can use zenbatchload to add APICs from the command line. To do this, you must create a file with contents similar to the following. Replace all values in angle brackets with your values minus the brackets. Multiple APICs can be added under the same /Devices/Network/Cisco APIC section.
"/Devices/Network/Cisco APIC"
my-apic setManageIp='192.0.2.77', zCiscoAPICUsername='admin', zCiscoAPICPassword='changeme'
You can then load the endpoint(s) with the following command.
zenbatchload <filename>
Configuring Management Addresses
When adding an APIC to Zenoss, you must enter a Hostname or IP Address. This address must be of one of the controller nodes for a fabric. You should not add each controller node as a separate device in Zenoss. Zenoss manages the entire cluster through one controller node at a time. Adding multiple controller nodes in the same cluster will result in Zenoss performing double or even triple monitoring of the same data.
Zenoss will automatically discover both the in-band and out-of-band management addresses for each controller node in the cluster on an ongoing basis. If at any point Zenoss is unable to communicate with a controller node, it will round-robin through the other controller nodes until it finds one that's reachable. Monitoring will continue through a functioning controller node. This allows Zenoss to provide uninterrupted monitoring of the fabric when individual controllers are taken offline for maintenance, or go offline for other reasons.
It is important to configure Zenoss appropriately to use the correct management address(es) for your APIC cluster. This is done by configuring the zCiscoAPICMgmtInterface property. The following options are available.
- out-of-band (default)
- in-band
- static
Choosing out-of-band will cause Zenoss to use the configured out-of-band (OOB) management addresses. In-band will cause Zenoss to use the in-band management addresses. Choosing static will result in Zenoss only using the provided address to manage the cluster and means that no failover to other controller nodes is possible. Static should only be used in situations where Zenoss is accessing a controller node through NAT and wouldn't be able to access the other controller nodes via their out-of-band or in-band management addresses.
Minimum Permissions
The username and password provided when adding an APIC to Zenoss must have the admin role for Zenoss to successfully model and monitor the fabric. It is acceptable to use an admin read-only role as Zenoss never performs writes.
To grant the user admin read-only permissions you must configure the user in the APIC portal to have both role admin and role read-only. If your APIC has a single role labeled read-only admin it will not work.
Limitations
The current release is known to have the following limitations.
- Modeling of APIC is performed only once per Zenoss modeling cycle which by default is 12 hours. This means it can be up to 12 hours before Zenoss is aware of changes to the APIC configuration.
- Service impact and root cause analysis with the compute domain only works when APIC is integrated with VMware vSphere. Not physical domains, Hyper-V, OpenStack or other integrations.
Installed Items
Installing this ZenPack will add the following items to your Zenoss system.
Configuration Properties
- zCiscoAPICUsername: APIC username. Default is admin.
- zCiscoAPICPassword: APIC password. Default is blank.
- zCiscoAPICPort: APIC REST API (web interface) TCP port. Defaults to 443.
- zCiscoAPICSSL: APIC REST API (web interface) SSL. Default is true.
- zCiscoAPICHealthInterval: Polling interval for component health scores.
- zCiscoAPICMgmtInterface: Management interface Zenoss will use: out-of-band, in-band or static. Defaults to out-of-band.
- zCiscoAPICIgnoreIds: List of ids to not model. Supports regular expressions. Ids can be APIC DNs or Zenoss IDs.
- zCiscoAPICIgnoreTypes: List of types to not model. Supports regular expressions. Types can be APIC class names or Zenoss module names. Using APIC class names is preferable to avoid making unnecessary APIC API calls.
Device Classes
- /Network/Cisco APIC
Modeler Plugins
- zenoss.Cisco.APIC
Datasource Types
- Cisco APIC Faults
- Cisco APIC Health
- Cisco APIC Stats
Monitoring Templates (all in /Network/Cisco APIC)
- APIC
- Health
- FabricPod
- FabricNode
- FabricController
- FabricLeaf
- FabricSpine
- FabricSwitch
- L1PhysIf
Event Classes
- /Cisco APIC
Event Class Mappings
- /Cisco APIC/Cisco APIC Fault Default Mapping
Zenoss Analytics
This ZenPack provides additional support for Zenoss Analytics. Perform the following steps to install extra reporting resources into Zenoss Analytics after installing the ZenPack.
- Copy analytics-bundle.zip from $ZENHOME/ZenPacks/ZenPacks.zenoss.CiscoAPIC/analytics/ on your Zenoss server.
- Navigate to Zenoss Analytics in your browser.
- Login as superuser.
- Remove any existing Cisco APIC ZenPack folder.
- Choose Repository from the View menu at the top of the page.
- Expand Public in the list of folders.
- Right-click on Cisco APIC ZenPack folder and choose Delete.
- Confirm deletion by clicking OK.
- Add the new Cisco APIC ZenPack folder.
- Choose Server Settings from the Manage menu at the top of the page.
- Choose Import in the left page.
- Remove checks from all check boxes.
- Click Choose File to import a data file.
- Choose the analytics-bundle.zip file copied from your Zenoss server.
- Click Import.
You can now navigate back to the Cisco APIC ZenPack folder in the repository to see the following resources added by the bundle.
Dashboards
- Fabric Health Dashboard
Reports
- Fabric Pod Overall Health Report
- Fabric Node Overall Health Report
Ad Hoc Views
- Fabric Pod Overall Health View
- Fabric Node Overall Health View
Topics
- Fabric Pod Overall Health Topic
- Fabric Node Overall Health Topic
Domains
- Cisco APIC Domain
Topics can be used to create ad hoc views using the following steps. Topics are a layer on top of domains that are more focused on a certain type of data.
- Choose Ad Hoc View from the Create menu.
- Expand Public then Cisco APIC ZenPack.
- Choose one of the topics.
Domains can also be used to create ad hoc views using the following steps.
- Choose Ad Hoc View from the Create menu.
- Click Domains at the top of the data chooser dialog.
- Expand Public then Cisco APIC ZenPack.
- Choose the Cisco APIC Domain domain.
Changes
1.3.0
- Fix of excessive topSystem API calls cause performance problems. (ZPS-5140, ZPS-7150)
- Fix for Token timeout. (ZPS-6628)
- Tested with Zenoss 6.4.1- 6.5.0, Zenoss Cloud and Impact 5.5.1
1.2.3
- Fix controllers appearing with an invalid role of "8". (ZPS-2546)
- Fix potential "health_dn" KeyError in health datasource. (ZPS-2380)
- Mask APIC credentials in debug log. (ZPS-616)
1.2.2
- Fix modeling failure related to unexpected node roles. (ZPS-1930)
1.2.1
- Collect health data individually and dynamically. (ZEN-22303)
- Tested against APIC 1.0(3f), 1.2(1k), 1.2(2h).
1.2.0
- Add attached host, server, network interface Impact relationships.
1.1.0
- Add OpenStack integration.
1.0.5
- Add "Peer Node" and "Peer Interface" properties to physical interfaces.
- Remove potentially cyclic EPG impact relationships. (ZEN-19310)
1.0.4
- Fix flooding APIC with aaaLogin and aaaRefresh calls. (ZEN-17881)
- Remove newlines from dim_ciscoapic_client_endpoint.ip. (ZEN-17914)
- Add "Firmware Status" property to fabric nodes.
1.0.3
- Fix duplicate of "Node Overall Health" graph on upgrade. (ZEN-17728)
- Add "Usage" property to physical interfaces.
- Add zCiscoAPICIgnoreIds and zCiscoAPICIgnoreTypes properties.
- Add client endpoint modeling.
1.0.2
- Fix handling of stats and events when APIC has a timezone offset. (ZEN-16582)
- Add more debug logging during modeling.
- Fix potential "TypeError" in UI before stats are collected. (ZEN-16684)
- Added zCiscoAPICMgmtInterface property. Support cluster fail-over. (ZEN-17385)
- Added several properties to Fabric Node and Contract modeling. (ZEN-17393)
- Added Cisco APIC Properties datasource type.
- Added service cluster properties: device package, vendor, model, version. (ZEN-17532)
- Fixed status field in details panel for all components. (ZEN-17536)
- Added physical interface property: operational state. (ZEN-17540)
1.0.1
- Fix "Not valid JSON" errors. (ZEN-16194)
- Fix "KeyError: 'None'" modeling error. (ZEN-16314)
1.0.0
- Initial release.