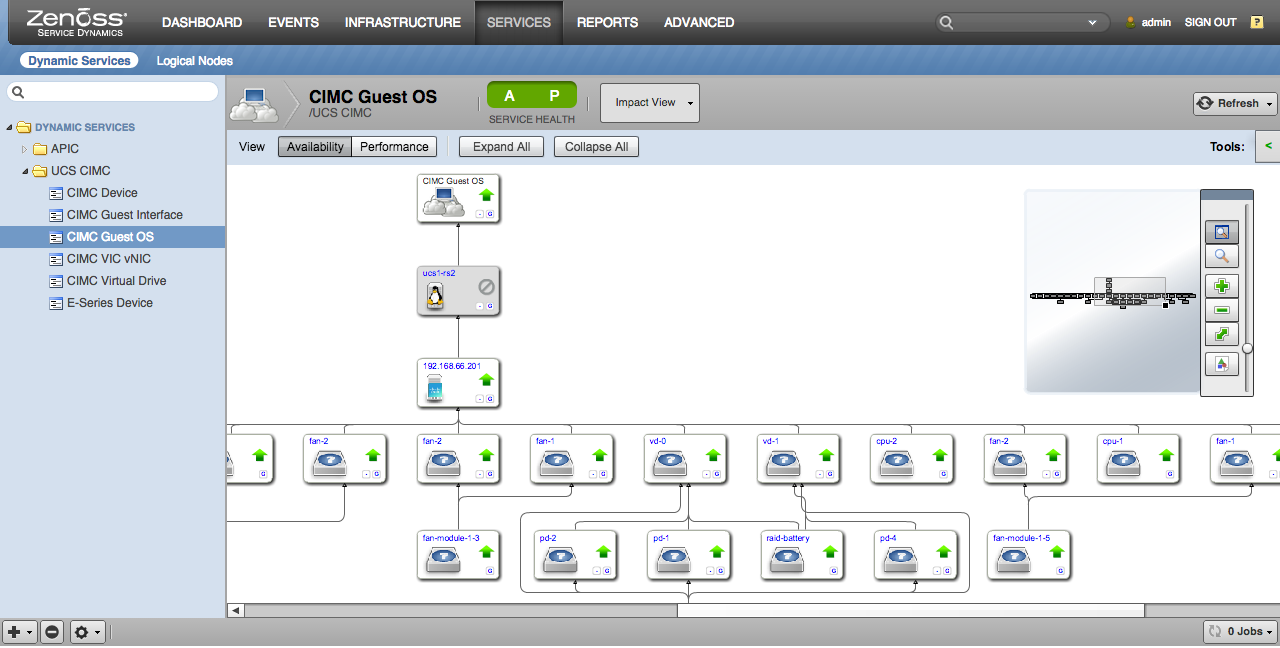
Cisco UCS
ZenPacks.zenoss.CiscoUCS
This ZenPack provides monitoring services for Cisco Unified Computing Systems(UCS). UCS Manager, UCS-Mini, stand-alone C-Series rack-mount servers and E-Series servers are supported.
Applications Monitored: Cisco UCS CIMC (1.5 and later), Cisco UCS Manager
Commercial
This ZenPack is developed and supported by Zenoss Inc. Commercial ZenPacks are available to Zenoss commercial customers only. Contact Zenoss to request more information regarding this or any other ZenPacks. Click here to view all available Zenoss Commercial ZenPacks.
Releases
Version 3.0.4 - Download
- Released: 2024-04-26
- Compatible with Zenoss Cloud and Zenoss 6.7
- Requires:
- CalculatedPerformance ZenPack (>=2.5.1)
- CiscoMonitor ZenPack (>=4.0)
- Dashboard ZenPack
- DynamicView ZenPack
- Predictive Threshold ZenPack
- PythonCollector ZenPack
- ZenPackLib ZenPack (>=2.0)
Version 3.0.3 - Download
- Released: 2023-06-15
- Compatible with Zenoss Cloud and Zenoss 6.7
- Requires:
- CalculatedPerformance ZenPack (>=2.5.1)
- CiscoMonitor ZenPack (>=4.0)
- Dashboard ZenPack
- DynamicView ZenPack
- Predictive Threshold ZenPack
- PythonCollector ZenPack
- ZenPackLib ZenPack (>=2.0)
This version of CiscoUCS fully replaces UCSCapacity!
If you are using UCSCapacity ZenPack, it should be upgraded to 2.0.0 before upgrading CiscoUCS 2.x to CiscoUCS 3.0.0. UCSCapacity can be removed after CiscoUCS has been upgraded. See Installation for more information.
Upgrade CiscoUCSCentral ZenPack to version 1.3.3 before upgrading CiscoUCS!
If you are using CiscoUCSCentral ZenPack, it should be upgraded to 1.3.3 before upgrading CiscoUCS 2.x to CiscoUCS 3.0.x. Failure to do so will result in import errors.
Version 2.8.1 Download
- Released: 2019-06-14
- Compatible with Zenoss Cloud, 6.3 - 5.3
- Requires: DynamicView ZenPack, PythonCollector ZenPack
Version 2.7.0 Download
- Released: 2018-04-18
- Compatible with Zenoss 4.2.X - 6.1.X
- Requires: DynamicView ZenPack, PythonCollector ZenPack
General Features
This ZenPack provides support for Cisco UCS Manager Platform and Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC). In general the following features are provided:
- System modeling
- System monitoring
- Capacity monitoring and projection (UCS Manager Only)
- Component Graphs
- Component Threshold
- DynamicView/Impact analysis
UCS Manager Features
UCS Manager monitoring data is collected using the UCS Manager XML API. When adding a UCS Manager to Zenoss it is important to provide the shared virtual IP address of your UCS domain's fabric interconnects. This allows Zenoss to continue monitoring when one fabric interconnect is undergoing maintenance or fails. Your Zenoss collector must be able to connect to the UCS Manager application on port 443/tcp.
Additional capacity features:
- Tracks current network and storage utilization within a UCS domain
- Notifies administrators when UCS resources are over capacity limits
- Identifies heavy fabric users and out-of-balance conditions
- Enables administrators to re-configure UCS resources to correct capacity issues
- Enables administrators to predict future capacity needs and proactively acquire hardware resources
- Add additional usability features and general enhancements
UCS Manager Discovery
The following components will be automatically discovered through the Cisco UCS Manager host, user and password you provide. The properties and relationships will be periodically remodeled to provide automatically up-to-date monitoring when the system configuration changes.
UCS Manager (Device)
- Properties: None
- Relationships: Service Profiles, Management Interfaces, Fabric Interconnects, Chassis, Fabric Extenders, Rack Servers
Adaptor Units
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number
- Relationships: Server Blade, Host Ethernet Interfaces
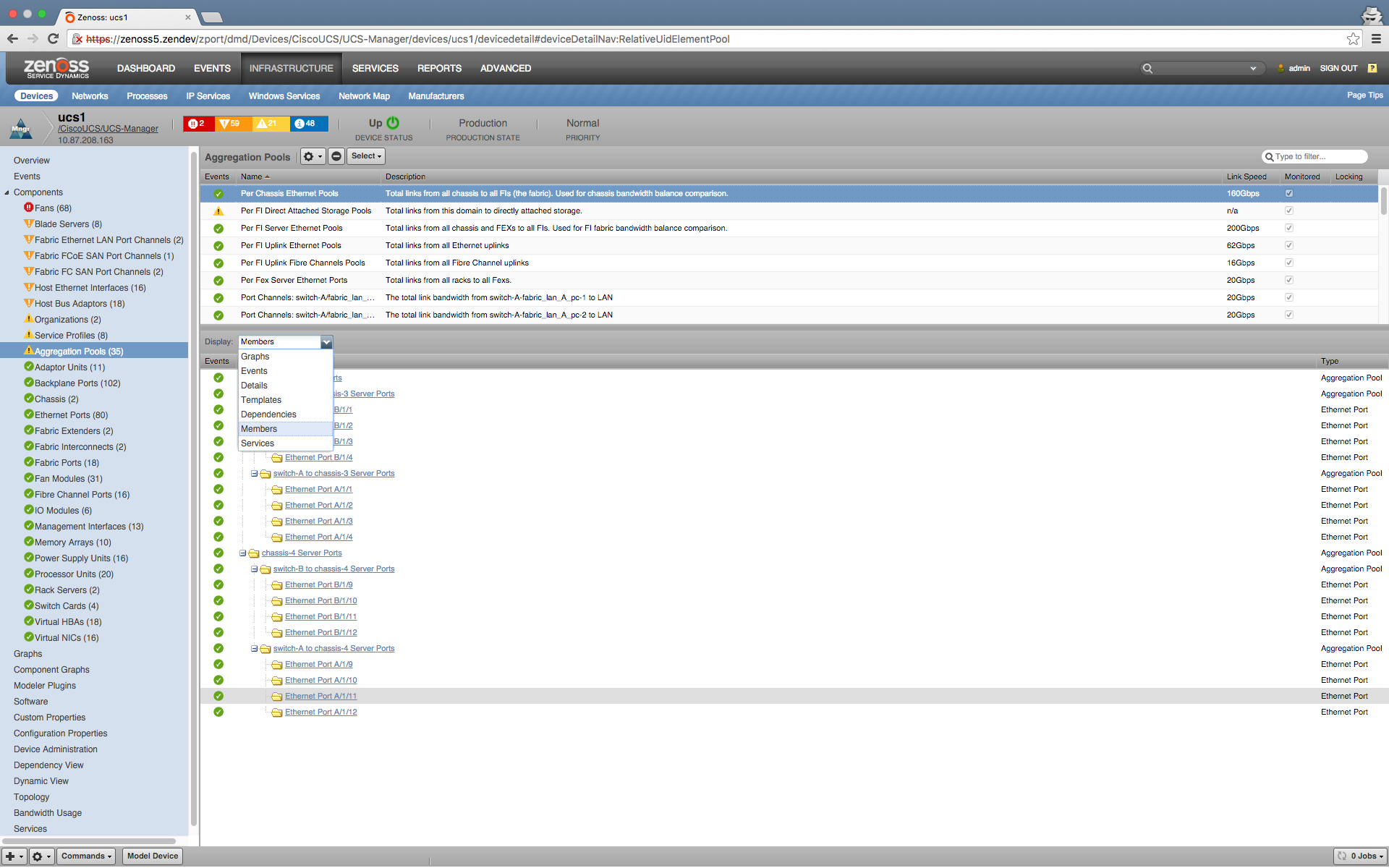
Aggregation Pools
- Properties: LinkSpeed, totalLinkSpeed, MinLinkSpeed
- Relationships: RelativeUidElementPool
Note
The bandwidthHeadroomRx and bandwidthHeadroomTx thresholds are disabled by default. The basic purpose of these thresholds is to identify when aggregation pools dip below a certain total threshold of reserved bandwidth. In some cases, this does not appear to be valuable information for the customer, especially when the customer normally operates with some pools configured at 2 Gbps, or even on some with a zero bandwidth allocation. This threshold looks more useful for environments with a standardized configuration where bandwidth allocations are consistent across pools, so identifying ones below a certain level would show an outlier and indicate a problem. There are already existing thresholds configured on each aggregation pool designed to generate an event when the bandwidth usage is at or above 90% and should provide customers good visibility to when there is an actual bandwidth limit issue.
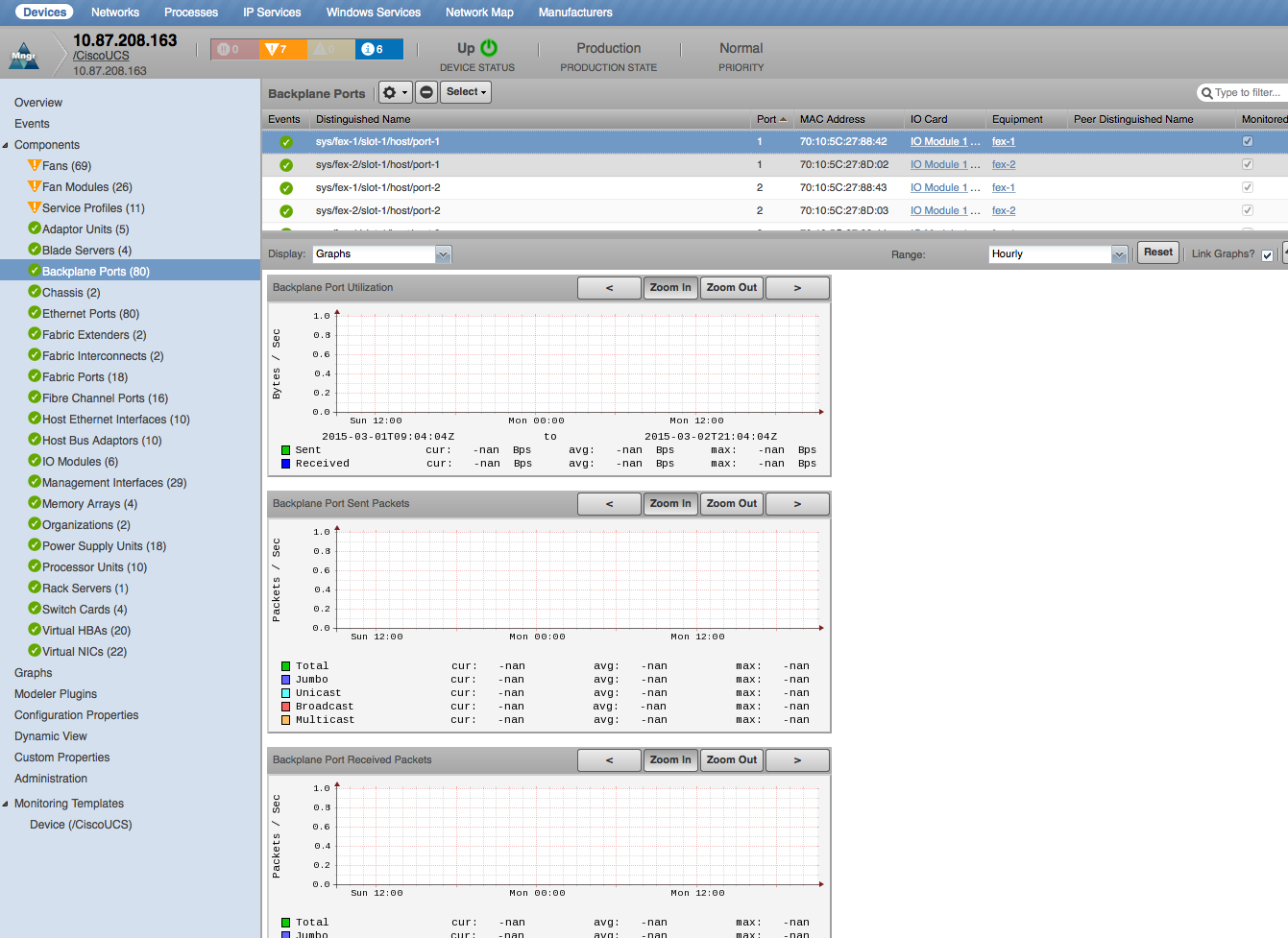
Backplane Ports
- Properties: DN, WWN, Operational Speed
- Relationships: IO Module
Blade Servers
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Presence, Operational State, Operational Power, Availability
- Relationships: Chassis, Memory Arrays, Processor Units, Adaptor Units, Bound Service Profile, Storage Controllers, Storage Local Disks, Storage Virtual Drives
Cartridge Servers
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Presence, Operational State, Operational Power, Availability
- Relationships: Chassis, Memory Arrays, Processor Units, Adaptor Units, Bound Service Profile, Storage Controllers, Storage Local Disks, Storage Virtual Drives
Chassis
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Operational State
- Relationships: UCS Manager, IO Modules, Servers, Fan Modules, Power Supply Units, Storage Controllers, Storage Local Disks, Storage Virtual Drives
Ethernet Ports
- Properties: DN, Switch ID, Slot ID, Port ID, MAC Address, Role, Type, Transport, Administrative State, Endpoint DN, Peer DN, Peer Slot ID, Peer Port ID
- Relationships: Switch Card, Fabric Ethernet LAN Port Channels, Fabric Fibre Channel Over Ethernet SAN Port Channels
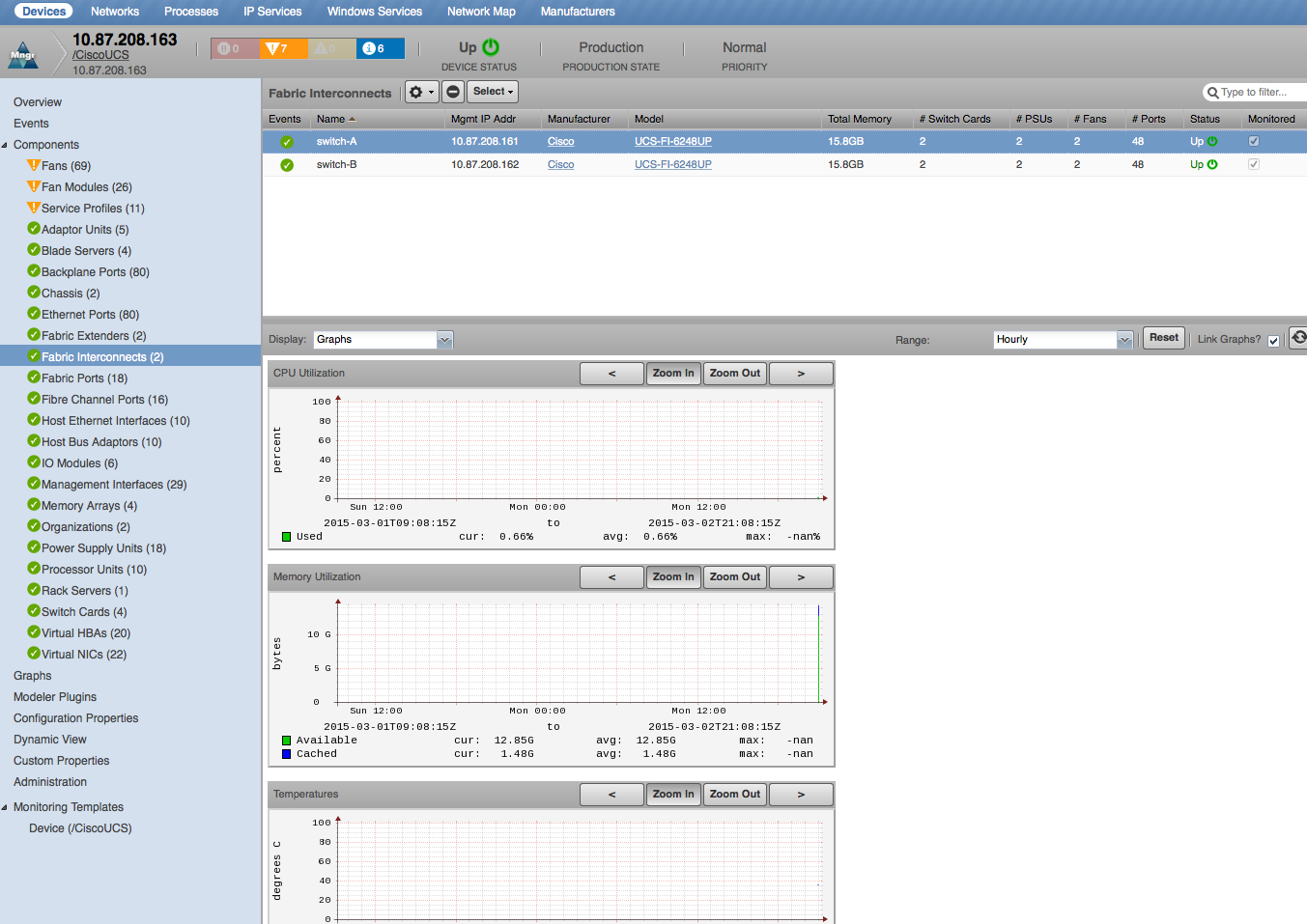
Fabric Interconnects
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Total Memory
- Relationships: UCS Manager, Switch Cards, Power Supply Units
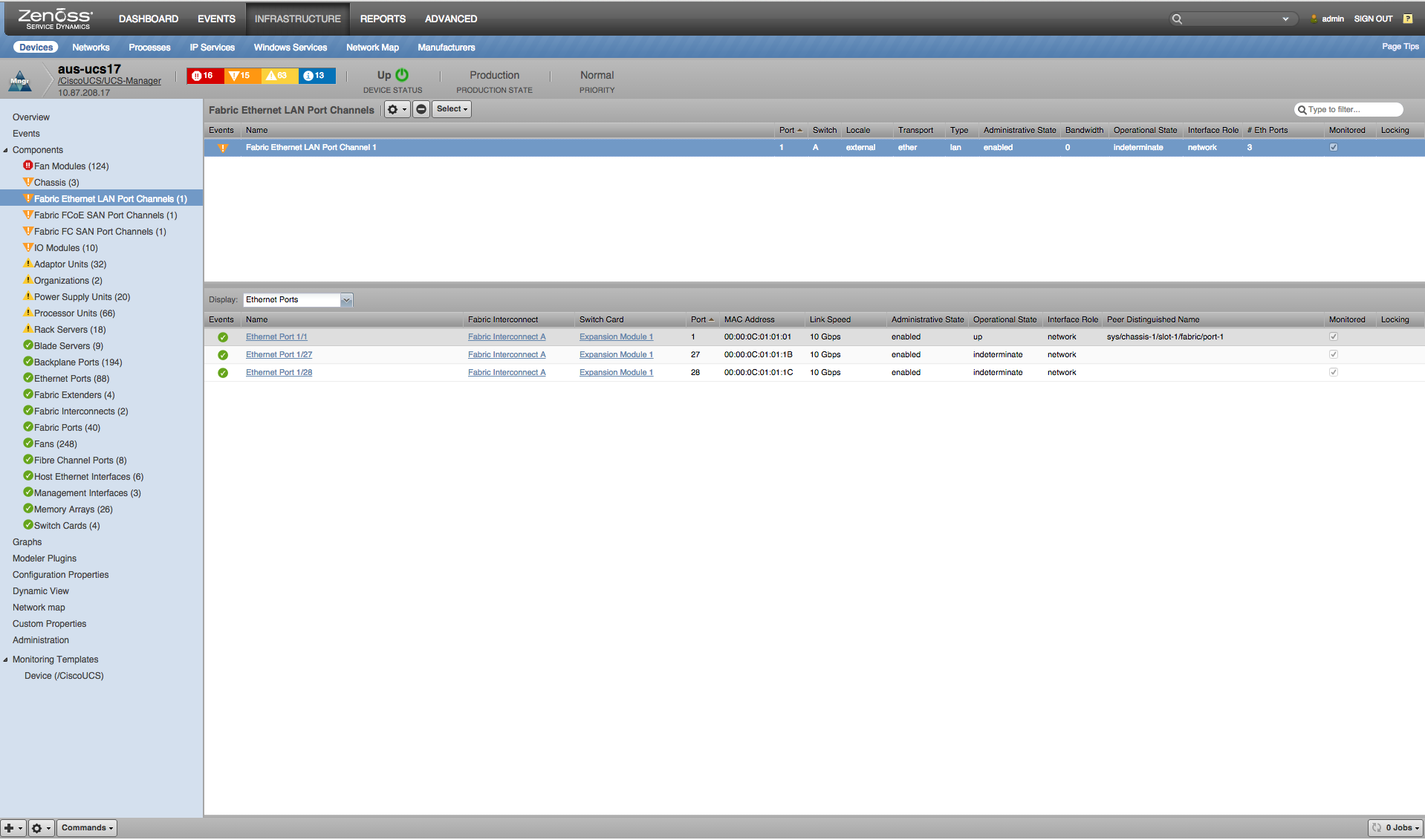
Fabric Ethernet LAN Port Channels
- Properties: DN, Port ID, Switch ID, Locale, Transport, Type, Admin State, Bandwidth, Operational State, Interface Role, Number of Members
- Relationships: Ethernet Ports
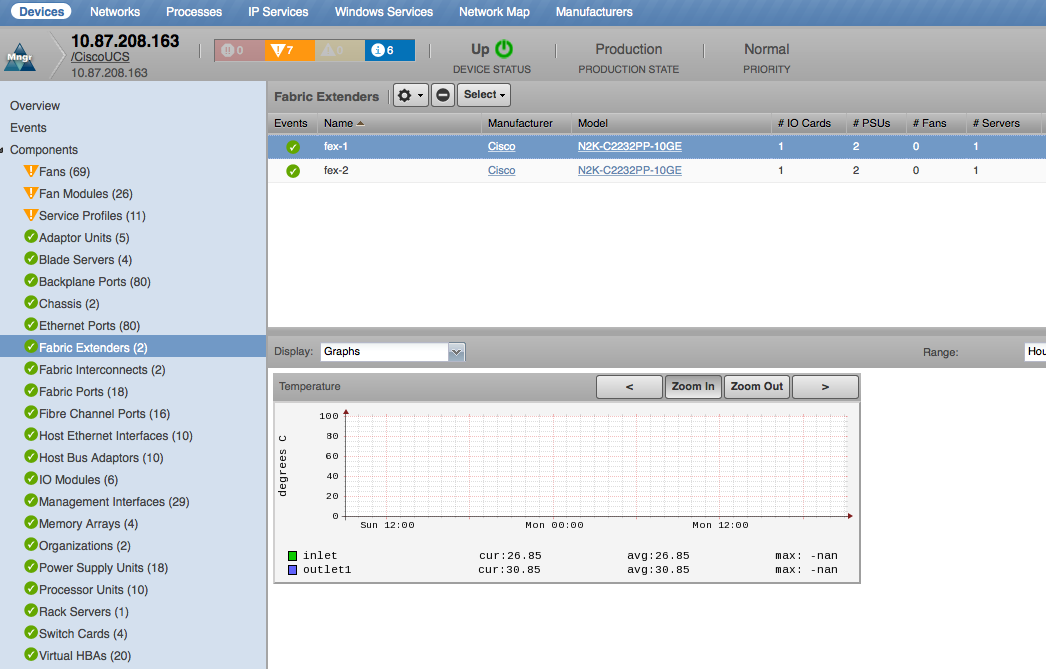
Fabric Extenders
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Total Memory
- Relationships: UCS Manager, Fabric Interconnects, IO Modules, Power Supply Units
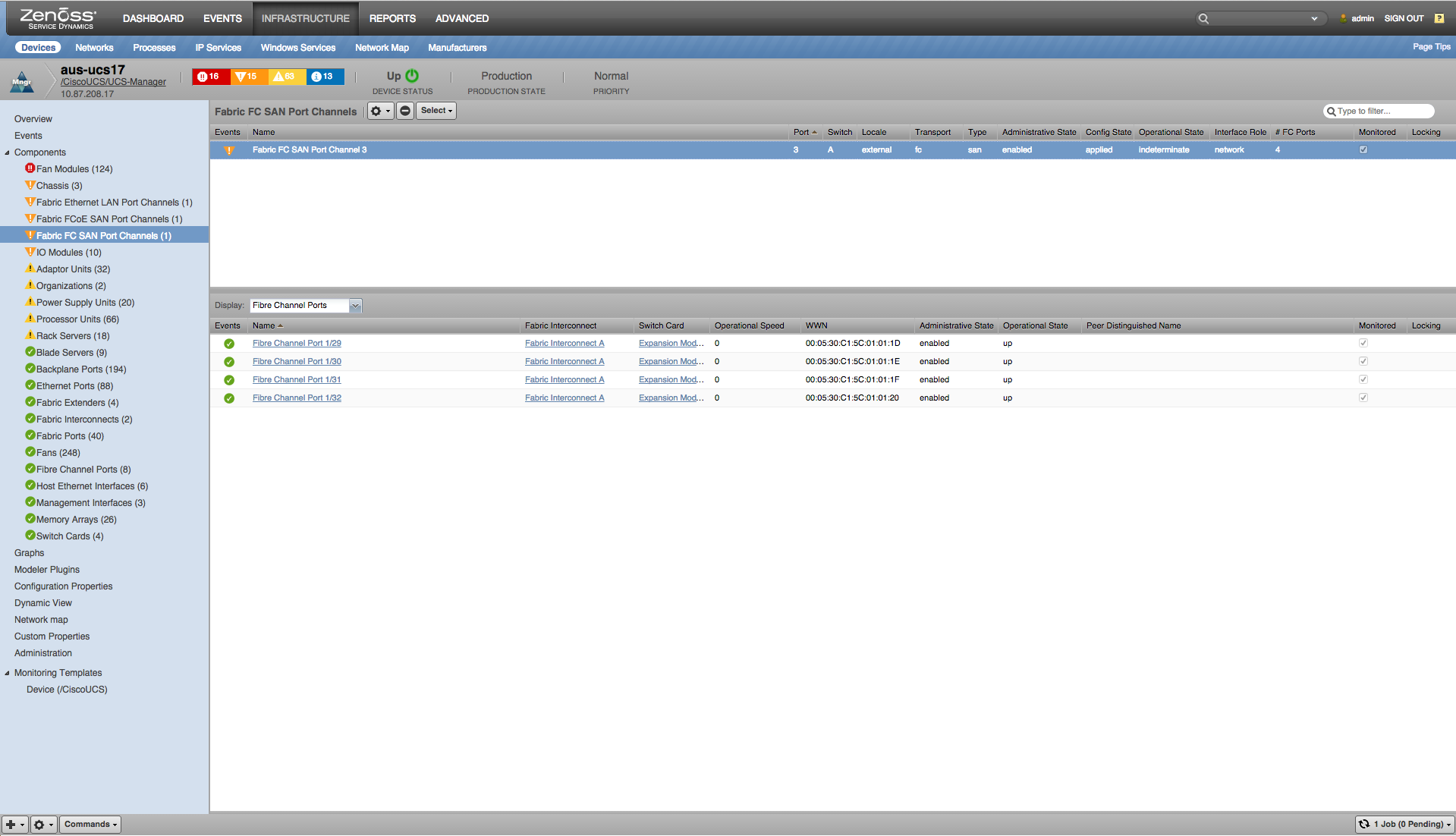
Fabric Fibre Channel SAN Port Channels
- Properties: DN, Port ID, Switch ID, Locale, Transport, Type, Admin State, Config State, Operational State, Interface Role, Number of Members
- Relationships: Fibre Channel Ports
Fabric Fibre Channel Over Ethernet SAN Port Channels
- Properties: DN, Port ID, Switch ID, Locale, Transport, Type, Config State, Operational State, Interface Role, Number of Members
- Relationships: Ethernet Ports
Fabric Ports
- Properties: DN, Switch ID, Slot ID, Port ID, MAC Address, Role, Type, Transport, Administrative State, Endpoint DN, Peer DN, Peer Slot ID, Peer Port ID
- Relationships: IO Module
Fans
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Tray
- Relationships: Fan Module
Fan Modules
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Tray
- Relationships: Equipment
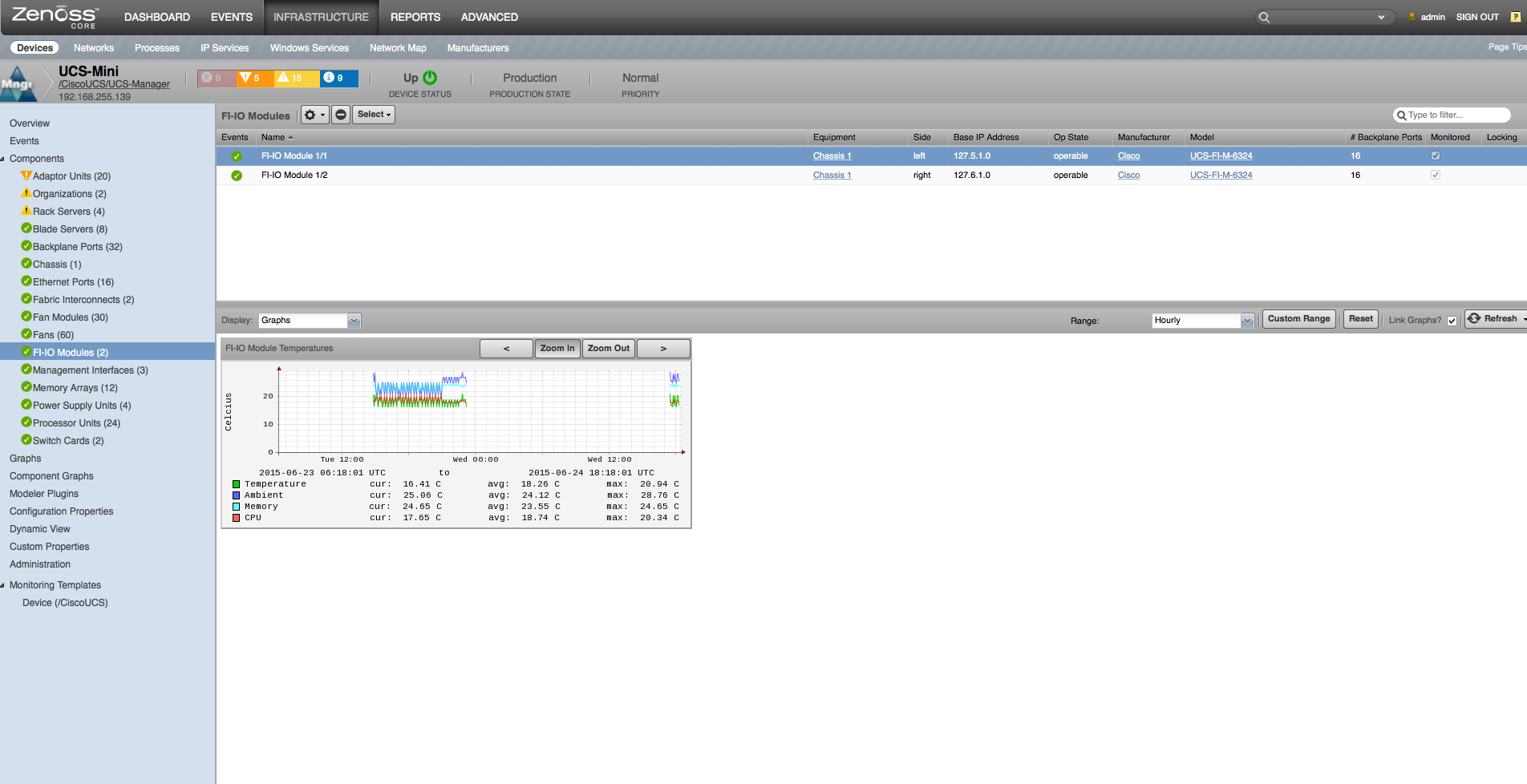
FI-IO Modules
- Properties: DN, Description, Revision, Slot, Manufacturer, Model
- Relationships: Chassis, Fabric Extender
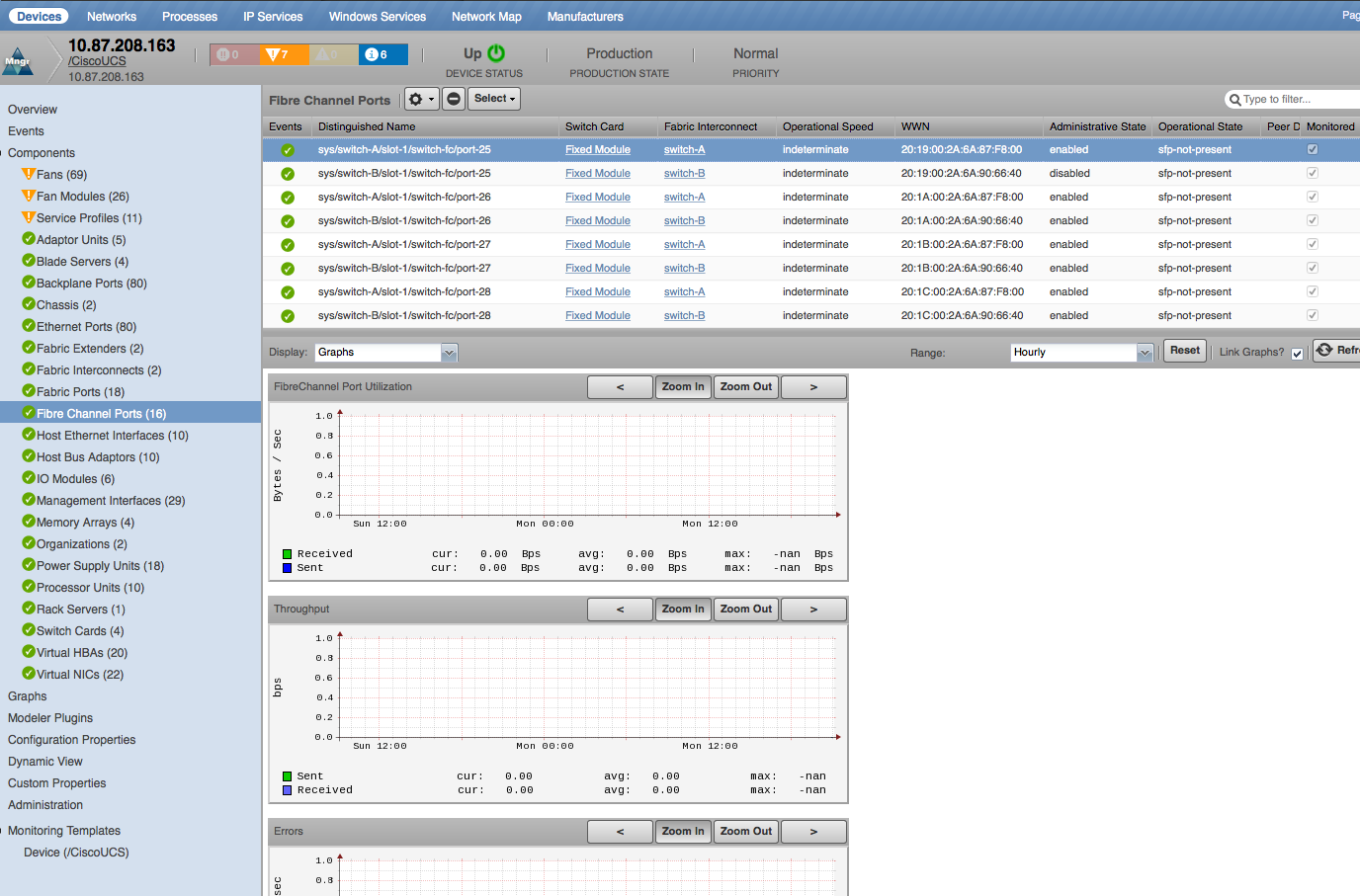
Fibre Channel Ports
- Properties: DN, WWN, Operational Speed
- Relationships: Switch Card, Fabric Fibre Channel SAN Port Channels
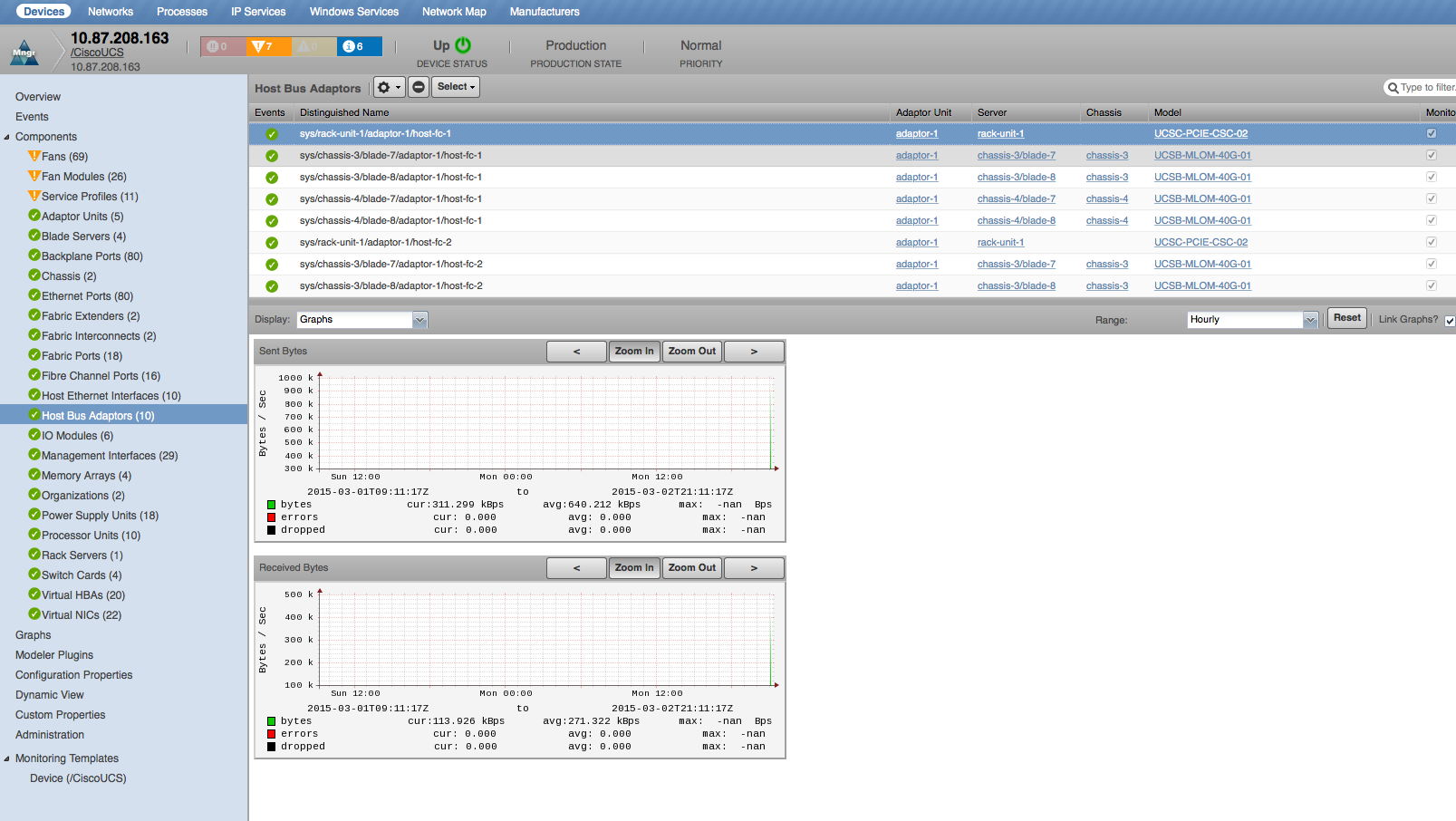
Host Bus Adaptors
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, MAC Address, PCI Address
- Relationships: Adaptor Unit
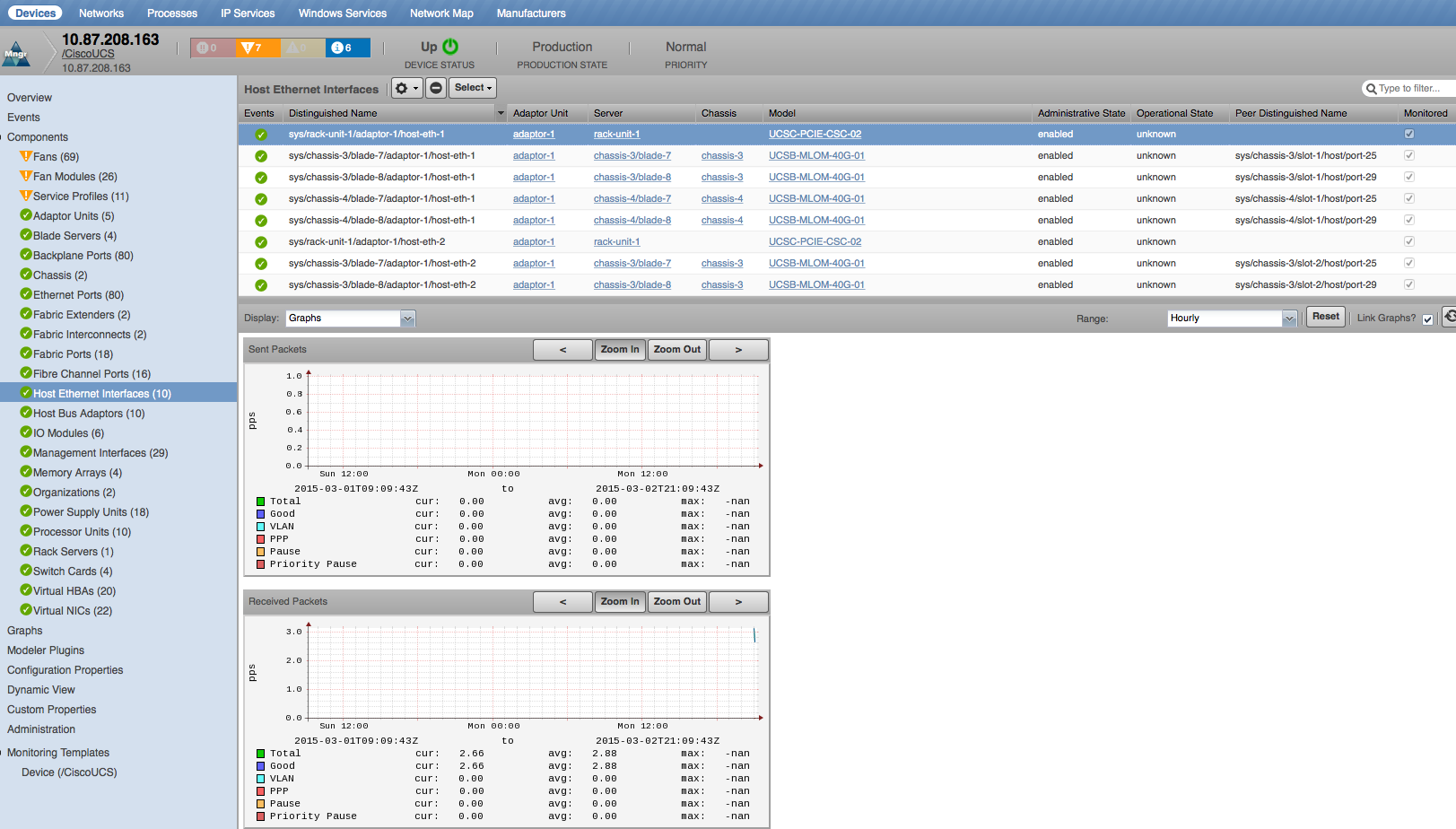
Host Ethernet Interfaces
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, MAC Address, PCI Address
- Relationships: Adaptor Unit
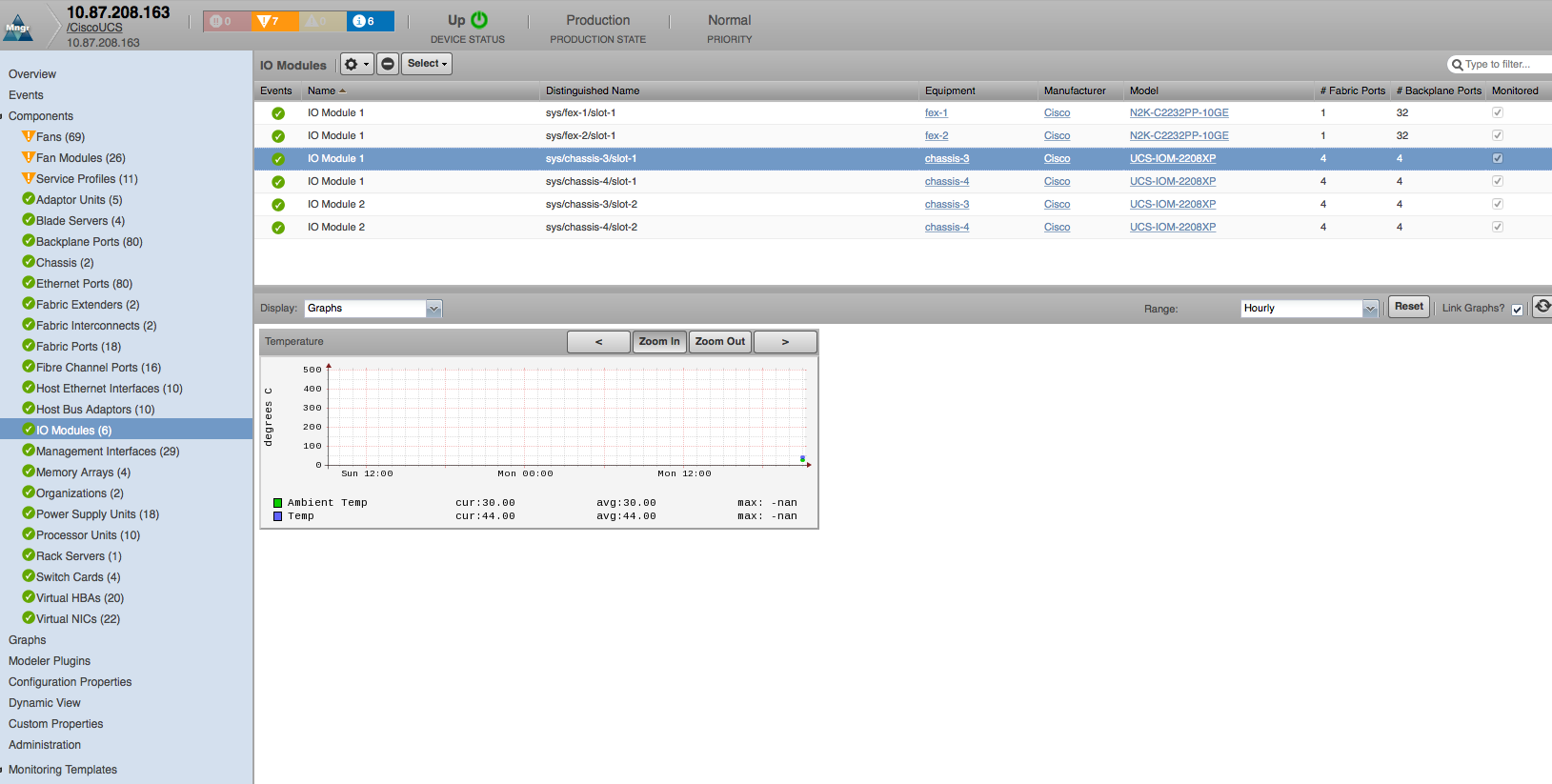
IO Modules
- Properties: DN, Description, Revision, Slot, Manufacturer, Model
- Relationships: Chassis, Fabric Extender
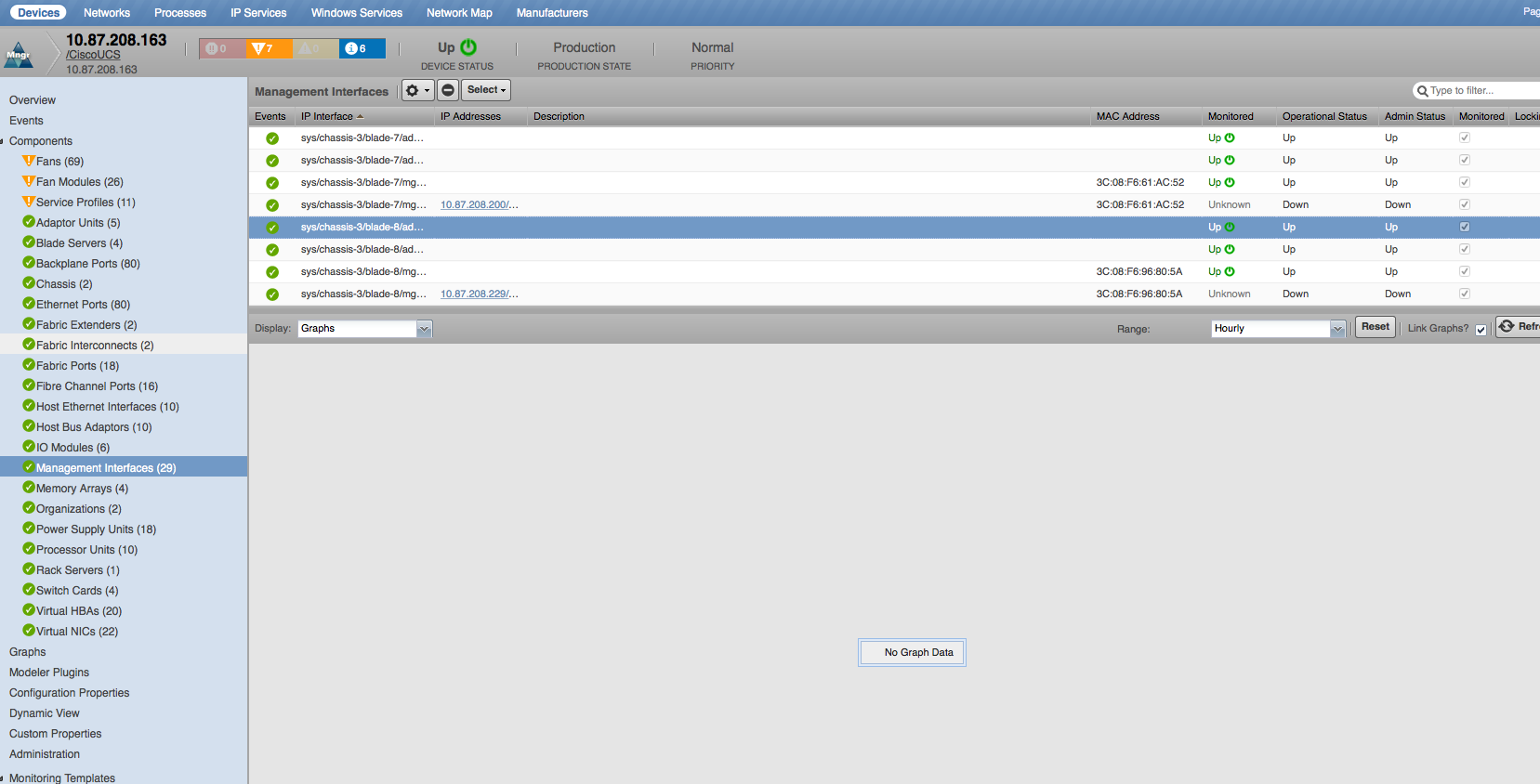
Management Interfaces
- Properties: Name, Type, MAC Address, Administrative Status, Operational Status
- Relationships: UCS Manager, IP Addresses
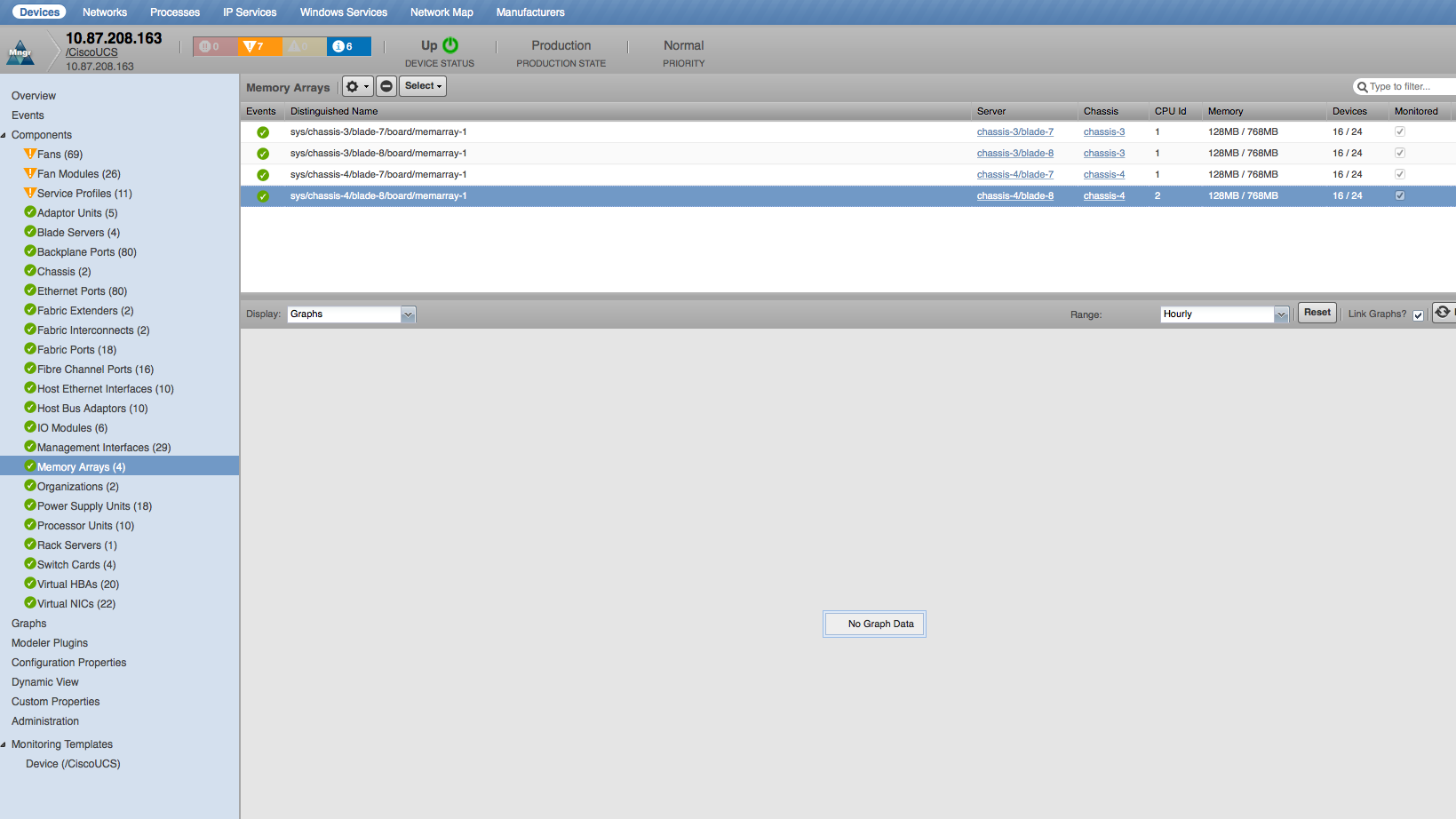
Memory Arrays
- Properties: DN, Serial Number, Revision, Error Correction, CPU ID, Max Devices, Populated Devices, Max Capacity, Current Capacity
- Relationships: Server Blade
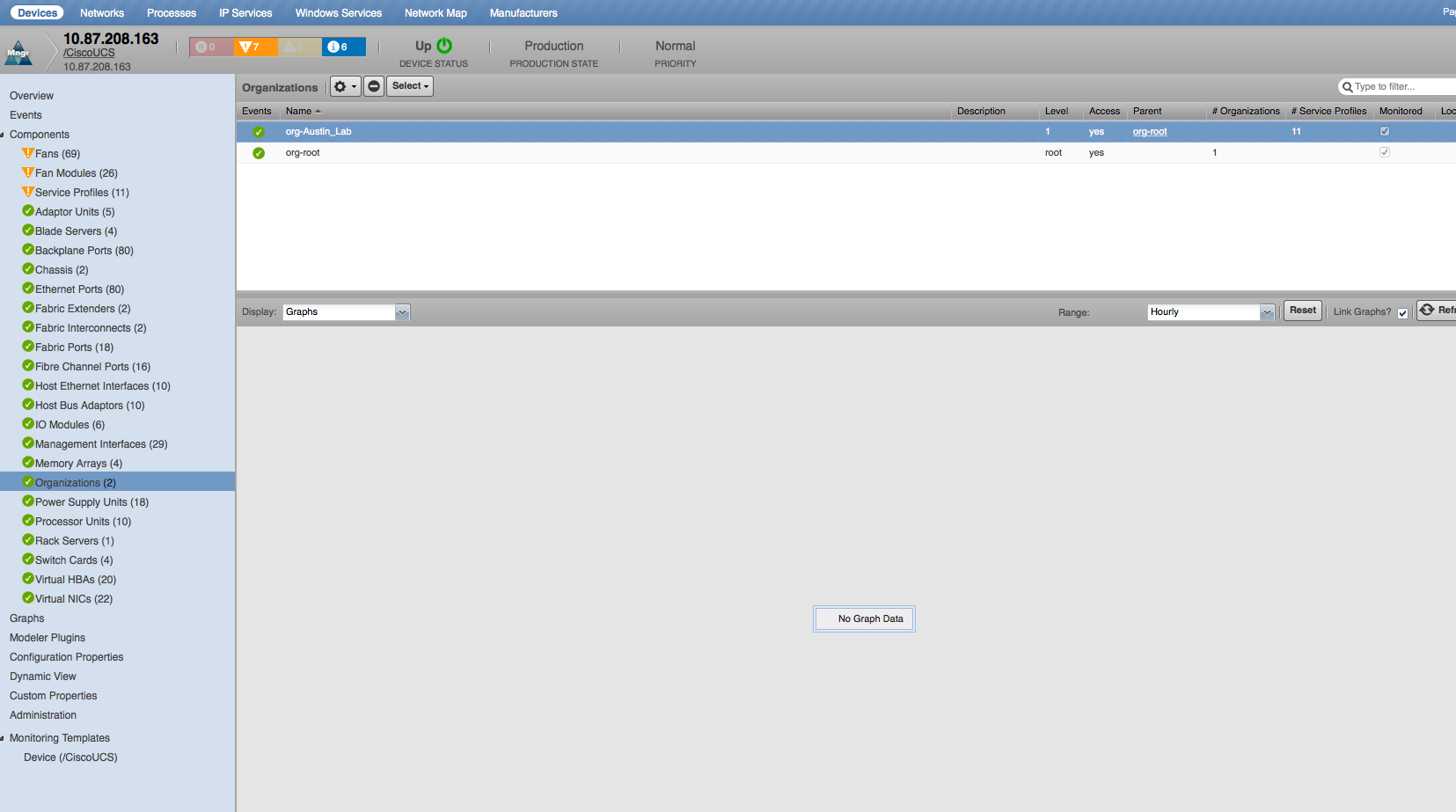
Organizations
- Properties: DN, Description, Level, Permanent Access
- Relationships: UCS Manager, Service Profiles, Organizations
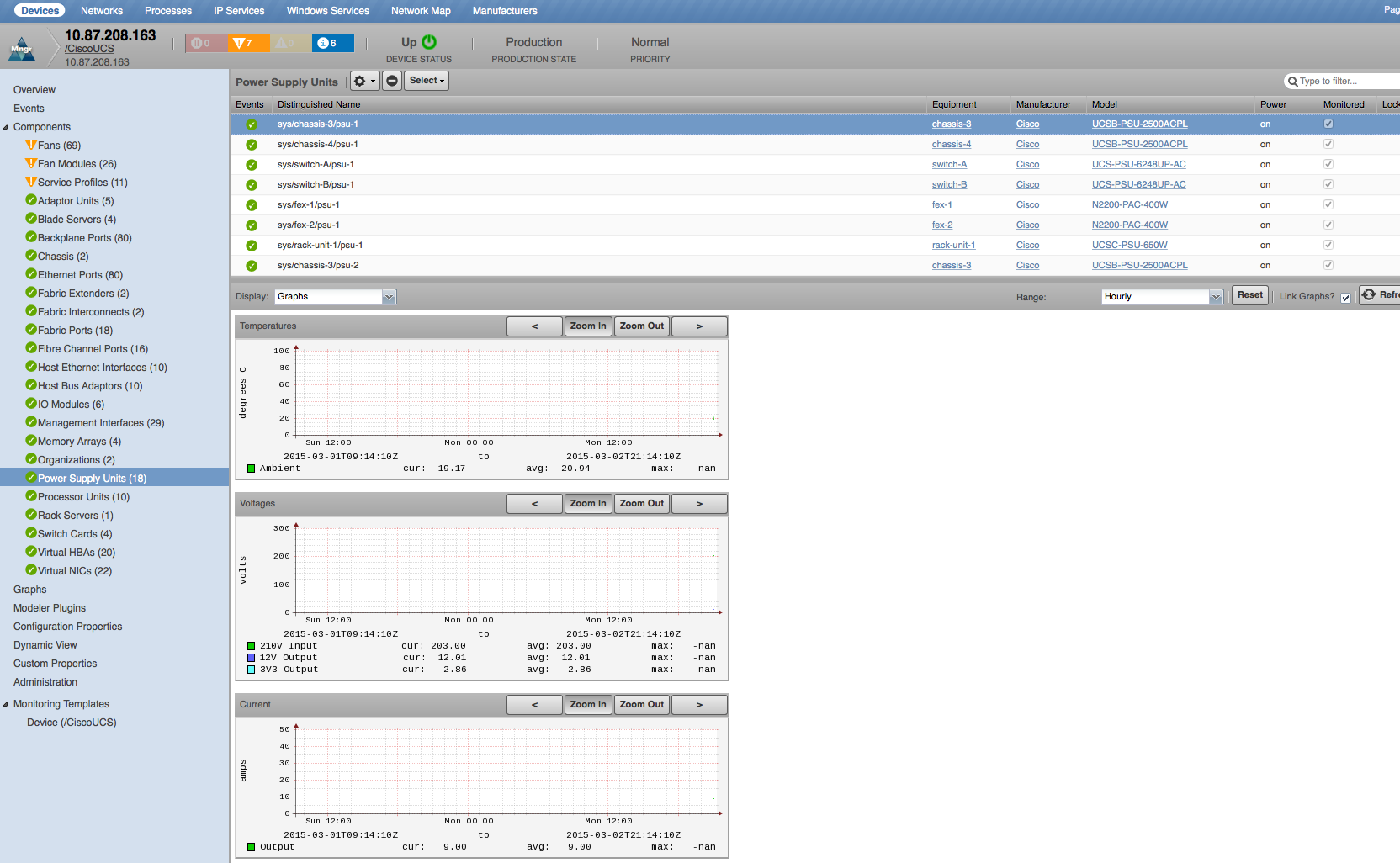
Power Supply Units
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Revision, Performance Threshold Sensor Status, Power State, Thermal Threshold Sensor Status, Voltage Threshold Sensor State
- Relationships: Equipment
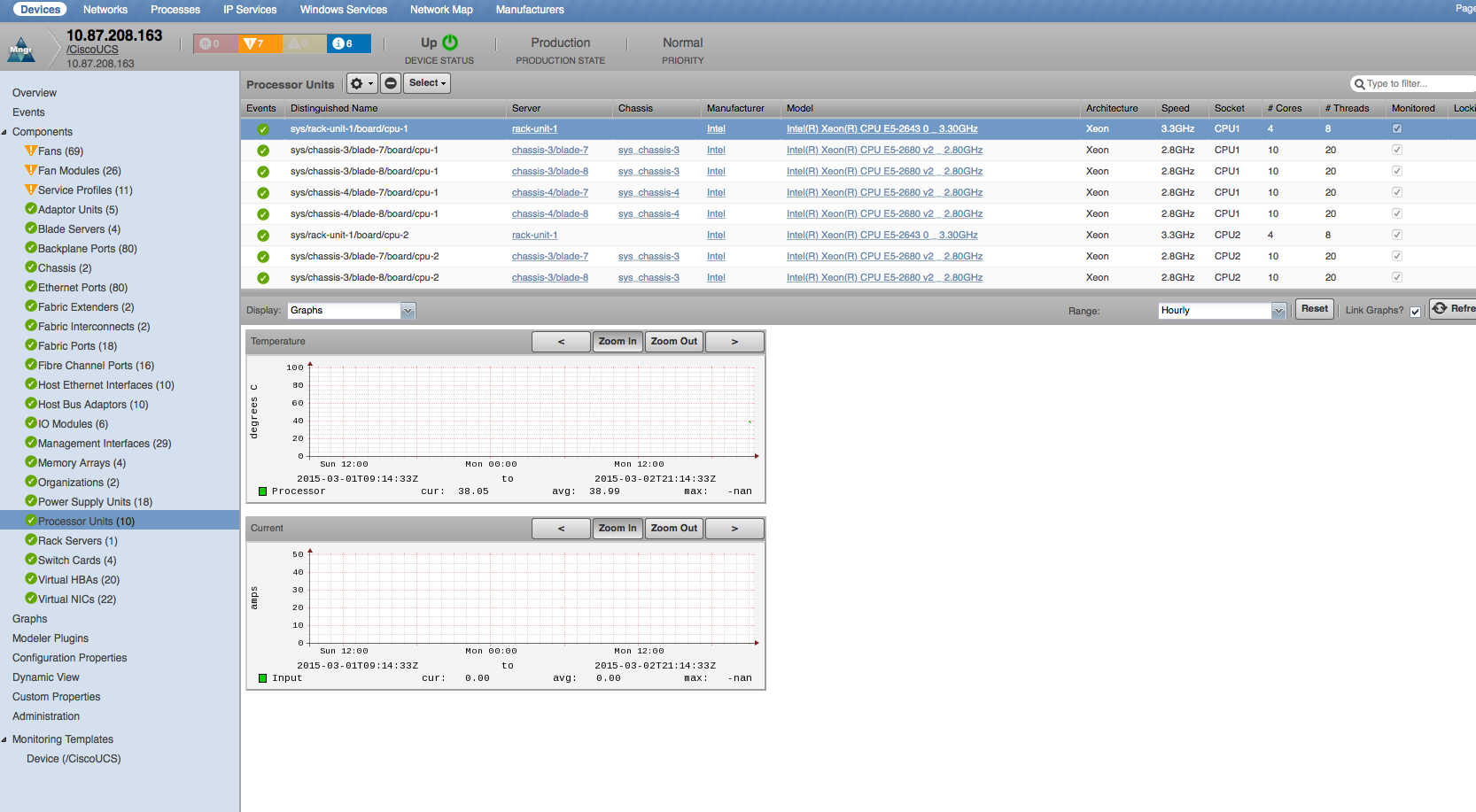
Processor Units
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Revision, Socket, Architecture, Cores, Threads, Stepping, Speed, Voltage
- Relationships: Server Blade
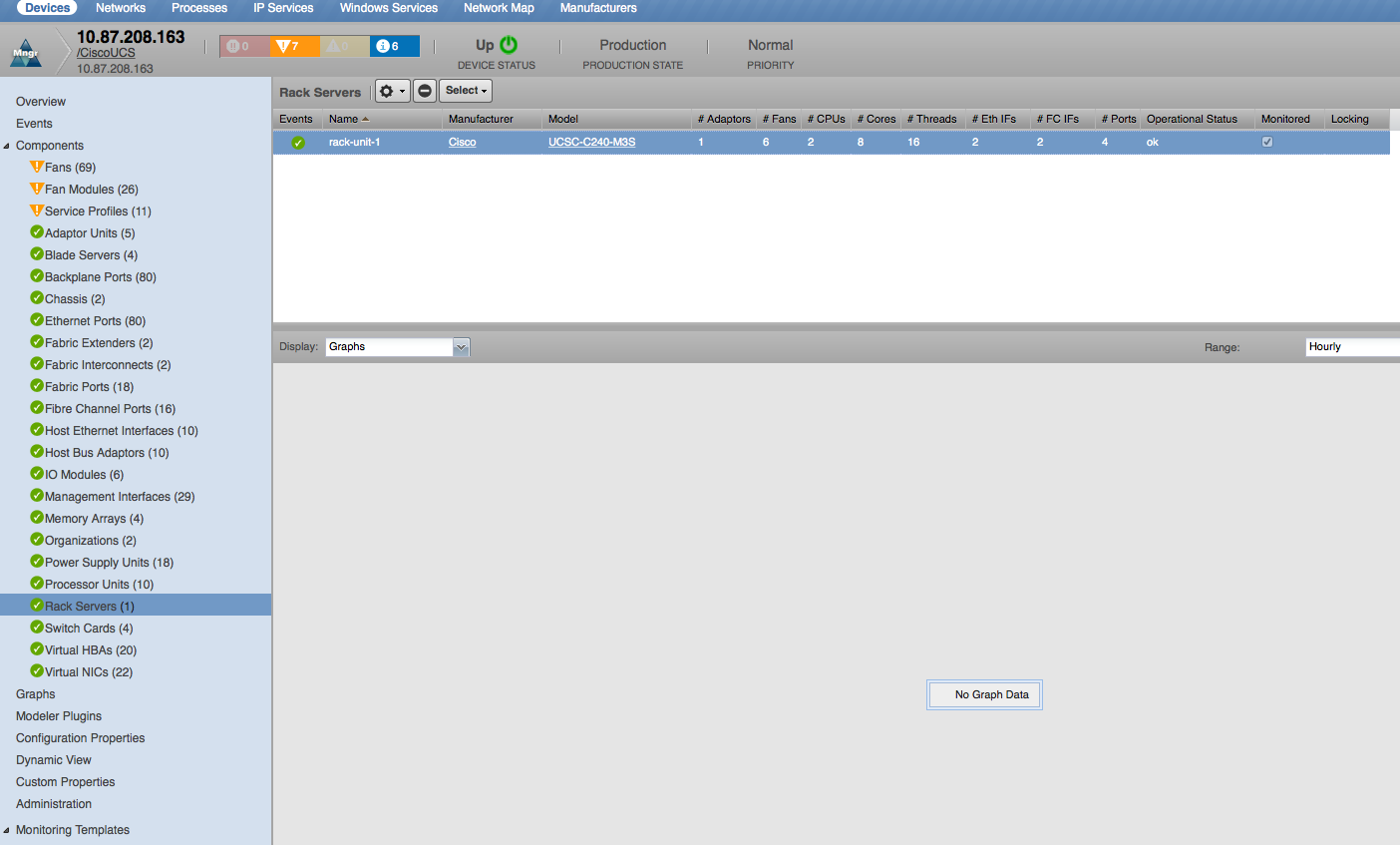
Rack Servers
- Properties: DN, Manufacturer, Model, Serial Number, Presence, Operational State, Operational Power, Availability
- Relationships: UCS Manager, Fabric Extenders, Fabric Interconnects, Memory Arrays, Processor Units, Adaptor Units, Bound Service Profile, Storage Controllers, Storage Local Disks, Storage Virtual Drives
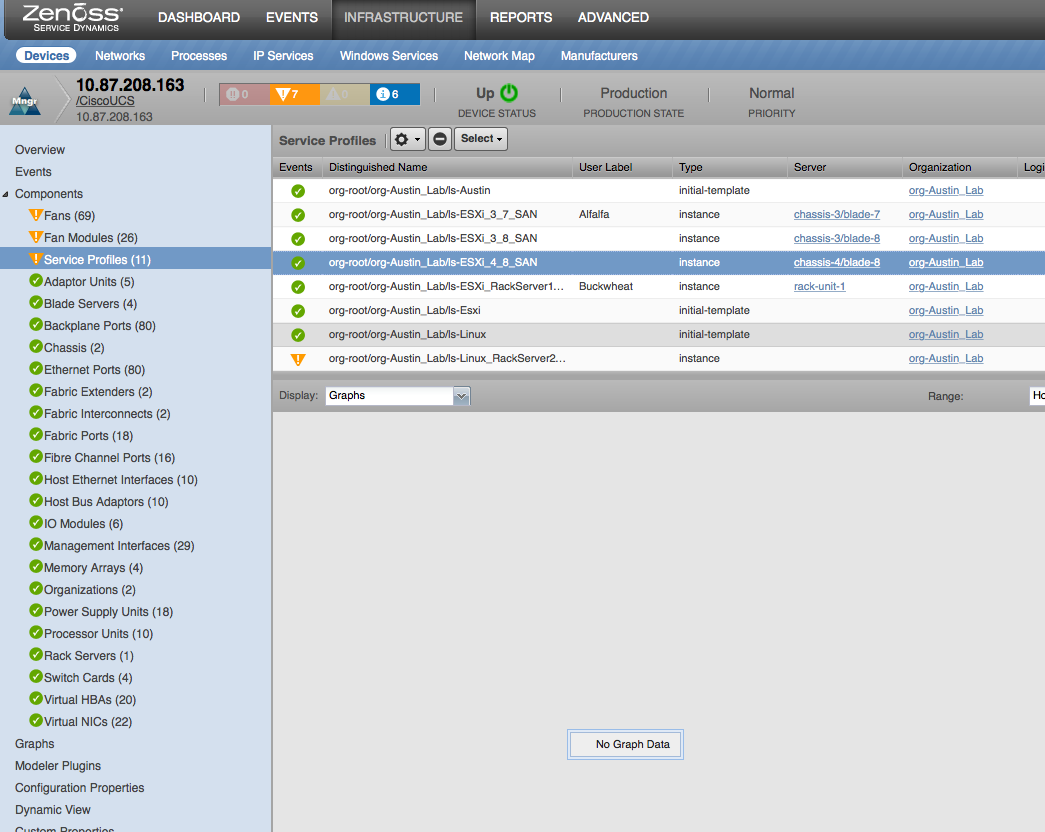
Service Profiles
- Properties: DN, Type, Description
- Relationships: UCS Manager, Virtual Ethernet NICs, Bound Server
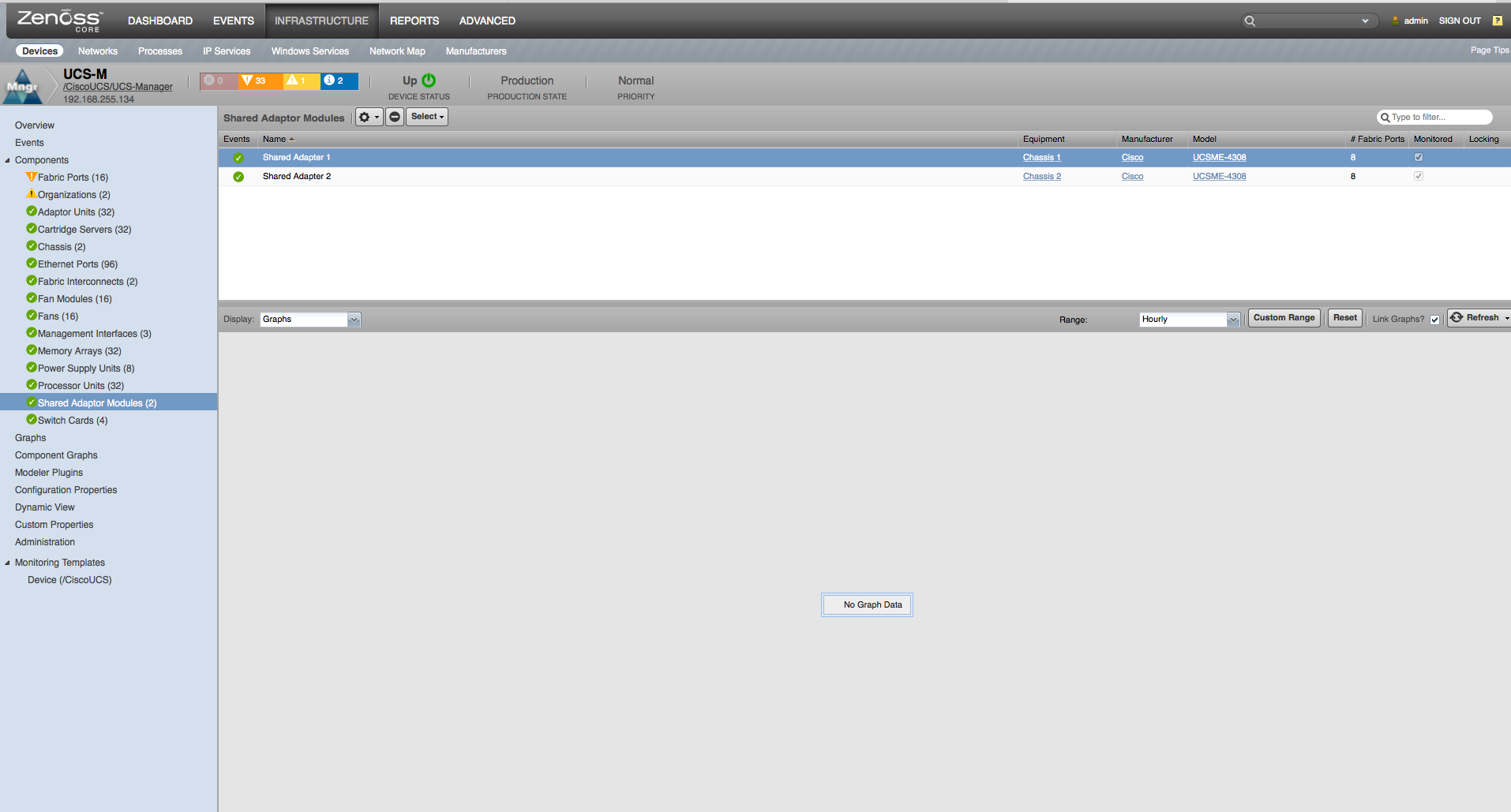
Shared Adaptors
- Properties: DN, Description, Revision, Slot, Manufacturer, Model
- Relationships: Chassis, Fabric Extender
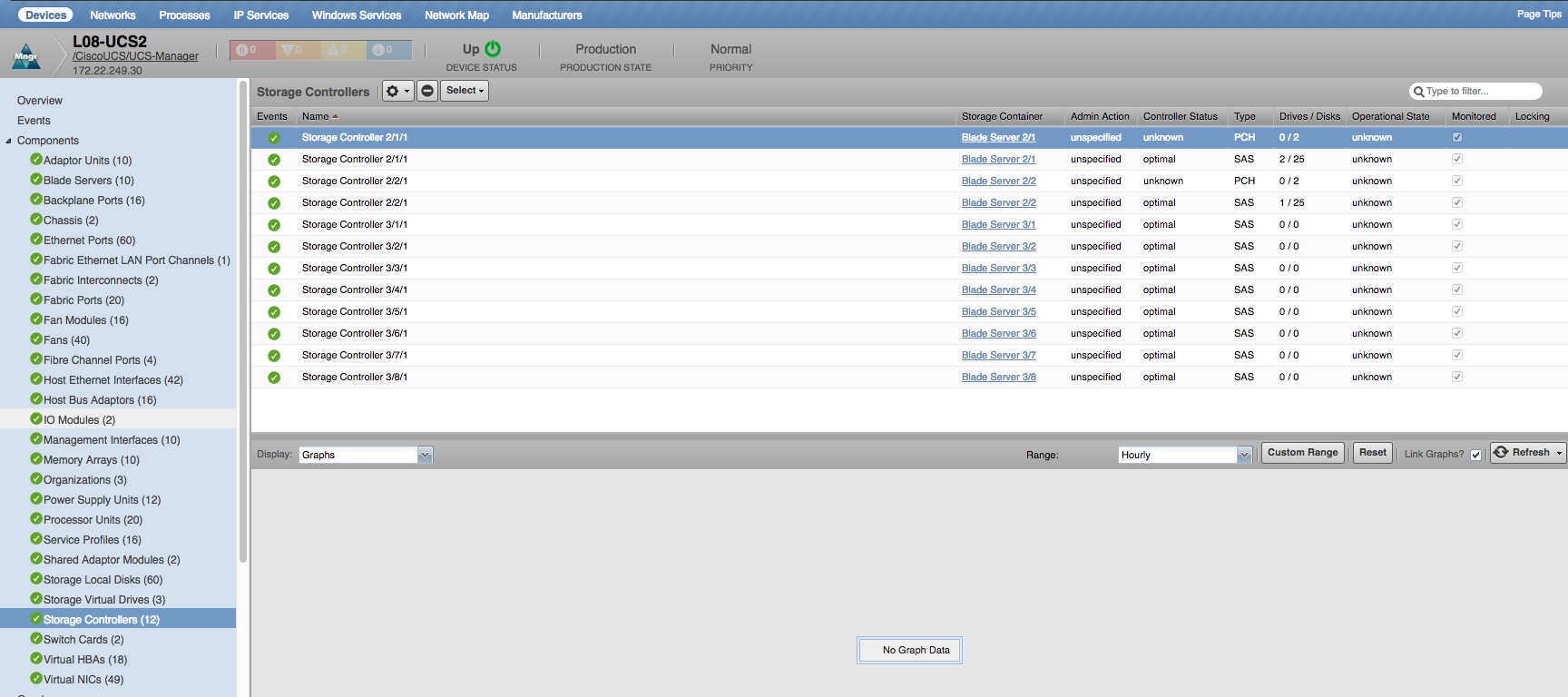
Storage Controllers
- Properties: DN, Storage Container, Admin Action, Controller Status, Controller Type, Number of Storage Virtual Drives, Number of Storage Local Disks, Operational Status
- Relationships: Chassis, Blade Servers, Cartridge Servers, Rack Servers, Storage Local Disks, Storage Virtual Drives
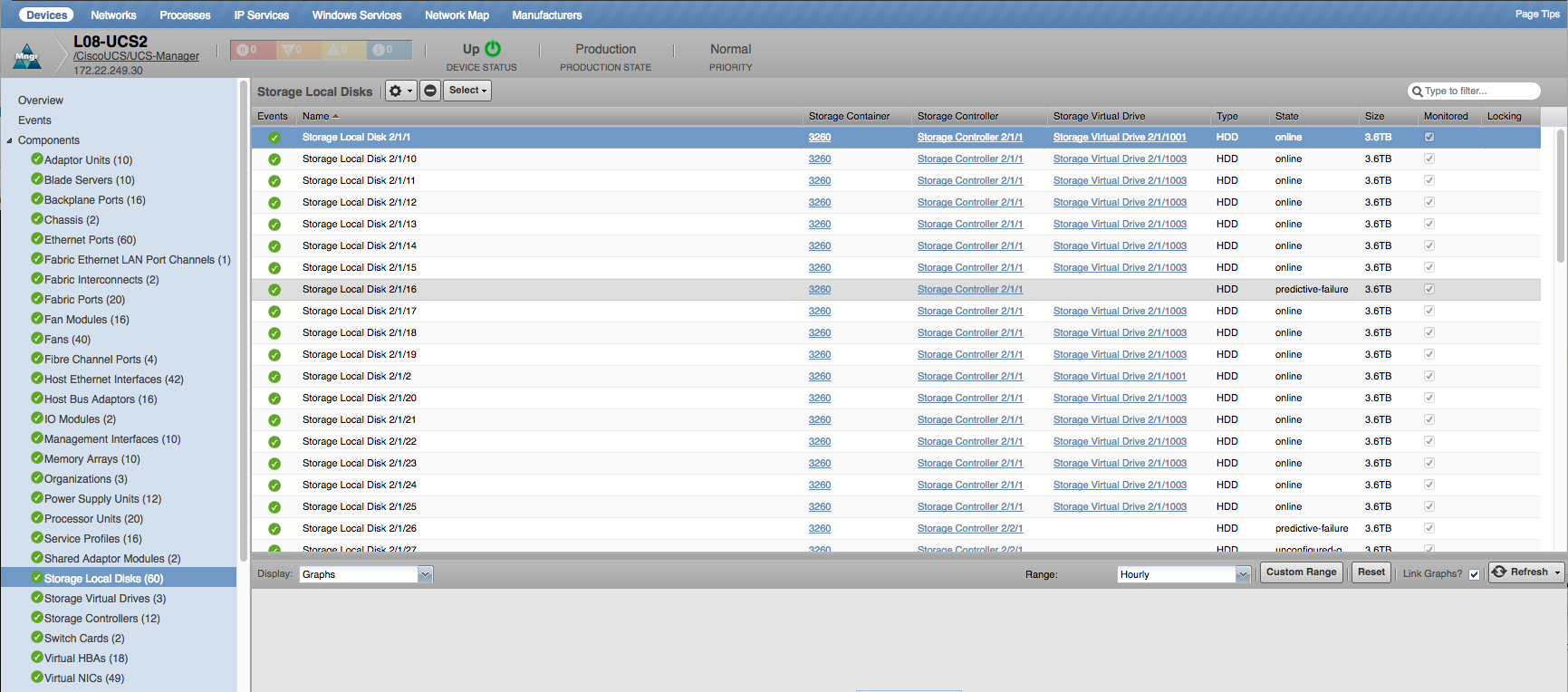
Storage Local Disks
- Properties: DN, Storage Container, Storage Controllers, Storage Virtual Drives, Disk Type, Disk Status, Disk Size
- Relationships: Chassis, Blade Servers, Cartridge Servers, Rack Servers, Storage Controllers, Storage Virtual Drives
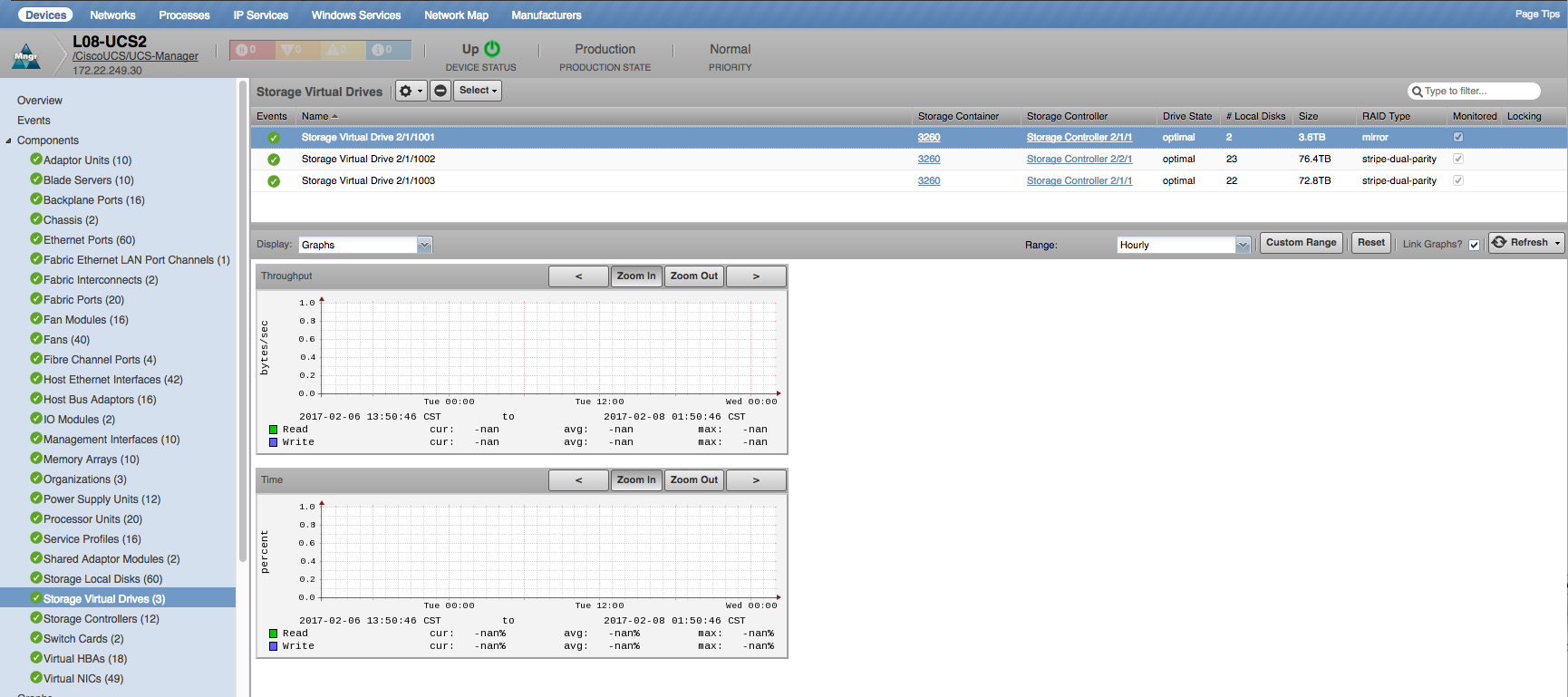
Storage Virtual Drives
- Properties: DN, Storage Container, Storage Controllers, Storage Virtual Drives, Drive State, Number of Storage Local Disks, Drive Size, RAID Type
- Relationships: Chassis, Blade Servers, Cartridge Servers, Rack Servers, Storage Controllers, Storage Local Disk
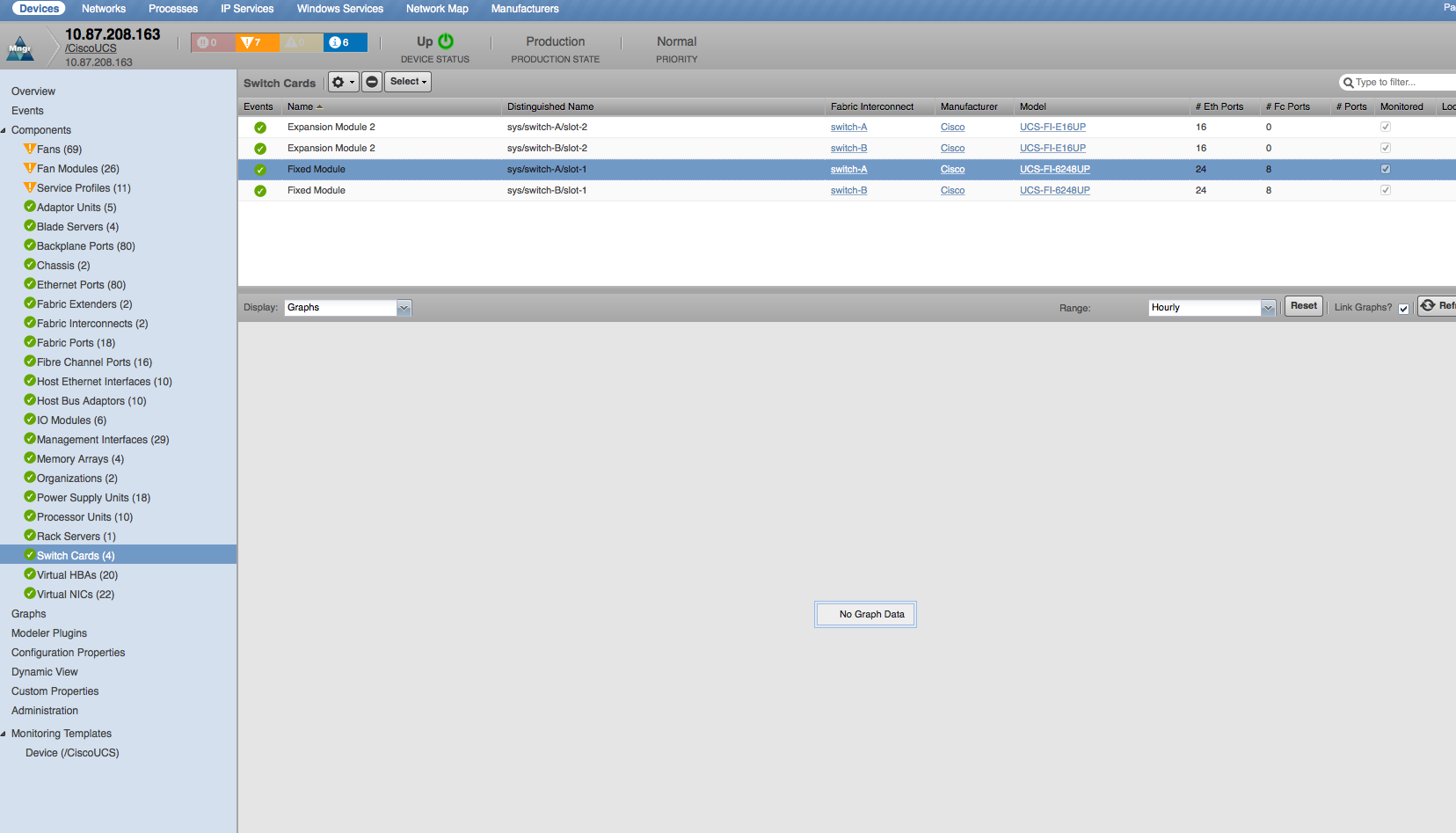
Switch Cards
- Properties: DN, Description, Revision, Slot, Manufacturer, Model
- Relationships: Fabric Interconnect, Ethernet Ports, Fibre Channel Ports
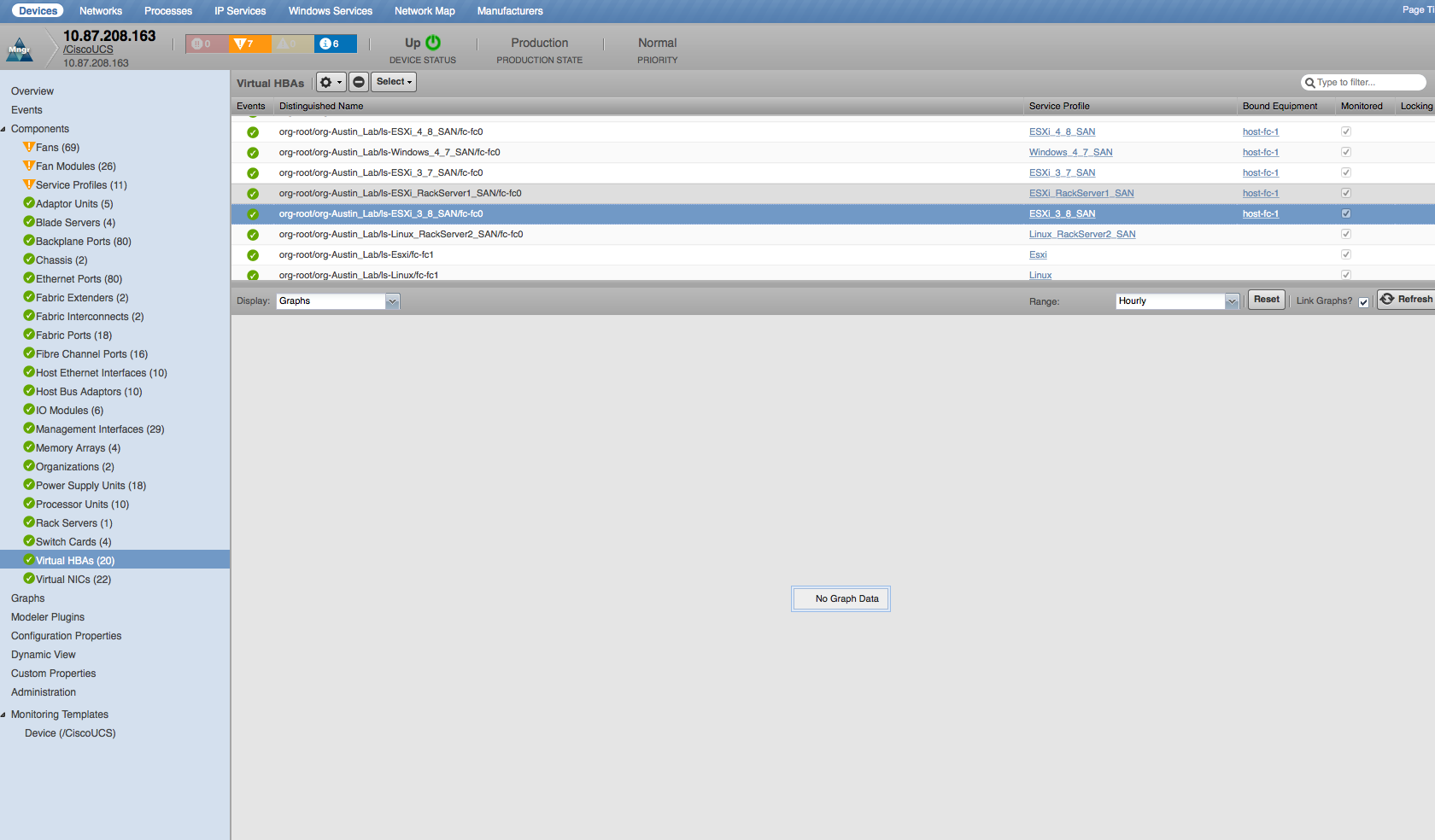
Virtual HBAs
- Properties: DN, MAC Address
- Relationships: Service Profile, Bound Equipment
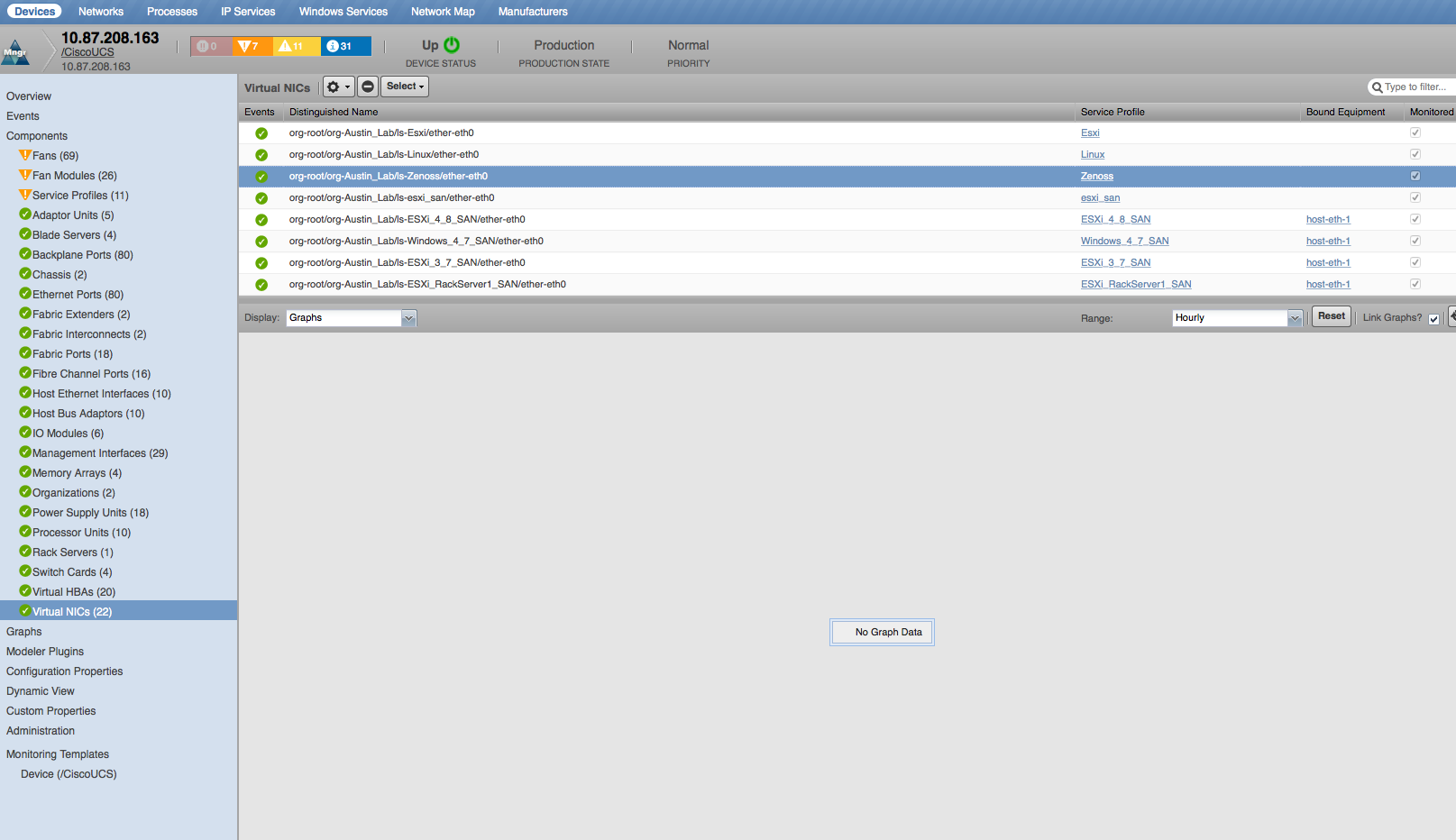
Virtual NICs
- Properties: DN, MAC Address
- Relationships: Service Profile, Bound Equipment
UCS Manager Performance Monitoring
The following metrics will be collected according to the statistics reporting interval, zCiscoUCSManagerPerfInterval.
Aggregation Pools (listed by template)
-
PerChassisServerPortPool:
- Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Port Utilization Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Server Port Utilization: Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent
-
PerFINetworkPortPool:
- Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFIServerPortPool:
- Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
SingleChassisServerPortPool:
- Port Pool Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Port Pool Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Port Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFINetworkFcPortPool:
- FibreChannel Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- FibreChannel Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- FibreChannel Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
FcPortPool:
- FC Port Pool Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- FC Port Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
SingleChassisStorageFcPortPool:
- FibreChannel Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- FC Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- FC Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFexServerPortPool:
- Port Pool Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Port Pool Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Port Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFIApplianceEthPortPool:
- Ethernet Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Ethernet Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Ethernet Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerChassisStorageFcPortPool:
- FibreChannel Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- FibreChannel Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- FibreChannel Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
DASPortPool:
- DAS Pool Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- DAS Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFIDASPortPool:
- FI DAS Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- FI DAS Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- FI DAS Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
EthPortPool:
- Ethernet Pool Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Ethernet Pool Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
-
PerFIStorageFcPortPool:
- Storage FC Port Bandwidth Capacity: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx (Percentage)
- Storage FC Port Bandwidth Capacity Balance: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance (Percentage)
- Storage FC Port Utilization: Projected High Pct Rx, Projected High Pct Tx, Rx, Tx, Rx Balance, Tx Balance, Received, Sent (bits/sec)
Backplane Ports
- Port Utilization(UCSCapServerIOCardPort): Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
- Port Utilization: Sent, Received (bytes/sec)
- Sent Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Received Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Loss Stats: Carrier Sense, Excess Collision, Giants, Late Collision, Multi Collision, Single Collision (losses/sec)
- Pause Stats: Transmit, Receive, Resets (pauses/sec)
- Errors: Transmit, Receive, Deferred Tx, Out Discard, Under Size, Align, FCS, Int Mac Rx, Int Mac Tx (errors/sec)
Blade Servers
- Voltage: Input (volts)
- Temperatures: IO, Rear (degrees C)
- Power: Consumed (watts)
- Current: Input (amps)
- Server Utilization: Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (bits/sec)
Cartridge Servers
- Voltage: Input (volts)
- Temperatures: IO, Rear (degrees C)
- Power: Consumed (watts)
- Current: Input (amps)
Chassis
- Power: Input, Output (watts) --- not available for C3260
- Chassis Remaining Capacity: Rx Remaining, Tx Remaining (bits/sec)
- Utilization: Rx Remaining, Tx Remaining, Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (bits/sec)
- NOTE: Chassis metrics and graphs are omitted for empty Chassis
Ethernet Ports
- Throughput: Sent, Received (bits/sec)
- Sent Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Received Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Loss Stats: Carrier Sense, Excess Collision, Giants, Late Collision, Multi Collision, Single Collision (losses/sec)
- Pause Stats: Transmit, Receive, Resets (pauses/sec)
- Errors: Transmit, Receive, Deferred Tx, Out Discard, Under Size, Align, FCS, Int Mac Rx, Int Mac Tx (errors/sec)
- Utilization: Rx, Tx, bandwidth (bits) (bits/sec)
Fabric Ethernet LAN Port Channels
- Channel Utilization: Sent, Received (bytes/sec)
- Transmit Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Received Packets: Total, Jumbo, Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast (packets/sec)
- Transmit Errors: Deferred Tx, Int Mac Tx, Transmit (errors/sec)
- Receive Errors: Int Mac Rx, Receive (errors/sec)
- Pause Stats: Transmit, Receive, Resets (pauses/sec)
- Collision Stats: Excess Collision, Late Collision, Multi Collision, Single Collision (collisions/sec)
- Misc Errors: Out Discard, Under Size, Align, FCS (errors/sec)
- Misc Loss Stats: Carrier Sense, SQETest, Giants, Symbol(losses/sec)
- Utilization (bits): Rx, Tx (bits) (bits/sec)
Fabric Extender
- Temperature: Inlet, Outlet (degrees C)
- Remaining Capacity: Rx Remaining, Tx Remaining (bits/sec)
- Utilization (bits): Rx Remaining, Tx Remaining, Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (bits/sec)
Fabric Fibre Channel SAN Port Channels
- Channel Utilization: Sent, Received (bytes/sec)
- Packet Stats: Received, Sent (packets/sec)
- Transmit Errors: Discard Tx, Transmit (errors/sec)
- Receive Errors: Discard Rx, Too Long Rx, CRC Rx, Receive, Too Short Rx (errors/sec)
- Misc Errors: Link Failures, Signal Losses, Sync Losses (errors/sec)
Fabric Fibre Channel over Ethernet SAN Port Channels
- Channel Utilization: Sent, Received (errors/sec)
- Channel Utilization: Rx, Tx (bits)
- Port Channel Errors: Receive, Sent (packets/sec)
- Packet Stats: Receive, Sent (packets/sec)
- Dropped Stats: Receive, Sent (dropped/sec)
Fabric Interconnects
- CPU Utilization: Used (percent)
- Memory Utilization: Available, Cached (bytes)
- Temperatures: PSU Inlet 1, PSU Inlet 2, Fan Inlet 1, Fan Inlet 2, Fan Inlet 3, Fan Inlet 4, Main Outlet 1, Main Outlet 2 (degrees C)
- Direct-Attached Storage Utilization: Rx Utilization, Tx Utilization (bits/sec)
- Remaining Capacity: Rx, Tx, Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
- Utilization (bits): Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
- LAN Cloud Utilization: Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
- Northbound Utilization: Rx, Tx, Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (bits/sec)
- SAN Cloud Utilization: Rx, Tx, Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (bits/sec)
Fan Modules (Chassis only)
- Temperature: Ambient (degrees C)
- Fan Speeds: Fan 1, Fan 2 (RPM)
Fabric Ports
- Utilization (bits): Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
FI-IO Modules (Chassis only)
- Temperature: Ambient, Temp (degrees C)
Fibre Channel Ports
- Throughput: Sent, Received (bits/sec)
- Errors: Transmit, Receive, Discard Tx, Discard Rx, Too Long Rx, Too Short Rx, CRC Rx, Link Failures, Signal Losses, Sync Losses (errors/sec)
- Port Utilization: Rx (bits), Tx (bits), bandwidth (bits/sec)
Host Ethernet Interfaces
- Sent Packets: Total, Good, VLAN, PPP, Pause, Priority Pause (packets/sec)
- Received Packets: Total, Good, VLAN, PPP, Pause, Priority Pause (packets/sec)
- Sent Bytes: Bytes, Errors, Dropped (Bytes/Sec)
- Received Bytes: Bytes, Errors, Dropped (Bytes/Sec)
- **Utilization: Rx (bits), Tx (bits), bandwidth(bits/sec)
Host Bus Adaptors
- Sent Bytes: Bytes, Errors, Dropped (Bytes/Sec)
- Received Bytes: Bytes, Errors, Dropped (Bytes/Sec)
- Utilization: Rx (bits), Tx (bits)
IO Modules (Chassis only)
- Temperature: Ambient, Temp (degrees C)
- IO Module Fabric Switch A Traffic: Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
- IO Module Fabric Switch B Traffic: Rx (bits), Tx (bits), bandwidth headroom (bits/sec)
- IO Module Fabric Utilization: Rx (bits), Tx (bits), bandwidth headroom (bits/sec)
Power Supply Units
- Voltages: 210V Input, 12V Output, 3V3 Output (volts)
- Temperatures: Ambient (degrees C)
- Power: Output (watts)
- Current: Output (amps)
Processor Units
- Temperature: Processor (degrees C)
- Current: Input (amps)
Rack Servers
- Rack Server Utilization: Rx (LAN), Rx (SAN), Tx (LAN), Tx (SAN) (*bits)
Service Profiles
- Service Profile Utilization: Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
Virtual HBAs
- vHBA Utilization: Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
Virtual NICs
- vNIC Utilization: Rx, Tx (bits/sec)
UCS Manager Event Management
Zenoss will create events for all UCS faults collected through the management API. The UCS fault life-cycle closely matches that of the Zenoss event life-cycle. When a UCS fault clears, the equivalent events will be cleared in Zenoss.
Upon initially connecting to the UCS Manager Zenoss will process the full list of open faults. Subsequently it will subscribe to and only receive new faults and updates to existing faults. Initial connections to UCS Manager can occur on a restart of UCS Manager, Zenoss or after a temporary connectivity issue between the two is resolved.
The following fields will be populated for each event.
Standard Zenoss Event Fields
- device (set to the UCS Manager device in the /CiscoUCS device class)
- component
- eventKey
- summary
- message
- severity
- eventClassKey
- agent (zenucsevents)
- eventGroup (ucs)
- monitor
Additional Event Fields
- ucs-code
- ucs-dn
- ucs-id
- user
- originaltime
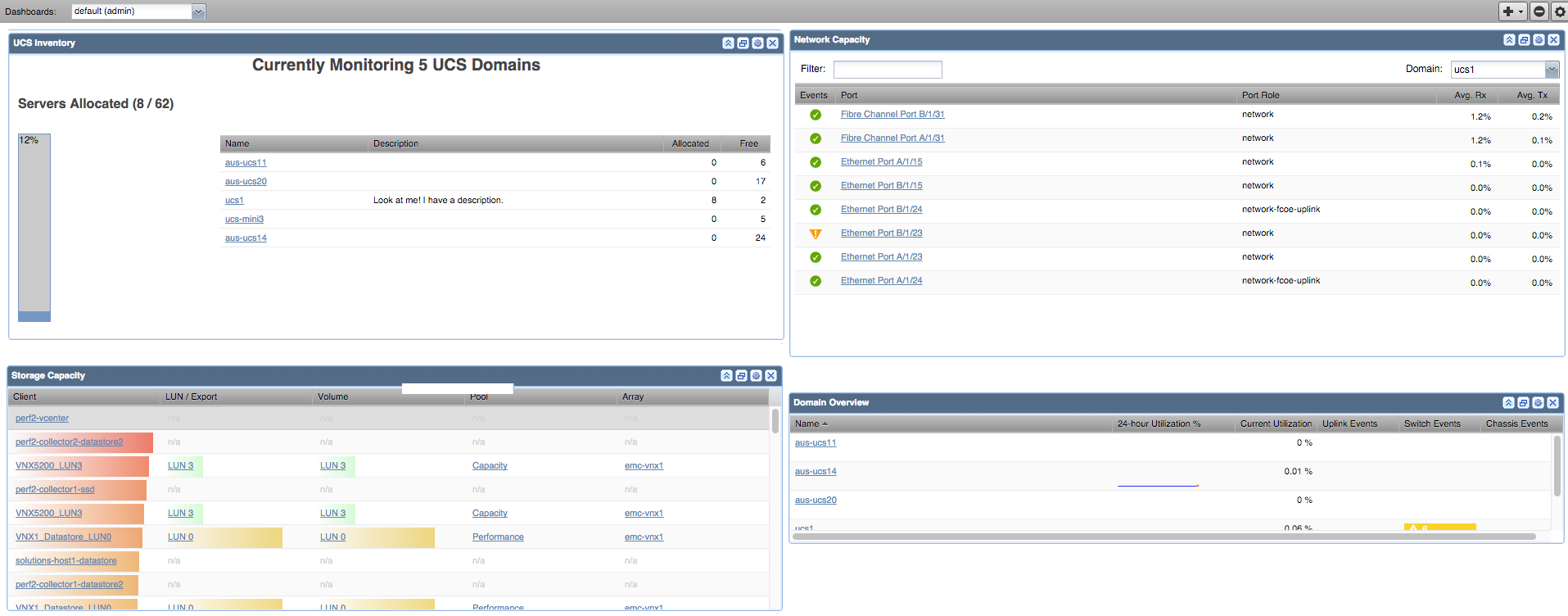
Dashboard Portlets
The CiscoUCS ZenPack adds portlets that provide an at-a-glance view into specific areas of the UCS Domain. Portlets are viewed on the first page upon login. Portlets can be added or removed using the dashboard and portlet controls.
Dashboard Portlets
- UCS Inventory Portlet -- Shows total number of blades and how many are associated with service profiles.
- Out of Balance Events -- Shows events generated when bandwidth usage is different among ports in an aggregation pool.
- Domain Overview -- Shows utilization and open event counts.
- Integrated Infrastructure -- Shows a unified view of events generated by UCS Storage, Network, Virtualization and Compute resources.
- Chassis Capacity Portlet -- Shows current chassis utilization across all domains.
- Fabric Extender Capacity Portlet - Shows current FEX utilization across all domains.
- Service Profile Portlet -- Shows current fabric utilization across all domains.
- Storage Capacity Portlet -- Shows current storage utilization across all domains.
- Network Capacity Portlet -- Shows current network utilization across all domains.
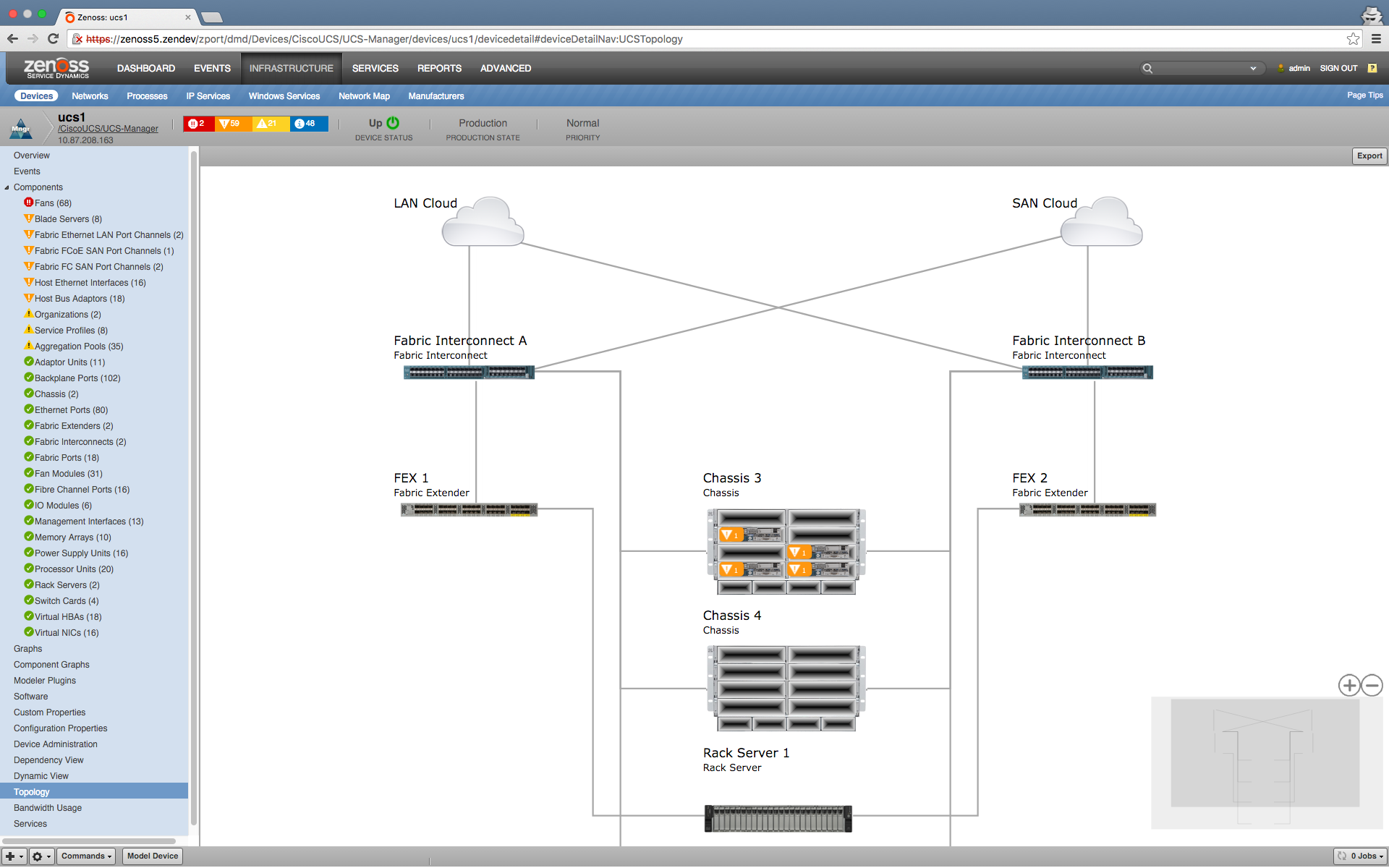
Topology View
The Topology View provides a high-level, architectural view of UCS domains and their physical network connections. The view displays how infrastructure in the UCS Domain is integrated. The view is scalable and exportable to a .png file. Additionally, clicking on a node or edge shows a more detailed view of the associating nodes/edges, events generated and dependency view.
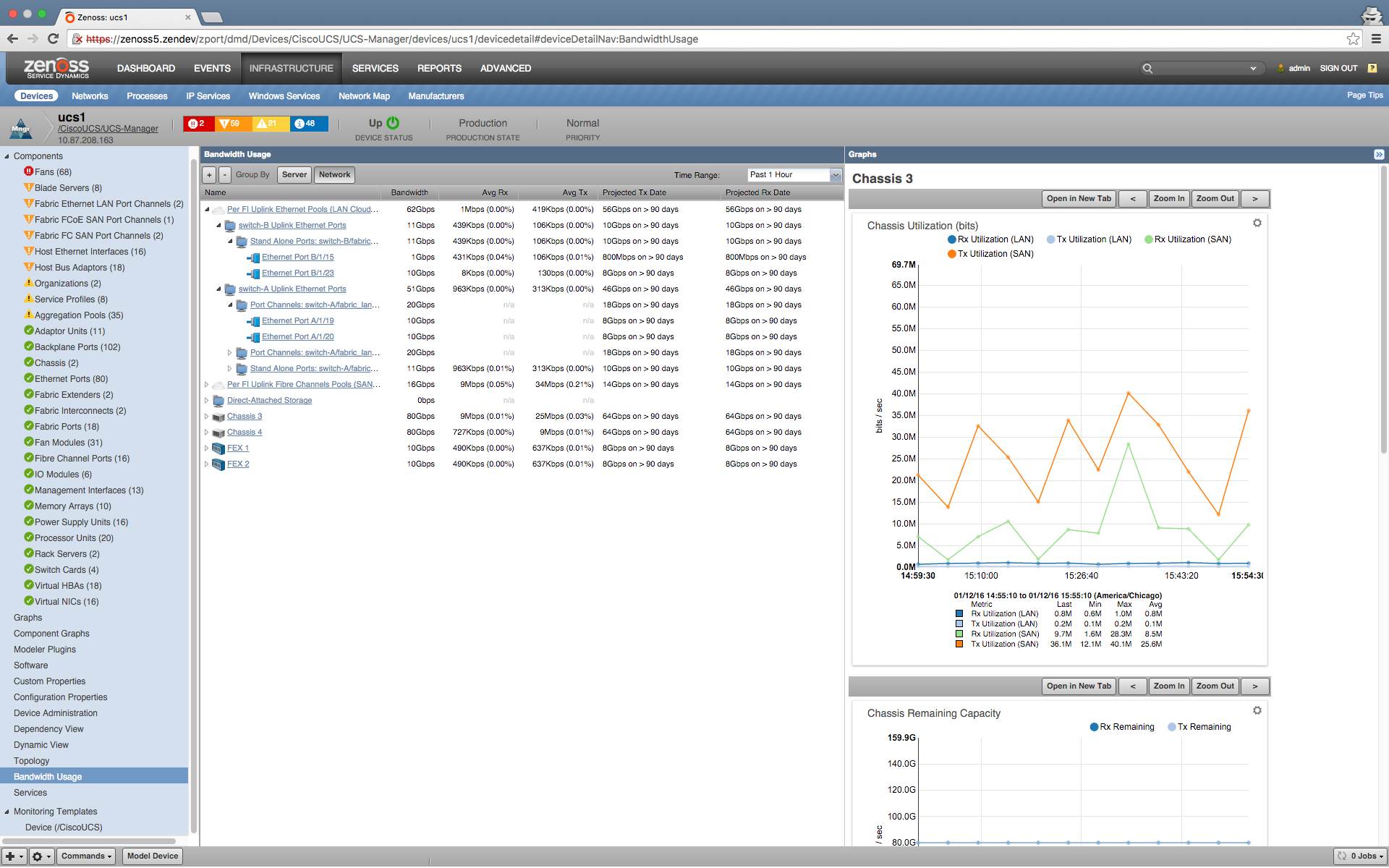
Bandwidth Usage View
The Bandwidth Usage View provides the bandwidth usage information of resources in the UCS server level and network level of a particular domain, and projected exhaustion date ranges for the following metrics:
- Average Rx, Average Tx
- Maximum Rx, Maximum Tx
- Average LAN Tx, Maximum LAN Tx
- Average Storage Tx, Maximum Storage Tx
- Projected Tx Date, Projected Rx Date ---Shows the number of days before the maximum capacity will be reached.
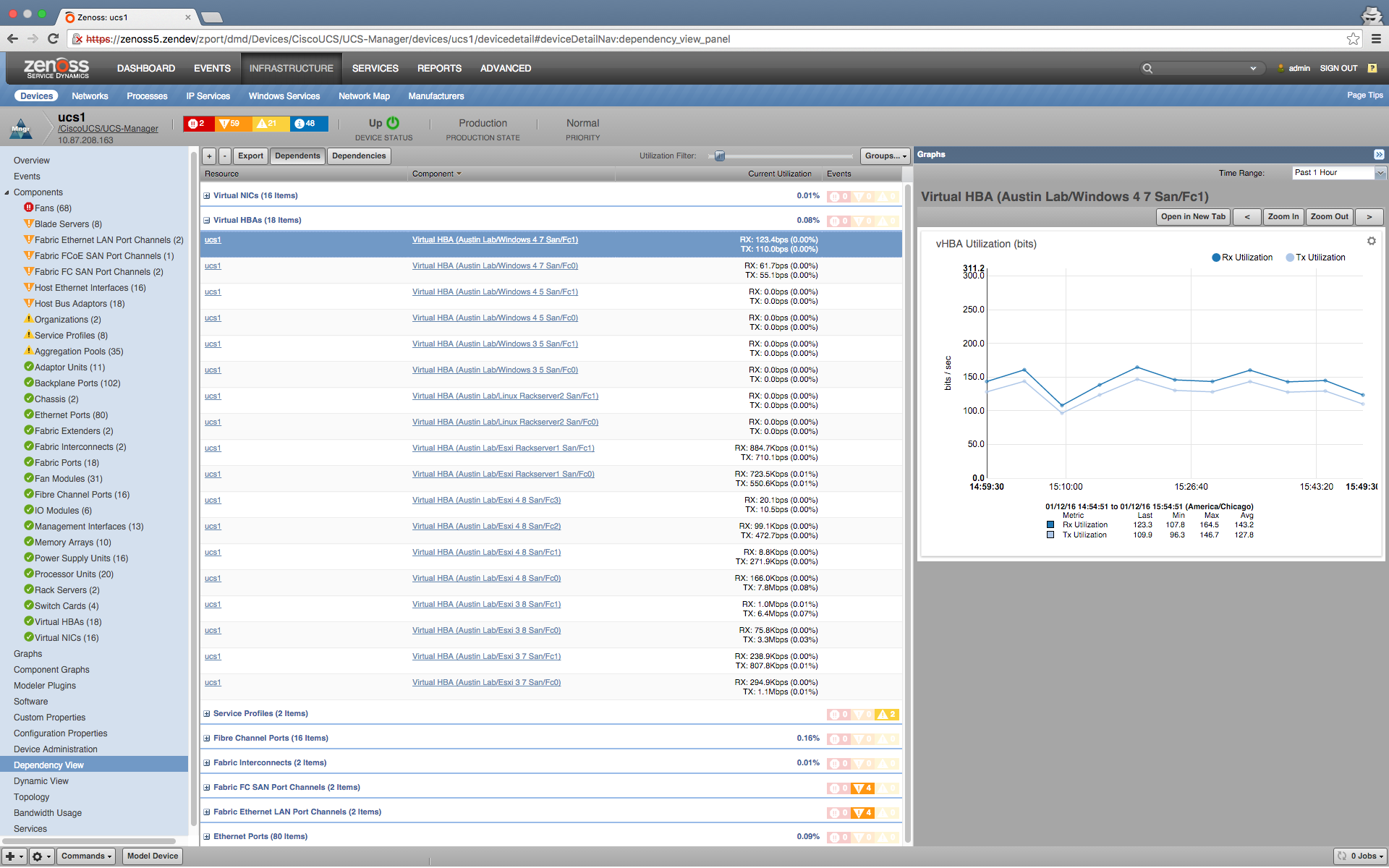
Dependency View
The Dependency View is a feature added to the Dynamic Service View ZenPack.
The Dependency View shows you the resources that are dependent on device, as well as the resources that the device depends upon. There are several places where you can see the Dependency view:
- Device Overview Page
- Device Component View
- Group Details Page
- Topology View
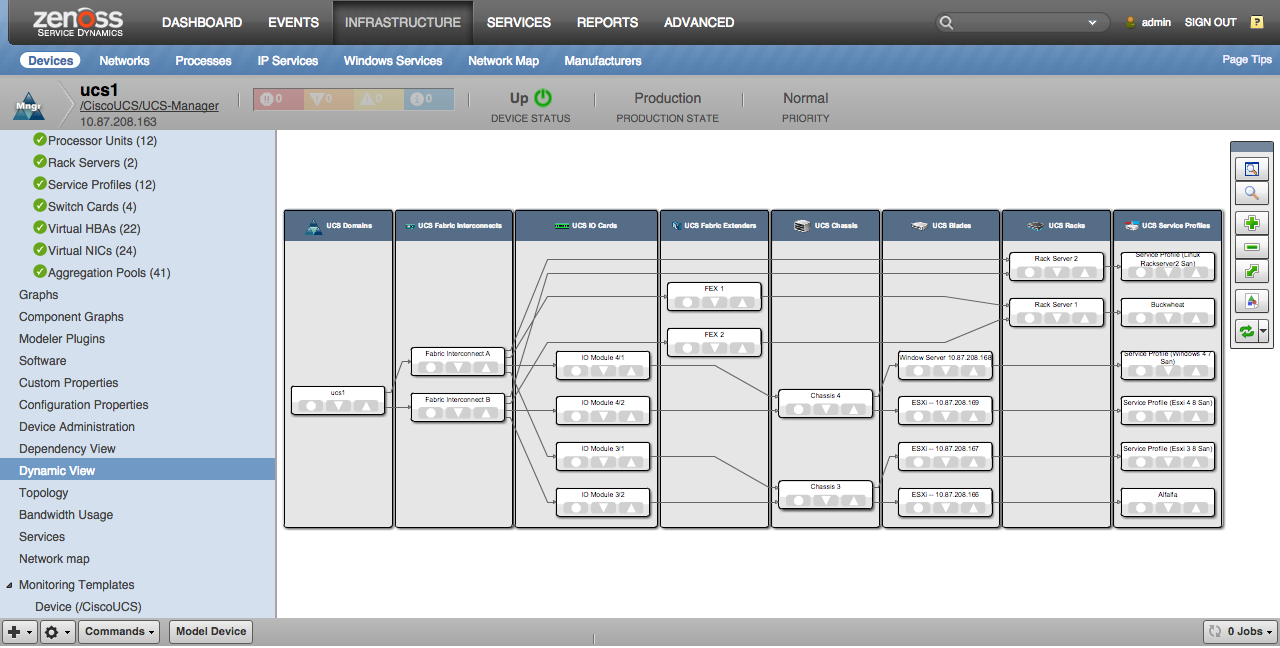
UCS Manager Dynamic View
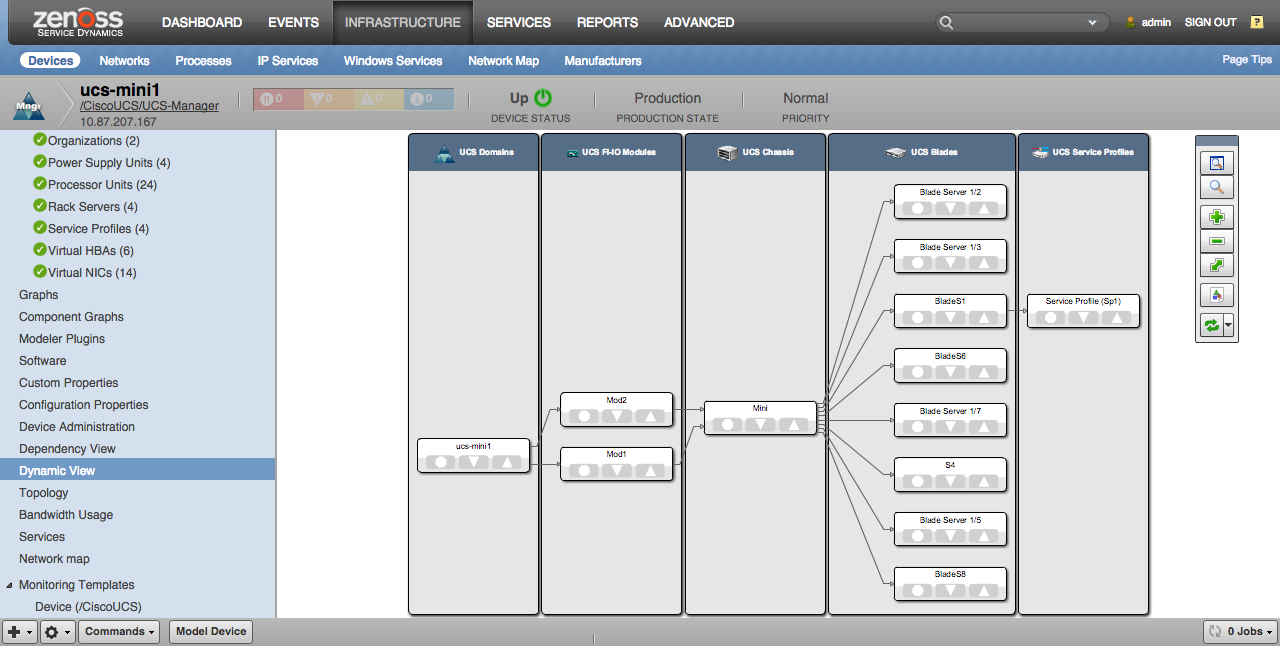
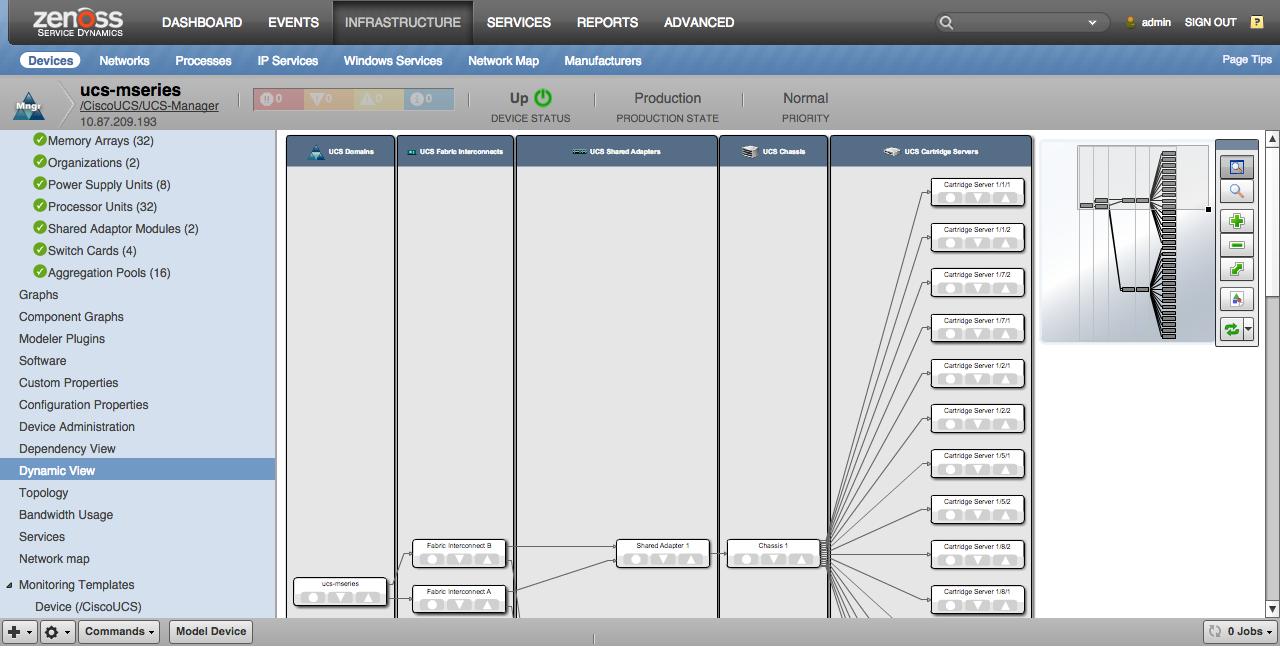
When the Dynamic View ZenPack is installed, a Dynamic View screen will be available on UCS Manager devices. This view shows a simplified topology of the more important elements being managed and how they're related. The view will show slightly different types of elements for UCS Classic, Mini and Modular.
UCS Classic
- Domains
- Fabric Interconnects
- IO Cards
- Fabric Extenders
- Chassis
- Blades
- Racks
- Service Profiles (only those bound to servers)
UCS Mini
- UCS Domains
- UCS FI-IO Modules
- UCS Chassis
- UCS Blades
- UCS Racks
- UCS Service Profiles (only those bound to servers)
UCS Modular
- UCS Domains
- UCS Fabric Interconnects
- UCS Shared Adapters
- UCS Chassis
- UCS Cartridge Servers
- UCS Service Profiles (only those bound to servers)
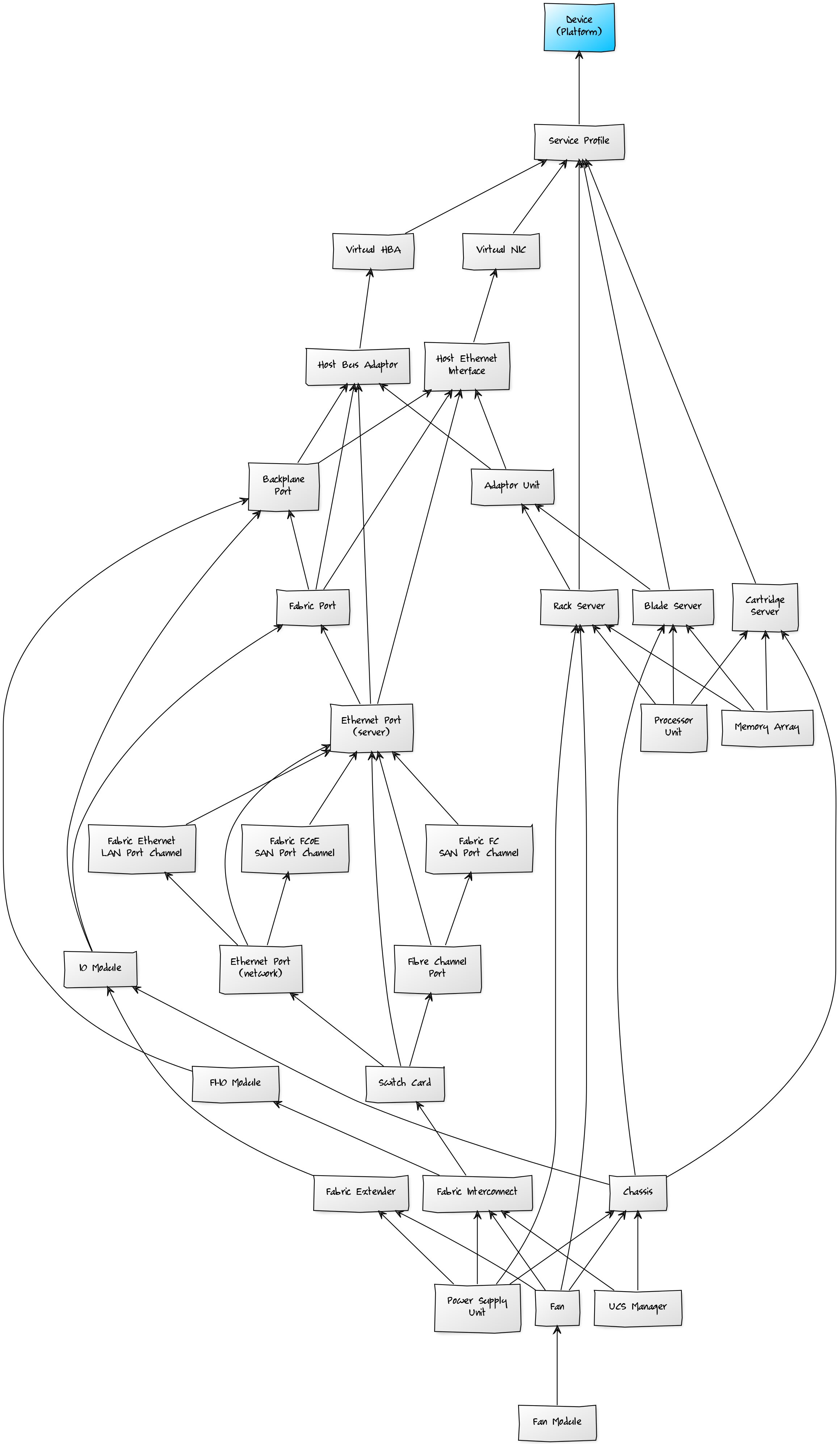
UCS Manager Service Impact and Root Cause Analysis
When combined with the Zenoss Service Dynamics product, this ZenPack adds built-in service impact and root cause analysis capabilities for services running on Cisco UCS Manager. The service impact relationships described below are automatically added. These will be included in any services that contain one or more of the explicitly mentioned components.
Compute Impact Relationships
- Service profiles impact their associated guest operating system.
Network Impact Relationships
- Virtual NICs and HBAs impact their service profile.
- Host ethernet interfaces impact their bound virtual NIC.
- Host bus adapters impact their bound virtual HBA.
- Backplane ports impact their peer host ethernet interfaces and host bus adaptors.
- Fabric ports impact their downstream backplane ports.
- Ethernet Ports (server) impact their peer fabric port.
- Ethernet Ports (network) impact their downstream server ethernet ports if unaggregated, or their port channel if aggregated.
- Fibre channel ports impact their downstream server ethernet ports if unaggregated, or their port channel if aggregated.
- Port channels impact their downstream server ethernet ports.
Hardware Impact Relationships
- Adaptor units impact their host ethernet interfaces and host bus adapters.
- Blade, cartridge and rack servers impact their adaptor units.
- Processor units impact their blade, cartridge and rack servers.
- Memory arrays impact their blade, cartridge and rack servers.
- Power supply units impact their fabric interconnect, fabric extender, chassis, or rack server.
- Fans impact their fabric interconnect, fabric extender, chassis or rack server.
- Fan modules impact their fans.
- Chassis impact their blade and cartridge servers, and their IO modules.
- IO modules impact their fabric and backplane ports.
- Fabric extenders impact their IO modules.
- Switch cards impact their ethernet and fibre channel ports.
- Fabric interconnects impact their switch cards.
Storage Impact Relationships
- Chassis impact storage controllers, storage virtual drives, storage local disks.
- Blade servers impact storage controllers, storage virtual drives, storage local disks.
- Cartridge servers impact storage controllers, storage virtual drives, storage local disks.
- Rack servers impact storage controllers, storage virtual drives, storage local disks.
- Storage controllers impact storage virtual drives, storage local disks.
- Storage local disks impact storage virtual drives.
- Storage virtual drives impact hard disks on service profile' associated guest operating system.
- Storage local disks impact hard disks on service profile' associated guest operating system.
Management Impact Relationships
- UCS Manager impacts the fabric interconnects for UCS classic, and the chassis for UCS Mini.
The impacts described above follow the default policy of a node being in the worst state of the nodes that impact it. For example, a switch card failure will imply that all related ports are also failed.
UCS Manager Reports
The following reports are included with this ZenPack. They can be found in the Cisco UCS Reports report organizer:
- Aggregate Port Pool Utilization
- Aggregation Bandwidth Utilization
- Bandwidth Utilization vs Capacity
- Free Memory Slots
- Hardware Inventory
- Interface 95th Percentile
- Interface Utilization
- Interface Volume
- Port Utilization
- Storage Utilization vs Capacity
UCS C-Series and E-Series Features
Stand-alone C-Series and E-Series monitoring data is collected using UCS Rack-Mount Servers CIMC XML API and E-Series Servers CIMC XML API respectively. These APIs are nearly-identical and therefore provide roughly the same monitoring functionality.
Note: CIMC firmware version 1.5 is the minimum supported version.
UCS C-Series and E-Series Discovery
The following components will be automatically discovered. The properties and relationships will be periodically remodeled to provide automatically up-to-date monitoring when the system configuration changes.
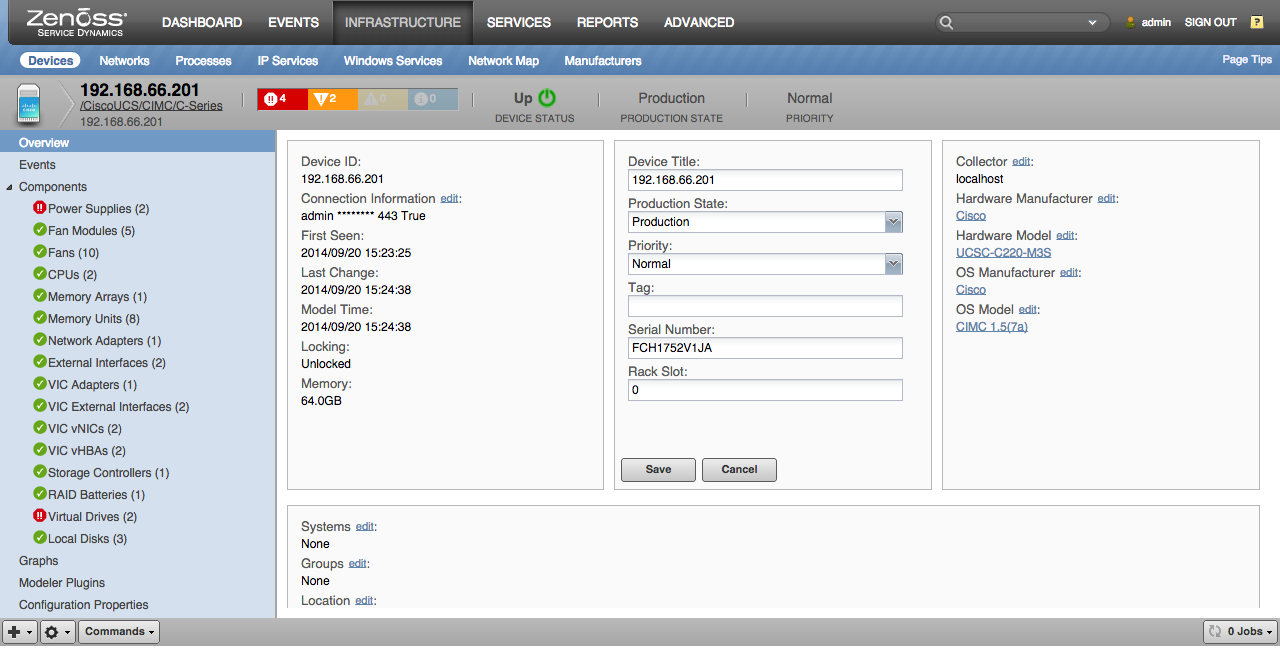
Servers (Device)
- Properties: Name, Mode, User Label, Number of CPUs, Number of CPU Cores, Number of CPU Cores Enabled, Number of CPU Threads, Memory Speed, Number of Adaptors, Number of Ethernet Host Interfaces, Number of Fibre Channel Host Interfaces, DN, UUID, Original UUID
- Relationships: Power Supplies, Fan Modules, CPUs, Memory Arrays, Network Adapters, VIC Adapters, Storage Controllers
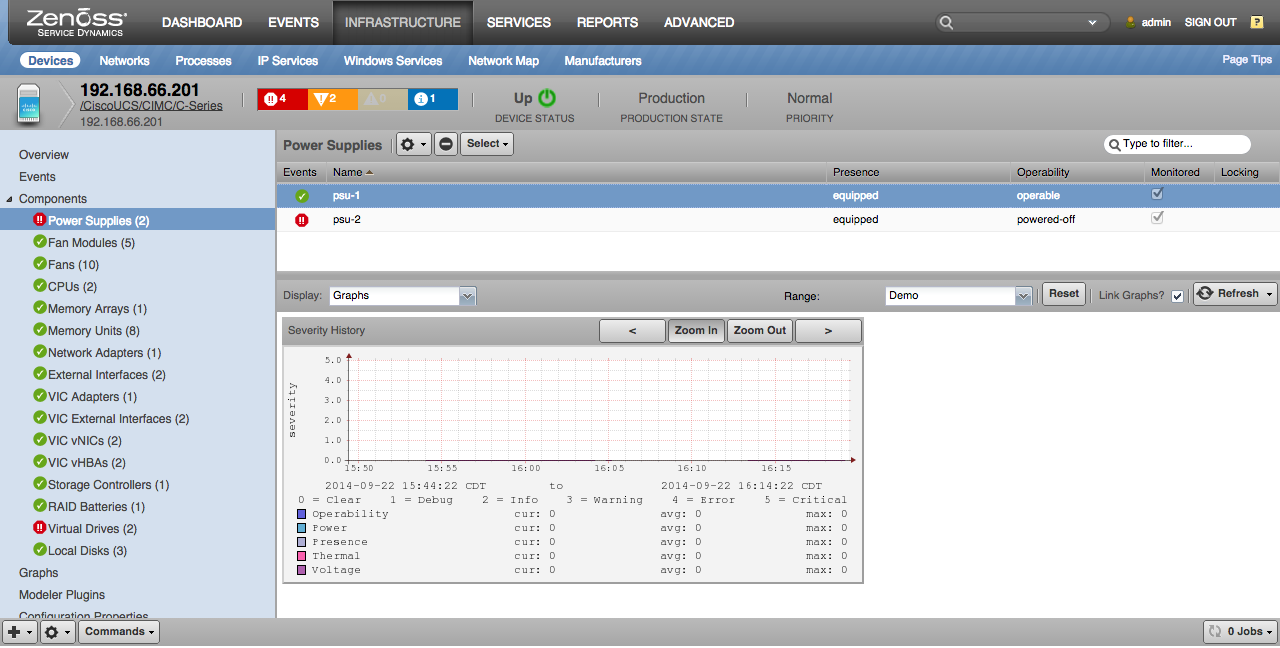
Power Supplies
- Properties: Presence, Power, Operability, Voltage Status, Thermal Status
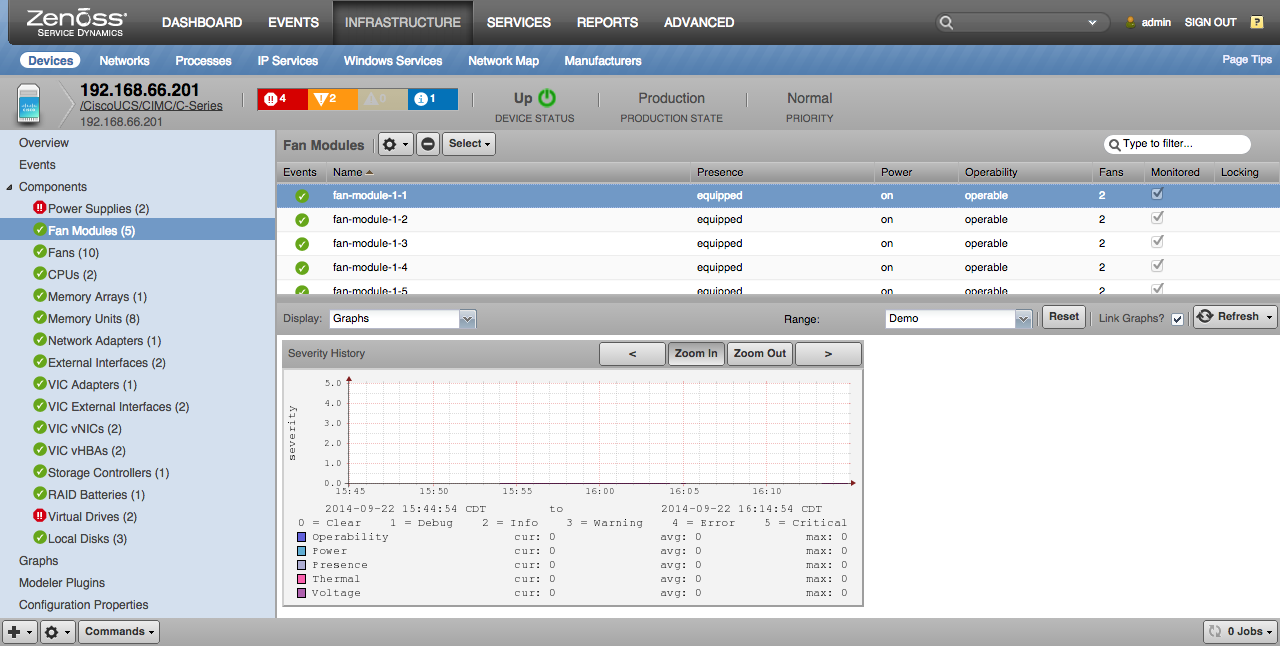
Fan Modules
- Properties: Tray, Presence, Power, Operability, Voltage Status, Thermal Status
- Relationships: Fans
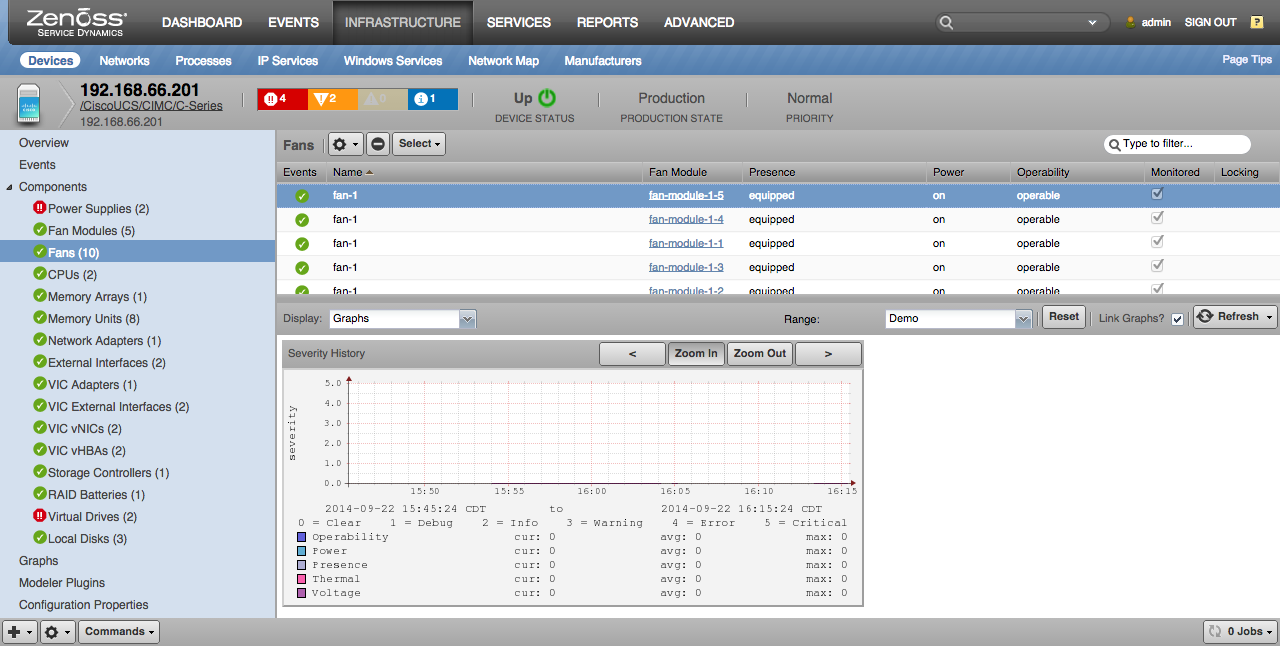
Fans
- Properties: Tray, Presence, Power Status, Operability Status, Voltage Status, Thermal Status
- Relationships: Fan Module
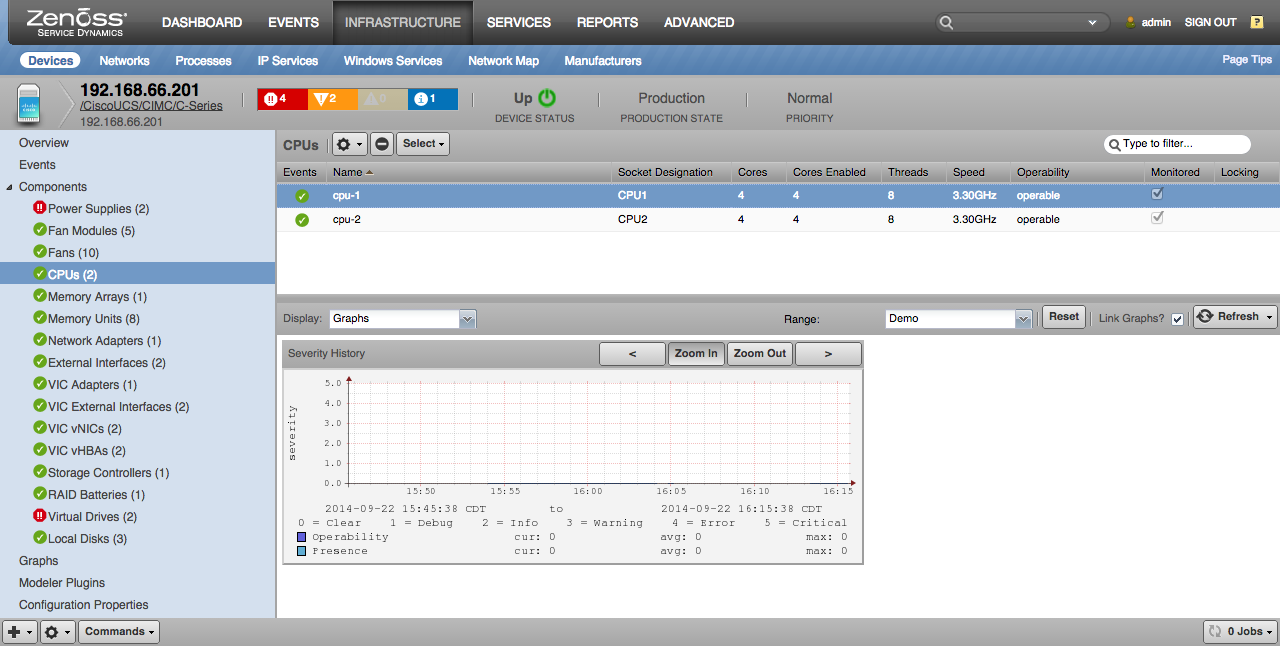
CPUs
- Properties: Socket Designation, Cores, Cores Enabled, Threads, Speed, Stepping, Presence, Operability
Memory Arrays
- Properties: Maximum Devices, Populated, Current Capacity, Presence
- Relationships: Memory Units
Memory Units
- Properties: Form Factor, Width, Location, Type, Capacity, Clock, Visibility, Presence, Operability, Operational State
- Relationships: Memory Array
Network Adapters
- Properties: Slot, Number of Interfaces
- Relationships: External Interfaces
External Interfaces
- Properties: ID, MAC Address
- Relationships: Network Adapter
VIC Adapters
- Properties: Description, PCI Slot, PCI Address, Presence, Administrative State, CIMC Management Enabled
- Relationships: VIC External Interfaces, VIC vNICs, VIC vHBAs.
VIC External Interfaces
- Properties: Port ID, Interface Type, Transport, MAC Address, Administrative Speed, Operational Speed, Link State
- Relationships: VIC Adapter, Downlink vNICs, Downlink vHBAs.
VIC vNICs
- Properties: Interface Type, PXE Boot, iSCSI Boot, Port Profile, usNIC Count, MAC Address, MTU, Channel Number, Class of Service
- Relationships: VIC Adapter, Uplink VIC External Interface
VIC vHBAs
- Properties: Interface Type, Persistent Bindings, SAN Boot, Port Profile, WWNN, WWPN, Channel Number
- Relationships: VIC Adapter, Uplink VIC External Interface
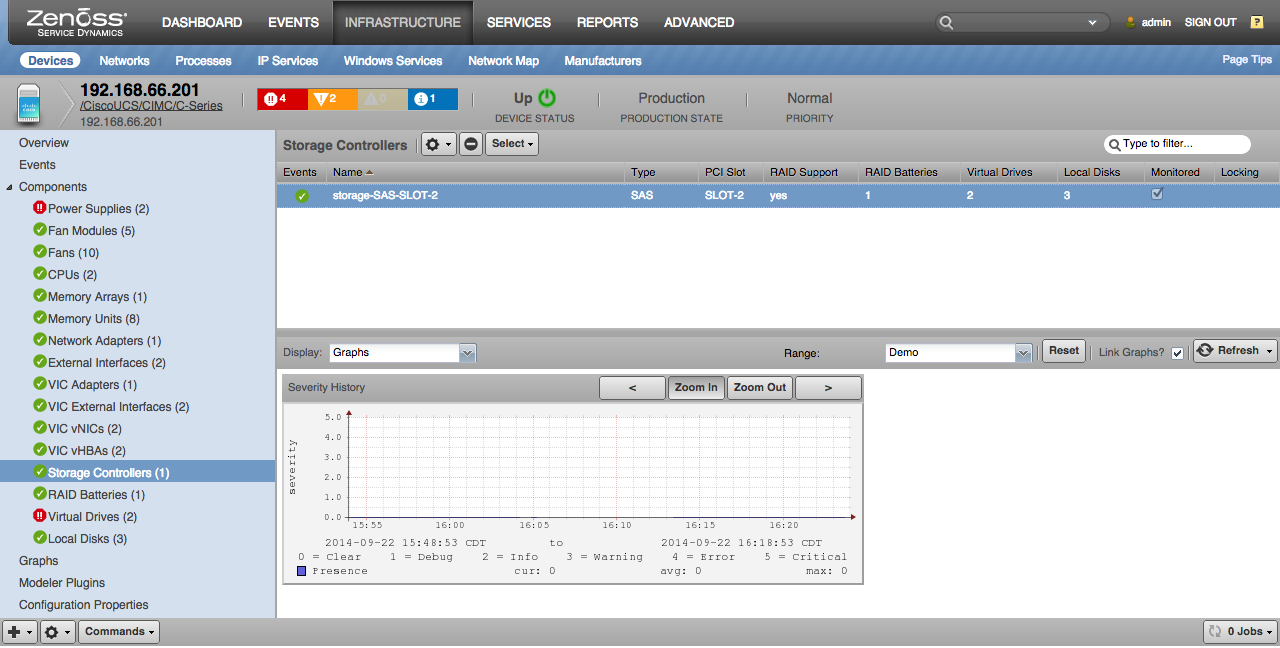
Storage Controller
- Properties: Type, PCI Slot, RAID Support, Presence
- Relationships: RAID Batteries, Virtual Drives, Local Disks
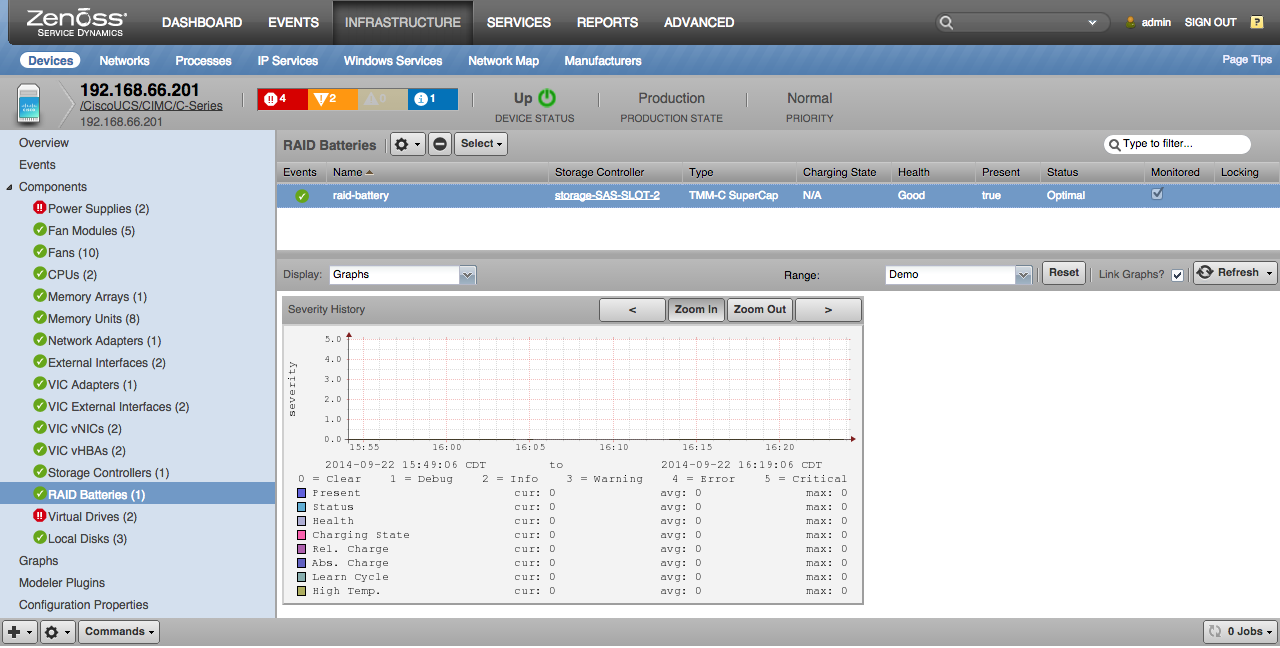
RAID Batteries
- Properties: Type, Charging State, Absolute State of Charge, Relative State of Charge, Firmware Version, Date of Manufacture, Learn Mode, Learn Cycle Requested, Learn Cycle Status, Next Learn Cycle, Present, Health, Status
- Relationships: Storage Controller
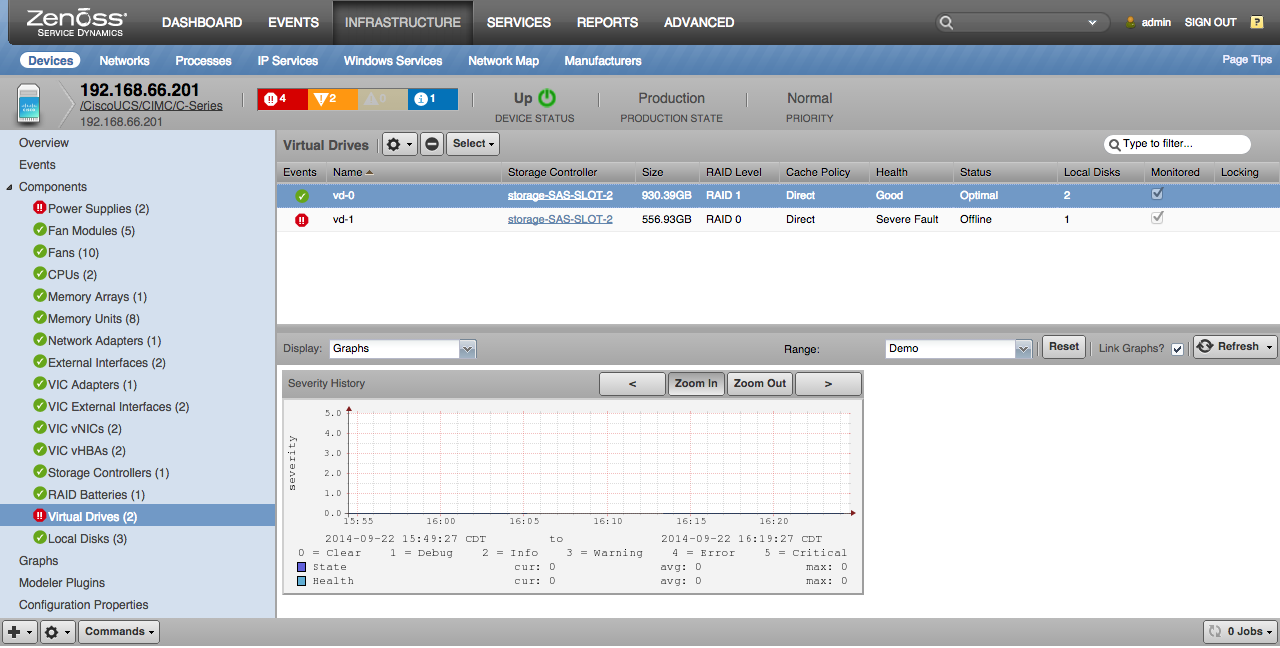
Virtual Drives
- Properties: Size, RAID Level, Strip Size, Drives Per Span, Span Depth, Auto-Snapshot, Auto-Delete Oldest, Disk Cache Policy, Read-Ahead Policy, Access Policy, Allow Background Init, Health, Status, Drive State
- Relationships: Storage Controller, Local Disks
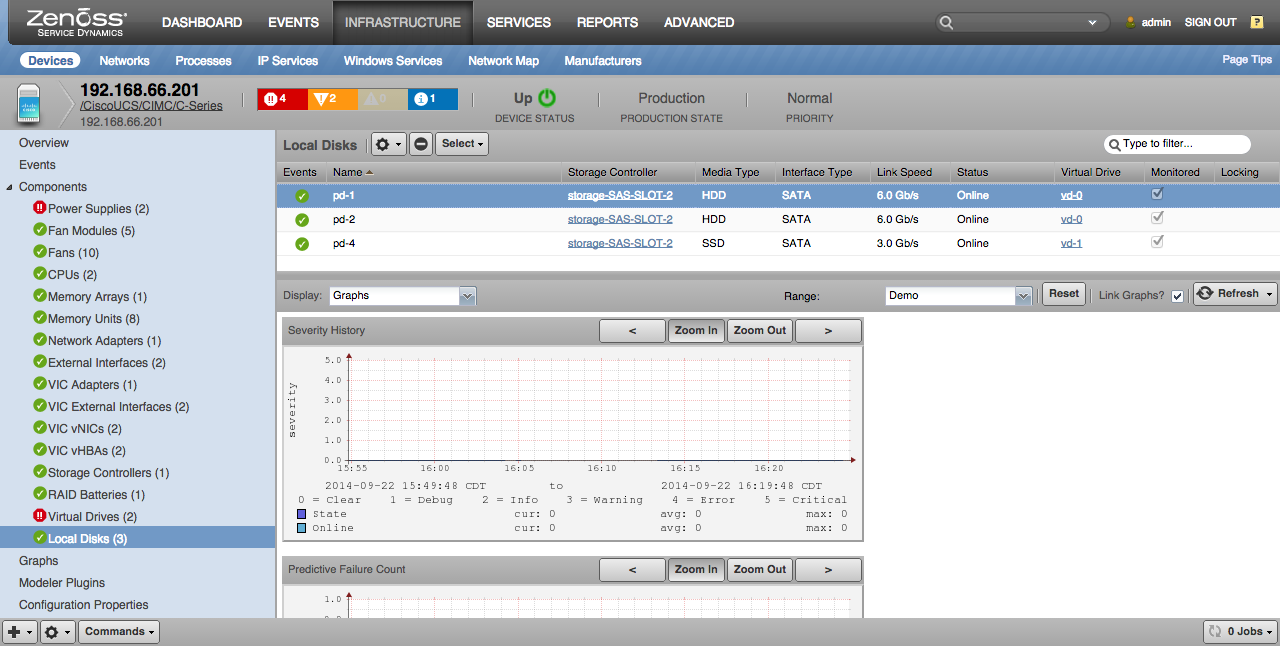
Local Disks
- Properties: Media Type, Interface Type, Link Speed, Firmware, Health, Status, Drive State, Online
- Relationships: Storage Controller, Virtual Drive
UCS C-Series and E-Series Performance Monitoring
The following metrics will be collected every 5 minutes by default. This can be controlled with the zCiscoUCSCIMCPerfInterval configuration property. Unless specifically noted these metrics are available from C-Series and E-Series servers.
Servers (Device)
- Fault Count: Faults (faults)
- Component Counts: CPUs, CPU Cores, Enabled Cores, CPU Threads, VICs, vNICs, vHBAs (components)
C-Series Servers (Device)
- Memory Availability: Total, Available (bytes)
- Consumed Power: Compute Board (watts)
- Input Current: Compute Board (amps)
- Input Voltage: Compute Board (volts)
- Temperature: Ambient, Front, Read, IOH 1 (degrees C.)
Power Supplies
- Severity History: Operability, Power, Presence, Thermal, Voltage (severity)
Fan Modules
- Severity History: Operability, Power, Presence, Thermal, Voltage (severity)
Fans
- Severity History: Operability, Power, Presence, Thermal, Voltage (severity)
CPUs
- Severity History: Operability, Presence (severity)
Memory Arrays (C-Series)
- Severity History: Presence (severity)
- Memory Capacity: Capacity (bytes)
- Memory Units: Maximum, Populated (devices)
Memory Arrays (E-Series)
- Severity History: Presence (severity)
- Memory Units: Maximum, Populated (devices)
Memory Units
- Severity History: Operability, Presence (severity)
Network Adapters
- None
External Interfaces
- None
VIC Adapters
- Severity History: Presence (severity)
VIC External Interfaces
- Severity History: Link State (severity)
VIC vNICs
- None
VIC vHBAs
- None
Storage Controllers
- Severity History: Presence (severity)
RAID Batteries
- Severity History: Present, Status, Health, Charging State, Relative Charge, Absolute Charge, Learn Cycle, High Temperature (severity)
- Current: Current (amps)
- Voltage: Design Limit, Voltage (volts)
- Temperature: Temperature (degrees C.)
Virtual Drives
- Severity History: State, Health (severity)
Local Disks
- Severity History: State, Online (severity)
- Predictive Failure Count: Count (count)
- Size: Coerced (bytes)
- Link Speed: Speed (bps)
UCS C-Series and E-Series Event Management
Zenoss will create events for all UCS faults collected through the CIMC API. Most CIMC faults disappear from the API after they're cleared. Zenoss will clear the corresponding Zenoss events when this occurs. The timestamp of corresponding Zenoss events will match the UCS fault's timestamp. So it is important that both Zenoss servers and the UCS servers have relatively accurate clocks.
The CIMC API doesn't provide a timezone offset for when faults occurred, so Zenoss has to assume that the time is UTC. If the server is configured to a timezone other than UTC, it will result in Zenoss misreporting the time events occurred by the opposite of the server's timezone offset.
Faults are collected from the CIMC interface once every 60 seconds by default. This can be changed using the zCiscoUCSCIMCEventsInterval configuration property.
The following fields will be populated for each event.
Standard Zenoss Event Fields
- device: The UCS server device in the /CiscoUCS/CIMC/* device class.
- component: The Zenoss modeled component related to the fault.
- eventKey: The CIMC "dn" for the fault. Unique to the fault type.
- summary: The CIMC "descr" for the fault truncated to 128 characters.
- message: The CIMC "descr" for the fault.
- severity: Mapped from the CIMC "severity" for the fault using the
following table.
- UCS critical = Zenoss critical
- UCS major = Zenoss error
- UCS minor = Zenoss warning
- UCS warning = Zenoss warning
- UCS condition = Zenoss info
- UCS info = Zenoss info
- UCS cleared = Zenoss clear
- eventClassKey: Set to "ucs-cimc|code" where code is the CIMC code.
- rcvtime: The CIMC "created" for the fault converted to UNIX timestamp.
- count: The CIMC "occur" for the fault.
The following additional fields and potentially more will also be populated for each event. These are the fields native to a UCS CIMC fault record. If a fault occurs that has other fields, those will be added with the same ucs.cimc prefix.
Additional Event Fields
- ucs.cimc.ack
- ucs.cimc.affectedDN
- ucs.cimc.cause
- ucs.cimc.code
- ucs.cimc.created
- ucs.cimc.descr
- ucs.cimc.dn
- ucs.cimc.highestSeverity
- ucs.cimc.id
- ucs.cimc.ic
- ucs.cimc.occur
- ucs.cimc.origSeverity
- ucs.cimc.prevSeverity
- ucs.cimc.rule
- ucs.cimc.severity
- ucs.cimc.tags
- ucs.cimc.type
UCS C-Series and E-Series Service Impact and Root Cause Analysis
When combined with the Zenoss Service Dynamics product, this ZenPack adds built-in service impact and root cause analysis capabilities for services running on Cisco UCS C-Series and E-Series servers. The service impact relationships described below are automatically added. These will be included in any services that contain one or more of the explicitly mentioned components.
Impact Relationships
- Server failure impacts guest operating system devices including VMware vSphere hosts.
- Power supply failure impacts the server.
- Fan module failure impacts fans in the module.
- Fan failure impacts the server.
- CPU failure impacts the server.
- Memory array failure impacts the memory units in the array.
- Memory unit failure impacts the server.
- Network adapter failure impacts external interfaces.
- External interface failure impacts guest operating system interfaces including VMware vSphere host NICs.
- VIC adapter failure impacts VIC external interfaces, vNICs and vHBAs.
- VIC external interface failure impacts downlink vNICs and vHBAs.
- VIC vNIC failure impacts guest operating system interfaces including VMware vSphere host NICs.
- Storage controller failure impacts virtual drives and local disks.
- RAID battery failure impacts virtual drives.
- Local disk failure impacts the server if not used in a virtual drive, or the associated virtual drive.
- Virtual drive failure impacts the server.
The impacts described above follow the default policy of a node being in the worst state of the nodes that impact it. For example, a fan module failure will imply that all related fans are also failed.
Usage
Installation
Installation should be performed as per usual instructions. If installing manually, ensure that all prerequisites ZenPacks listed in the Releases section are installed.
Upgrading the CiscoUCS ZenPack to Version 3.0.0 without UCSCapacity
- If upgrading from CiscoUCS 2.8.0 to 3.0.0 with out UCSCapacity ZenPack installed, proceed to upgrade normally.
Upgrading the CiscoUCS ZenPack to Version 3.0.0 with UCSCapacity 1.6.0
Note: For the customers with UCSCapacity ZP 1.6.0 installed, it is recommended to contact zenoss support prior to upgrade.
CiscoUCS ZenPack version 3.0.0 integrates the features from the older UCSCapacity ZenPack. Therefore it is important to upgrade UCSCapacity to 2.0.0 to preserve metric data and migrate all features and templates to CiscoUCS.
-
NOTE: Failure to follow these instructions will cause data loss and damage to Zenoss!
-
If upgrading from 2.8.0 to 3.0.0 with UCSCapacity ZenPack installed, you must first upgrade the UCSCapacity ZenPack to 2.0.0 and then upgrade CiscoUCS ZenPacks.
The required order of operations in this case is:
- Upgrade UCSCapacity ZenPack to version 2.0.0
- Upgrade CiscoUCS ZenPack to version 3.0.0
- Restart all services as normally required
-
Note that after upgrade of both UCSCapacity ZP to 2.0.0 and CiscoUCS ZP to 3.0.0, Aggregation Pools will be removed until the next modeling cycle. Historic metric data is retained and will resume collection after they are remodeled.
Configuring UCS Managers
In order to avoid monitoring and modeling issues, you have to use unique MAC addresses within your network, it can be configured over MAC Pools component on Cisco UCS Manager instance.
The Cisco UCS C3260 Rack Server is only supported by the UCS Manager XML API. There is no CIMC API support for the C3260 at this time.
MAC Pools
A MAC pool is a collection of network identities, or MAC addresses, that are unique in their layer 2 environment and are available to be assigned to vNICs on a server. If you use MAC pools in service profiles, you do not have to manually configure the MAC addresses to be used by the server associated with the service profile.
In a system that implements multi-tenancy, you can use the organizational hierarchy to ensure that MAC pools can only be used by specific applications or business services. Cisco UCS Manager uses the name resolution policy to assign MAC addresses from the pool.
You can specify your own MAC addresses or use a group of MAC addresses provided by Cisco. To assign a MAC address to a server, you must include the MAC pool in a vNIC policy. The vNIC policy is then included in the service profile assigned to that server.
You can read more about MAC Pools on the official Cisco website.
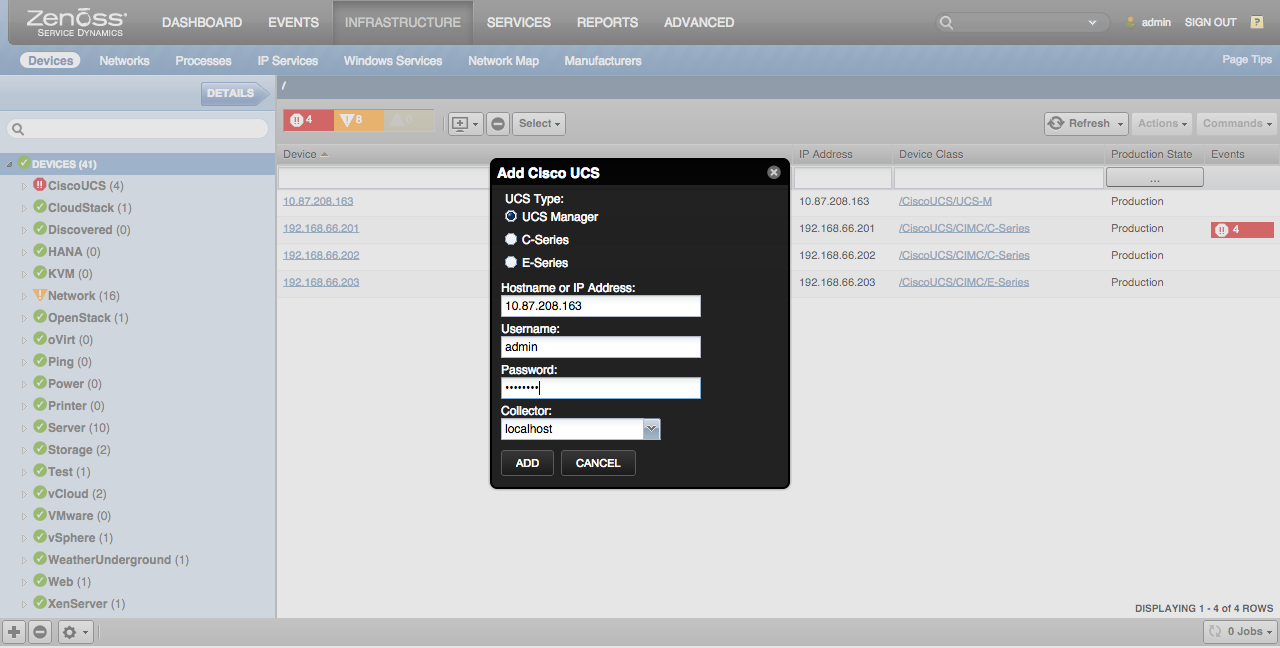
Adding UCS Managers
Use the following steps to start monitoring UCS Managers using the Zenoss web interface.
- Navigate to the Infrastructure page.
- Choose Add Cisco UCS from the add device button
- Fill out the form.
- Choose UCS Manager as the UCS Type
- Hostname or IP Address should be the floating IP address of the UCS Manager. It should not be the physical IP address of either fabric interconnect.
- Username and Password should be a user with at least read-only permission to UCS Manager.
- Collector should be the Zenoss collector that should discovery and monitor this system.
- Click ADD.
Alternatively you can use zenbatchload to add Cisco UCS Managers from the command line. To do this, you must create a file with contents similar to the following. Replace all values in angle brackets with your values minus the brackets. Multiple endpoints can be added under the same /Devices/CiscoUCS/UCS-Manager section.
/Devices/CiscoUCS/UCS-Manager ucsm1 setManageIp=<address>, zCiscoUCSManagerUser=<username>, zCiscoUCSManagerPassword=<password>
You can then load the endpoint(s) with the following command.
zenbatchload <filename>
-
NOTE: To add an LDAP user, you would prepend "ucs" to the Domain name as such:
ucs-<DomainName>\<username>For example:
ucs-AcmeDomain\wilycoyote
Adding Stand-Alone UCS C-Series Servers
Use the following steps to start monitoring standalone UCS C-Series servers using the Zenoss web interface.
- Navigate to the Infrastructure page.
- Choose Add Cisco UCS from the add device button
- Fill out the form.
- Choose C-Series as the UCS Type
- Hostname or IP Address should be the resolvable name or IP address of the server's CIMC management interface. It should not be the address of the operating system running on the server.
- Username and Password should be the CIMC management username and password. The default values for these are admin and password respectively.
- Collector should be the Zenoss collector that should discovery and monitor this server.
- Click ADD.
Alternatively you can use zenbatchload to add stand-alone Cisco UCS C-Series servers from the command line. To do this, you must create a file with contents similar to the following. Replace all values in angle brackets with your values minus the brackets. Multiple servers can be added under the same /Devices/CiscoUCS/CIMC/C-Series section.
/Devices/CiscoUCS/CIMC/C-Series server1 setManageIp=<address>, zCiscoUCSManagerUser=<username>, zCiscoUCSManagerPassword=<password>
You can then load the endpoint(s) with the following command.
zenbatchload <filename>
Adding UCS E-Series Servers
Use the following steps to start monitoring UCS E-Series servers using the Zenoss web interface.
- Navigate to the Infrastructure page.
- Choose Add Cisco UCS from the add device button
- Fill out the form.
- Choose E-Series as the UCS Type
- Hostname or IP Address should be the resolvable name or IP address of the server's CIMC management interface. It should not be the address of the operating system running on the server.
- Username and Password should be the CIMC management username and password. The default values for these are admin and password respectively.
- Collector should be the Zenoss collector that should discovery and monitor this server.
- Click ADD.
Alternatively you can use zenbatchload to add Cisco UCS E-Series servers from the command line. To do this, you must create a file with contents similar to the following. Replace all values in angle brackets with your values minus the brackets. Multiple servers can be added under the same /Devices/CiscoUCS/CIMC/E-Series section.
/Devices/CiscoUCS/CIMC/E-Series server1 setManageIp=<address>, zCiscoUCSManagerUser=<username>, zCiscoUCSManagerPassword=<password>
You can then load the endpoint(s) with the following command.
zenbatchload <filename>
Installed Items
Configuration Properties
- zCiscoUCSCIMCEventsInterval: Event collection interval in seconds. Default is 60.
- zCiscoUCSCIMCPerfInterval: Metric collection interval in seconds. Default is 300.
- zCiscoUCSCIMCSSLProtocol: The SSL/TLS protocol used to connect to a CIMC device. With the zProperty you can select one of the following SSL/TLS protocols: SSLv23, TLSv1, TLSv1.2. For the CIMC 3.0 it should be set to SSLv23 or TLSv1.2 protocol, and for the other versions, you can use the TLSv1 protocol. Default is SSLv23.
- zCiscoUCSCIMCReuseSessions: Whether to reuse existing sessions during CIMC collection. Default is true.
- zCiscoUCSManagerUser
- zCiscoUCSManagerPassword
- zCiscoUCSManagerPort: Port to use to connect to the UCS Manager or CIMC XML APIs. Default is 443 and typically should not be changed.
- zCiscoUCSManagerUseSSL: Whether to use SSL when connecting to the UCS Manager or CIMC XML APIs. Default is true and typically should not be changed.
- zCiscoUCSManagerPerfInterval: How often to collect statistics. Default is 300 seconds. This configuration is only used when the reporting interval cannot be modeled from UCS Manager.
Device Classes
- /CiscoUCS: Root Cisco UCS device class. Typically devices should not be put in this device class.
- /CiscoUCS/UCS-Manager: Device class for UCS Manager endpoints.
- /CiscoUCS/CIMC/C-Series: Device class for stand-alone UCS C-Series rack-mount servers.
- /CiscoUCS/CIMC/E-Series: Device class for UCS E-Series servers.
Modeler Plugins
- zenoss.ucs.CiscoUCSInstanceMap: UCS Manager modeler plugin.
- zenoss.ucs.CIMCServer: Stand-alone C-Series and E-Series modeler plugin.
Datasource Types
- Cisco UCS XML API: UCS Manager XML API datasource type. For UCS Manager.
- UCS CIMC: CIMC XML API datasource type. For C-Series and E-Series.
NOTE: You can skip the data collection for particular datapoints defined under CIMC XML API datasources with xpath_skip_query property located in the datapoints, use XPath syntax while adding the custom skip rules.
Monitoring Templates
-
/CiscoUCS (used for UCS-Manager)
- General Components
- Device
- UCSBladeServer
- UCSCartridgeServer
- UCSChassis
- UCSEthPort
- UCSFabricEthLanPc
- UCSFabricFcoeSanPc
- UCSFabricFcSanPc
- UCSFabricInterconnect
- UCSFanModule
- UCSFcPort
- UCSHostEthIf
- UCSPowerSupplyUnit
- UCSProcessorUnit
- UCSSharedAdaptor
- Pool Components
- DASPortPool
- EthPortPool
- FcPortPool
- PerChassisServerPortPool
- PerChassisStorageFcPortPool
- PerFexServerPortPool
- PerFIApplianceEthPortPool
- PerFIDASPortPool
- PerFINetworkFcPortPool
- PerFINetworkPortPool
- PerFIServerPortPool
- PerFIStorageFcPortPool
- SingleChassisServerPortPool
- SingleChassisStorageFcPortPool
- Capacity Templates
- UCSCapBladeServer
- UCSCapChassis
- UCSCapDevice
- UCSCapEthPort
- UCSCapFabricEthLanPc
- UCSCapFabricExtender
- UCSCapFabricFcoeSanPc
- UCSCapFabricFcSanPc
- UCSCapFabricInterconnect
- UCSCapFabricIOCardPort
- UCSCapFcPort
- UCSCapHostEthIf
- UCSCapHostFcIf
- UCSCapIOCard
- UCSCapMiniChassis
- UCSCapRackServer
- UCSCapServerIOCardPort
- UCSCapServiceProfile
- UCSCapVnicEther
- UCSCapVnicFc
- General Components
-
/CiscoUCS/CIMC (shared for C-Series and E-Series)
- Device
- Memory
- PowerStats
- TemperatureStats
- PowerSupply
- FanModule
- Fan
- CPU
- MemoryArray
- MemoryUnit
- NetworkAdapter
- ExternalInterface
- VICAdapter
- VICExternalInterface
- VICvNIC
- VICvBHA
- StorageController
- RAIDBattery
- LocalDisk
- VirtualDrive
-
/CiscoUCS/CIMC/E-Series
- MemoryArray
Event Classes
- /CiscoUCS
- /CiscoUCS/Event
- /CiscoUFS/Fault
- /Status/Blade
- /Status/Chassis
- /Change/Set/UCS
Event Class Mappings
- LOCAL0-3-SYSTEM_MSG (in /CiscoUCS): Handles syslog messages from UCS Manager.
- UCS Events Default (in /CiscoUCS/Event): Handles events from UCS Manager XML API.
- UCS Faults Default (in /CiscoUCS/Fault): Handles faults from UCS Manager XML API.
- ucs-cimc-configResolveClass (in /Status): Handles polling failures from CIMC XML API.
- ucs-cimc-defaultmapping (in /Status): Default handler for faults from CIMC XML API.
- ucs-cimc-status (in /Status): Handles status events from CIMC XML API.
Collector Daemons
- zenucsevents: UCS Manager events and metrics
- zenpython: UCS Capacity metrics and CIMC metrics
Zenoss Analytics
Note
These steps are applicable only for Zenoss Analytics 5.x.x. In Analytics 6.0.0, any third-party reporting tool can be used to generate reports.
This ZenPack provides additional support for Zenoss Analytics. Perform the following steps to install extra reporting resources into Zenoss Analytics after installing the ZenPack.
- Copy analytics-cimc-bundle.zip and analytics-ucsm-bundle.zip from $ZENHOME/ZenPacks/ZenPacks.zenoss.CiscoUCS*/ZenPacks/zenoss/CiscoUCS/analytics/ on your Zenoss server.
- Navigate to Zenoss Analytics in your browser.
- Login as superuser.
- Remove any existing Cisco UCS ZenPack folder.
- Choose Repository from the View menu at the top of the page.
- Expand Public in the list of folders.
- Right-click on Cisco UCS ZenPack folder and choose Delete.
- Confirm deletion by clicking OK.
- Add the new Cisco UCS ZenPack folder.
- Choose Server Settings from the Manage menu at the top of the page.
- Choose Import in the left page.
- Remove checks from all check boxes.
- Click Choose File to import the data files.
- Choose the analytics-cimc-bundle.zip file copied from your Zenoss server.
- Click Import.
- Choose the analytics-ucsm-bundle.zip file copied from your Zenoss server.
- Click Import.
You can now navigate back to the Cisco UCS ZenPack folder in the repository to see the following resources added by the bundle.
Domains
- Cisco UCS CIMC Domain
- Cisco UCS Manager Domain
Domains can be used to create ad hoc views using the following steps:
- Choose Ad Hoc View from the Create menu.
- Click View as list icon at the top of the data chooser dialog.
- Choose either the Cisco UCS CIMC Domain or Cisco UCS Manager domain depending on your reporting needs.
NOTE: Ad Hoc Views may require minimum 24 hours to populate data.
Tested UCS Versions
| Type | Version |
|---|---|
| UCS-Mini | 3.0, 3.1(1x), 3.1(2b) |
| B-Series | 2.2, 3.1(1x) |
| C-Series | 2.2, 3.1(1x), M4, M5 |
Troubleshooting
CIMC Session Leakage
If you see collection errors messages like
CIMC Maximum sessions reached (554), this may indicate connections are
not being released properly. This can happen for several reasons, but
can also result from manual testing of Zenpython or other application
accessing the Cisco XML API. Setting zCiscoUCSCIMCReuseSessions to
false, which will close sessions after each collection and hopefully
mitigate this issue. See Configuration Properties for more information on
this zProperty.
In cases where a CIMC device contains lots of components and it takes more than zCollectorClientTimeout's value to model the device, the modeling session will be interrupted due to the timeout. It leads to inappropriate data modeling in Zenoss and session leakage on the modeled CIMC device. The solution will be to increase zCollectorClientTimeout property to 300 seconds or higher, by default, it's 180 seconds. You can set the property in "Configuration Properties" section on a specific CIMC device or whole device class. After the timeout is changed, the leaked session must be closed on the actual CIMC device, there are several ways how it can be done with a privileged user:
-
Wait until the leaked sessions are eventually expired(usually, it takes 15 minutes).
-
Go to the CIMC web interface, select "Admin" tab, click on "User Management" and terminate the leaked sessions on "Sessions" tab.
-
Go to the CIMC web interface, select "Admin" tab, click on "Communication Services", under "XML API Properties" on "Communication Services" tab disable and re-enable "XML API" mark.
-
Connect to CIMC via SSH and run the following commands:
scope xmlapi set enabled no commit set enabled yes commit
Another recommendation will be to create a read-only user on a CIMC device and use it for monitoring purposes in Zenoss.
CIMC SSL Connection Errors
In case you see one of the following errors while connecting to a CIMC device:
- ('SSL routines', 'SSL3_READ_BYTES', 'ssl handshake failure')
- ('SSL routines', 'SSL3_GET_KEY_EXCHANGE', 'wrong signature length')
You have to check whether the zCiscoUCSCIMCSSLProtocol zProperty on your CIMC device in Zenoss corresponds to the appropriate SSL/TSL protocol used on the actual target CIMC device.
Cisco UCS Manager - Huge Spikes on Utilization Graphs
If you observe negative or unrealistic values in both graphs and reports related to some specific Cisco UCS Manager, the first thing would be to check whether the firmware version of the Cisco UCS Manager is greater than 2.2.8f. Confirm that the issue was resolved by a software update to the 2.2.8f version on the UCS side.
Changes
3.0.4
- Disable BandwidthHeadroom thresholds for Aggregation Pools (ZPS-5933)
- Fix UCS Chassis Capacity dashboard portlet invalid link (ZPS-6010)
- Rework name formation for Rack Server components (ZPS-6814)
- Change event class from '/Capacity' to '/Perf' for Aggregator Pool thresholds (ZPS-6945)
- Added proper error events for failed modeling cases for UCS.CIMC devices (ZPS-8805)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss 6.7 and Service Impact 5.6.0, Analytic 6.0.0.
3.0.3
- Added compatibility with Analytics 6.0.0.
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss 6.7 and Service Impact 5.6.0, Analytic 6.0.0.
3.0.2
- Fix duplicates of fan module components. (ZPS-6047)
- Fix CIMC session leakage. (ZPS-6110)
- Fix "AttributeError: search" tracebacks during graph update. (ZPS-6194)
- Fix zenchkrels errors for service profiles. (ZPS-6338)
- Fix Authentication failure (Authorization Required 552). (ZPS-5921)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss 6.4.1 and Service Impact 5.5.1.
3.0.1
- Add impact relationships for Aggregation Pools. (ZPS-5836)
- Fixes Domain Overview Portlet. (ZPS-5839)
- Correspond UCSProtocol timeout value to the collection interval. (ZPS-5881)
- Fixes event transform for UCS Fault. (ZPS-5941)
- Fixes incorrect events for PSU's. (ZPS-5939)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss 6.4.0 and Service Impact 5.5.1
3.0.0
- Add all UCSCapacity features
- Upgade to ZenPackLib 2.X
- Fix "Edit with Domain Designer" issue on Cisco UCS Manager Domain. (ZPS-1671)
- Fix massively growing counts for Cisco UCS faults. (ZPS-3202)
- Do not autogenerate CiscoUCS reports while opening. (ZPS-4175)
- Show a spinner wheel when generating Storage reports. (ZPS-4305)
- Ensure CIMC session closing after collection when zCiscoUCSCIMCReuseSessions is false. (ZPS-4555)
- Guard against empty object maps in modeler. (ZPS-5617)
- Allow user specified severity fields for UCS Manager events. (ZPS-5199)
- Fix slider in Dependency View to update resources by utilization. (ZPS-5643)
- Update Topology View for S3260 storage chassis. (ZPS-3576)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss 6.3.2 and Service Impact 5.3.4
2.8.1
- Do not autogenerate CiscoUCS reports while opening. (ZPS-4175)
- Shows a spinner wheel when generating Storage reports. (ZPS-4305)
- Ensure CIMC session closing after collection when zCiscoUCSCIMCReuseSessions is false. (ZPS-4555)
- Fix and optimize various impact relationship calculations. (ZPS-5793)
- Fix errors when adding Virtual NICs to Impact services. (ZPS-5872)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, and Zenoss Resource Manager 6.3.2.
2.8.0
- Transparent background for overview panel to inherit panel owner styles. (ZPS-3798)
- Fix events generation for VIC External Interfaces. (ZPS-4080)
- Support for C-Series C220/C240 M4 and M5 models. (ZPS-3769)
- Tested with Zenoss Cloud, Zenoss Resource Manager 6.2.0, Zenoss Resource Manager 5.3.3 and Service Impact 5.3.1
2.7.0
- Reduce processing time for UCS service profile changes. (ZPS-2552)
- Add capacity thresholds to port channels. (ZPS-2697)
- Skip "online is false" events for Hot Spare local disks. (ZPS-1356)
- Extend troubleshooting steps for "CIMC Session Leakage" section in the documentation. (ZPS-2771)
- Fix "The attribute was not found" CIMC warnings in ZenHub log. (ZPS-2250)
- Change all battery_* aliases to batt_*. (ZPS-2610)
- Fix extraneous "adminSpeed" and "operSpeed" warnings in ZenHub log. (ZPS-3127)
- Fix "Failed converting '' to float" warnings in zenpython log. (ZPS-3380)
- Add more debug logging for modeling, monitoring and the CIMC connection client. (ZPS-3361)
- Change log level to debug for 'no value found for ..' warnings while monitoring CIMC devices. (ZPS-3390)
- Fix broken or hanging session connections. (ZPS-2635)
- Change names of duplicated aliases. (ZEN-29093)
- Improve error handling in zenucsevents service. (ZPS-2551)
- Lower default configsipsize from 25 to 5 in zenucsevents.conf in order to facilitate pulling large configs from ZenHub. (ZPS-797)
- Tested with Resource Manager 4.2.5 SP 743, 5.3.3 and 6.1.2, Impact 5.3.0, and Analytics 5.1.0
2.6.2
- Reduce "no status maps" events by adding support for more CIMC states. (ZPS-1670)
- Fix memory leak in zenucsevents service. (ZPS-1706)
- Fix collection interval of datasources calculated from UCS Manager datapoints. (ZPS-2077)
2.6.1
- Add UCS device types to multi-device add wizard. (ZPS-1421)
- The severity comment graph points were properly aligned on the CIMC graphs. (ZPS-1361)
- Increase default modeling timeout from 3 to 10 minutes. (ZPS-1519)
- Fix "ssl handshake failure" error on adding a CIMC 3.0 device. Add zCiscoUCSCIMCSSLProtocol zProperty. (ZPS-1365)
- Add a "Cisco UCS Manager - Huge Spikes on Utilization Graphs" record to the Troubleshooting section. (ZPS-1190)
2.6.0
- Update/remove thresholds for fabric port channels.
- Replace here.linkSpeed with here.operSpeed for UCSFabricEthLanPc and UCSFabricFcSanPc thresholds.
- Remove thresholds from UCSFabricFcoeSanPc, since it does not have speed of any kind.
- Update external storage mappings.
- Add LUN count to vHBA grid, and links in details.
- Add vHBA/LUN count to service profile grid, and links in details.
- Update Impact relationships: Add LUN to service profile. Remove LUN to vHBA.
- Added support for UCS Storage.
- Added support for storage controllers.
- Added support for storage local disks.
- Added support for storage virtual drives.
- Added support for UCS Storage mapping between hard disks on Service
Profile OS's and storage local disks/storage virtual drives.
- Requires LinuxMonitor versions >= 2.2.0 for Linux guest operating system.
- Requires Microsoft.Windows versions >= 2.7.0 for Windows guest operating system.
- Fix clearing of events when fault deletion was missed. (ZPS-725)
- Fix spurious "unable to subscribe for events" events and logs. (ZPS-858)
- Added support for UCS Manager collection intervals. (ZEN-25830)
- Enhanced automatic clears for CIMC events. (ZPS-904)
- Fix "Maximum sessions reached" error on CIMC 2.0(6d) firmware. (ZPS-837)
2.5.5
- Fix warnings in modeling results. (ZPS-645)
- Fix CIMC "Maximum sessions reached" error. (ZPS-227)
2.5.4
- Fix collection stall caused by interrupted connectivity. (ZPS-503)
2.5.1
- Clarify and reduce chassis and server events (ZEN-25740)
- Fix zCredentialsZProperties override warning on Zenoss 5.2 (ZEN-26164)
2.5.0
- Added support for UCS Manager 3.1.
- Added support for C3260 chassis managed by UCS Manager.
- Added support for multiple chassis UCS Mini domains. (ZEN-24746)
- Added UCSM Domain Type (Classic or Mini) to device overview.
- Added DynamicView and Impact support for CIMC devices.
- Added icons for UCS CIMC components. (ZEN-14383)
- Added display of distinguished name for CIMC components. (ZEN-14384)
- Added support for alternative port/SSL for CIMC device connections.
- Separated "UCS Manager" and "UCS CIMC" Analytics bundles. (ZEN-24837)
- Improved CIMC session handling support to reduce session exhaustion errors. (ZEN-15925)
- Fixed many issues in "Cisco UCS Manager" and "Cisco UCS CIMC" Analytics domains.
- Fixed unrecognized component statuses for CIMC components. (ZEN-16386)
- Fixed "NoneType" errors in zenimpactstate update log. (ZEN-24872)
- Fixed "zCredentialsZProperties" error on Zenoss 4. (ZEN-25521)
- Fixed "failed converting" errors in zenucsevents log. (ZEN-25465)
- Fixed OS/HW edit link on device overview. (ZEN-24791)
- Associated blade server slot events with blade server. (ZEN-17539)
- Fixed unnecessary updates being made during modeling. (ZEN-24420)
- Removed passwords from debug log output. (ZEN-23587)
2.4.5
- Fix collection stall caused by interrupted connectivity. (ZPS-503)
2.4.4
- Fix migration issue related to ucsLayer2Catalog.
2.4.3
- Fix for undefined componentType variable. (ZEN-23459)
2.4.2
- Fix for all CIMC fault events occurring in August 2014. (ZEN-23438)
2.4.1
- Optimization improvements for UCS Layer2 Linkable components. (ZEN-19856)
- Status map for storageLocalDisk has been updated with JBOD and Global Hot Spare drive states. (ZEN-22829)
2.4.0
- Show bound equipment stats for vNICs.
- Fix UCS overview display issue on Zenoss 4. (ZEN-22862)
2.3.4
- Fix re-opening of events when UCS deletes them. (ZEN-22420)
2.3.3
- Fix potential Impact modeling performance issue.
2.3.2
- Fix failure to receive UCS events. (ZEN-21847)
- Fix modeling issues with more than 10 chassis. (ZEN-21483)
2.3.1
- Add rack servers to hardware inventory report. (ZEN-20901)
- Prevent adding invalid text as address for UCS domain. (ZEN-20825)
- Fix potential ImportError when used with older vSphere versions. (ZEN-20789)
- Fix potential unicode decode error during modeling. (ZEN-21164)
2.3.0
- On Migration, replaces the following graphs if they exist
(ZEN-19377):
- Chassis: Power
- Ethernet Port: Errors, Loss Stats, Pause Stats, Received Packets, Sent Packets, Throughput
- Fabric Extender: Temperature
- Fabric Interconnect: CPU Utilization, Memory Utilization, Temperatures
- Fan Module: Fan Speeds, Temperature
- Fibre Channel Port: Errors, Throughput
- Host Ethernet Interface: Received Bytes, Received Packets, Sent Bytes, Sent Packets
- Power Supply Unit: Temperatures, Voltages, Current, Power
- Processor Unit: Temperature, Current
- Add zCiscoUCSManagerPerfInterval property to configure stats collection interval. (ZEN-19932)
- Move devices from /CiscoUCS and /CiscoUCS/UCS-M into /CiscoUCS/UCS-Manager. (ZEN-19887)
- Add Racks to Dynamic View for Mini (ZEN-19792)
2.2.1
- Fix relationship from HBAs to their adaptor.
- Fix potential missed linkage of service profiles to vSphere hosts. (ZEN-18631)
2.2.0
- Major upgrade adding new components:
- Now supports M and Mini
- Added FI-IO Modules, Shared Adaptors, Cartridge Servers
- Added Uplink Port Channel components for Fabric Ethernet LAN Port Channels, Fabric Fibre Channel SAN Port Channels and Fabric Fibre Channel over Ethernet SAN Port Channels
- Updates model, monitoring and analytics
- Now supported Zenoss >= 4.2
- Replace /CiscoUCS/UCS-M device class with /CiscoUCS/UCS-Manager.
2.1.1
- Fix potential '__dict__' modeling error. (ZEN-17195)
2.1.0
- Major upgrade adding new components:
- Backplane Ports, Fabric Extenders, Fabric Ports, Fans, IO Modules
- Host Bus Adaptors, Organizations, Rack Servers, Virtual HBAs
- Updates model, monitoring and analytics
- Now supported Zenoss >= 4.2
1.9.3
- Remove unused Software link from UCS device navigation. (ZEN-14567)
1.9.2
- Log CIMC API call details at DEBUG level. (ZEN-15770)
- Handle missing CIMC classes gracefully. (ZEN-15924)
- Add support for monitoring stats in Zenoss 5. (ZEN-15395)
- Handle local disk "online" status correctly.
- Use TLSv1 instead of SSLv3 for CIMC. (ZEN-16326)
- Fix "FunctionCache" installation error on Zenoss 4.1. (ZEN-16339)
1.9.1
- Change normal RAID battery statuses from error to clear. (ZEN-15531)
- Stop sending events that will be immediately aged. (ZEN-15004)
1.9.0
- Add support for C-Series and E-Series servers.
- Default to monitoring over HTTPS instead of HTTP.
- Make Free Slots and Hardware Inventory reports exportable.
1.8.5
- Reconnect for events after 10 seconds. (ZEN-12858)
- Improve model and performance ETL for Analytics.
- Add support for zCredentialsZProperties.
1.8.4
- Associate more events with modeled components. (ZEN-9955)
1.8.3
- Fix collection issue introduced in 1.8.2. (ZEN-10211)
1.8.2
- Fix y-axis scale on Chassis Power graph.
- Reduce logins to UCS Manager to absolute minimum.
1.8.1
- Fix clearing for UCS fault events.
- Create events for all open faults upon initial connection.
- Add description to UCS fault events with no description.
- Add "--task" command line option to zenucsevents.
1.8.0
- Add discovery of Management Interfaces.
- Fix association of syslogs and SNMP traps for alternative management addresses.