Control Center
ZenPacks.zenoss.ControlCenter
This ZenPack monitors the Control Center application management and orchestration system.
Features of the Control Center ZenPack include:
- Dynamically generated templates based completely on the ControlCenter API
- Monitoring of Pools, Hosts, Services, Running services
- Graphs for Memory, CPU, and Page Faults
- Selected Thresholds
Commercial
This ZenPack is developed and supported by Zenoss Inc. Commercial ZenPacks are available to Zenoss commercial customers only. Contact Zenoss to request more information regarding this or any other ZenPacks. Click here to view all available Zenoss Commercial ZenPacks.
Support
This ZenPack is included with commercial versions of Zenoss and enterprise support for this ZenPack is provided to Zenoss customers with an active subscription.
Releases
Version 1.2.0- Download
- Released on 2016/06/02
- Requires ZenPacks.zenoss.PythonCollector > 1.5
- Compatible with Zenoss Core 5.1.x, Zenoss Resource Manager 5.1.x
Version 1.0.1- Download
- Released on 2015/07/04
- Requires ZenPacks.zenoss.PythonCollector > 1.5
- Compatible with Zenoss Core 5.0.x, Zenoss Resource Manager 5.0.x
Version 1.0.0- Download
- Released on 2015/02/18
- Compatible with Zenoss Core 5.0.x, Zenoss Resource Manager 5.0.x
Prerequisites
- ControlCenter must be running and listening on a target device's HTTPS port.
- ControlCenter access credentials for the monitor user must be provided.
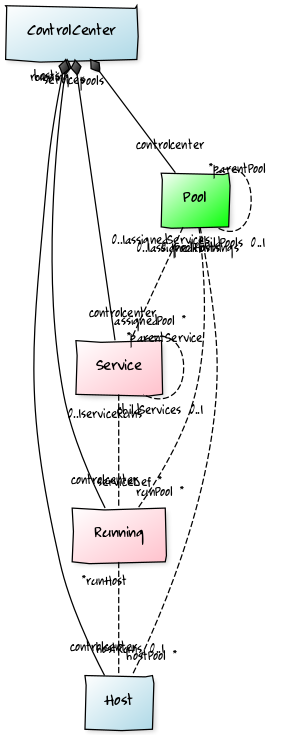
ControlCenter Structure and Discovery
ControlCenter Structure
The following ControlCenter components will be automatically discovered through the modeling process.
CC-Pools
- Description: Resource pools that Zenoss services are associated with. Non-Zenoss services will not have a pool and will not be reflected in the Pool grid counts.
- Attributes: Memory Capacity, CPU Core Capacity
- Relationships: CC-Hosts, CC-Services, CC-Running
CC-Hosts
- Description: Host systems that run Zenoss services.
- Attributes: CPU Cores, IP Address, Memory
- Relationships: CC-Pool, CC-Running
CC-Services
- Description: Service definitions that specify service properties and states. Only Zenoss services have an associated CC-Pool.
- Attributes: Target State
- Relationships: Parent Service, Child Services, CC-Pool, CC-Running
CC-Running
- Description: These are the running services defined in CC-Services. Only Zenoss services have an associated CC-Pool.
- Attributes: Instances, Status, Service ID, Parent Service ID, Host ID
- Relationships: CC-Pool, CC-Host, CC-Service
CC-Volumes
- Description: ControlCenter storage volume
- Attributes: TotalBytes, UsedBytes, DataFile, Driver, Status
- Relationships: None
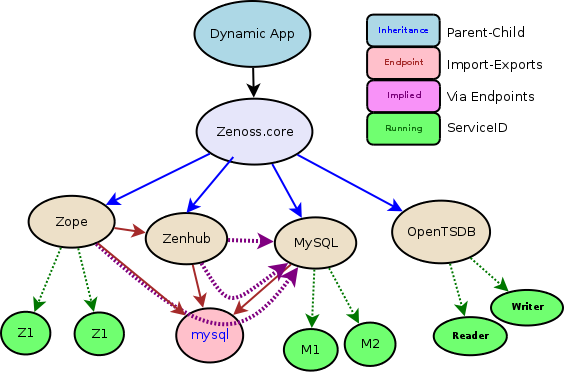
Impact Support
In the ControlCenter, the natural objects are Pools, Hosts, Services, and Running services. The following basic hierarchy is supported:
- Pools: Contain Hosts, Services, Running services, and other Pools
- Hosts: Contain Running services
- Services: Define all services that will run on Hosts
- Running: Are running service instances of the Service definitions
In addition to the base hierarchy above we also have relationships between the objects based on TCP/UDP "Endpoint" port connections.
In order to make the Impact relationships easier to understand we use the following rules:
- Objects who have a parent-child relationship are mapped directly
- Objects that have Endpoints are mapped to their respective targets
- Indirect Endpoints are re-mapped onto their Service definition
- Running services are mapped to their Service definition
Impact Configuration
In order to easily get a full impact diagram for ControlCenter, identify and add
the top-level service only (Zenoss.resmgr)
Installed Items
Installing this ZenPack will add the following items to your Zenoss system:
Device Class
This ZenPack adds the /ControlCenter Device Class which is already configured for ControlCenter monitoring after updating the values for the Configuration Properties referenced below.
Configuration Properties
The credential setup for the CCZP is very simple. You are only required to enter credentials (username, password) when you monitor a non-local installation of your ControlCenter.
- zControlCenterHost (Defaults to device name)
- zControlCenterPort (Defaults to HTTPS TCP/443)
- zControlCenterUser
- zControlCenterPassword
- zControlCenterPerfCycle: Performance collection interval (Default 300s)
- zControlCenterModelCycle: Modeling interval (Default 3600s)
Modeler Plugin
- zenoss.ControlCenter
Datasource Types
- Automatically generated from the ControlCenter API
Monitoring Templates
- Automatically generated from the ControlCenter API
Installation and Configuration
Installation consists of the following steps which will be covered in depth:
- Install the ZenPack on Zenoss
- Install the target device in Zenoss
- Bind the plugin modeler template to server
- Set the zXYZConnectionStrings property
- Model the device
Install the ZenPack
- If the CCZP was installed automatically, you don't need to do or restart anything.
- If CCZP was not installed by default, install the CCZP zenpack as usual. Make sure you restart all services before continuing.
Install the Target Device in Zenoss
Install the target server as you normally would.
- Note: The target device must be a valid DNS resolvable address.
Set the Credentials
note
If your CCZP lives on the same ControlCenter you are monitoring, you don't need to do anyting: CCZP get's its credentials from the local container that runs it.
warning
If you are modeling a different ControlCenter that is remote to the CCZP installation, you must set the credentials as follows:
- Select your device from the Infrastructures Tab
- Click on Configuration Properties
- Search for zControlCenter
- Set your username for zControlCenterUser
- Set your password for zControlCenterPassword
You must use the same username and password you would normally use to log into the CC interface. This is typically the zenoss account. Test the CC login page directly if you have any doubts.
Batch Configuration with zenbatchload
You can also add your devices in batch for convenience and automation.
-
Create a text file (filename: /tmp/db2.txt). Each server has a stanza like
/Devices/ControlCenter zPythonClass='ZenPacks.zenoss.ControlCenter.ControlCenter' 'mp6.zenoss.loc' -
Run the command on the terminal
zenbatchload /tmp/db2.txt
Model the ControlCenter
- From the device view, select Model Device from the gear menu.
- If all goes will Zenoss should model the device.
- Since the Pools, Hosts, Services, and Running services are just components of the server, you should see them hanging off of the device as components.
Changes
1.2.0
- Update device status: ZEN-23413
- Improve device status events
- Added health-checks for running services
1.1.0
- Added distributed storage Volumes
- Added health-checks for running services
1.0.1
- Upgrade ZenPackLib to YAML format
- Fix ZEN-16534: Allow Linux host linking in Impact
1.0.0
- Initial release