Multi-Realm IP Networks
ZenPacks.zenoss.MultiRealmIP
The ZenPacks.zenoss.MultiRealmIP ZenPack extends the modeling, monitoring, and event management features of Zenoss platform to accommodate overlapping IP namespaces.
Note: This ZenPack is not installed when Zenoss platform is installed. To download it, visit the Zenoss Support site.
With this ZenPack, Zenoss platform can prefix a realm identifier to the IP addresses of a network, enabling unified monitoring.
There are two primary use cases for using multi-realm IP management.
- A large company that manages multiple locations that have the same network spaces defined across these multiple locations and as a result have created multiple overlapping IP spaces and Zenoss platform needs a way to identify each separate IP space in the system.
- Service Providers responsible for monitoring multiple customers where the customers have created independent networks and IP spaces that are unique to their location, but not unique to the Service Provider.
The essential workflow for creating and using IP Realms is that first you need to create the IP realms and then associate these realms with a collector. The associations between IP Realms and actual devices is made automatically by the device's association with the collector. All devices on a collector are associated with the realm for that collector.
Commercial
This ZenPack is developed and supported by Zenoss Inc. Commercial ZenPacks are available to Zenoss commercial customers only. Contact Zenoss to request more information regarding this or any other ZenPacks. Click here to view all available Zenoss Commercial ZenPacks.
Support
This ZenPack is included with commercial versions of Zenoss and enterprise support for this ZenPack is provided to Zenoss customers with an active subscription.
Prerequisites
Before setting up multi-realms, you must delete all Zenoss platform networks. (These are automatically recreated.)
| Prerequisite | Restriction |
|---|---|
| Product | Zenoss platform 4.x, 5.x |
| Required ZenPacks | ZenPacks.zenoss.DistributedCollector |
Example System
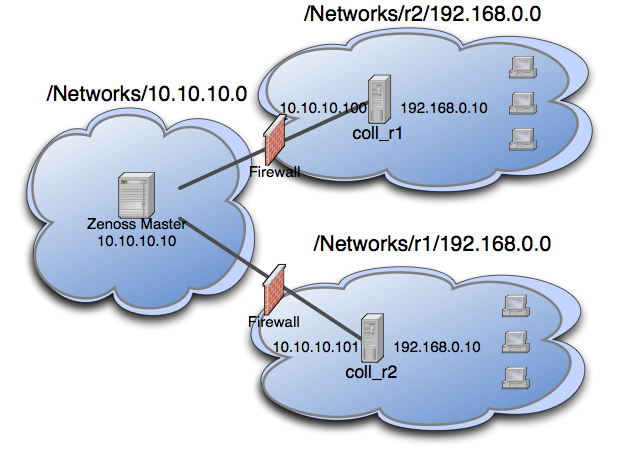
The following diagram lays out an example setup. It has a central Zenoss platform server in the 10.10.10.0/24 network. The network local to the server is considered the default network within the system. The default network is treated exactly the same as a Zenoss platform system without this ZenPack installed.
There are two other networks shown (r1 and r2) which are behind a
firewall and have the same IP space 192.168.0.0/24. Each realm has a
distributed collector located within it. The collector can be accessed
from the Zenoss platform server using a IP translation from the firewall
to map the address accessible from in front of the firewall to an
address behind the firewall. Remote collectors in a multi-realm setup
must be accessible from the central server using SSH.
Example IP Realm
System Setup
Set up Zenoss platform following the example system described previously.
Tip: If you do not have overlapping IP space this example can be created using collectors within the same network. To create the example, add a machine multiple times once per collector, making sure to change the name of the device as it is added. The result is similar to a real realm setup.
Under multi-realm IP networks, device names must be unique even though the IP addresses will overlap.
On certain server configurations, if a distributed collector is configured, a "zenpack command failed" error occurs when installing this ZenPack. If you encounter this error, then run the following grant (as MySQL root):
grant super on *.* to 'zenoss'@'{FQDN_of_Zenoss_host}' identified by 'zenoss';
where the first zenoss is the user account that Zenoss platform uses
to access MySQL, and the second zenoss is that account's password.
Adding Realms
- Go to Infrastructure > Networks.
- From the Add menu, select Add IP Realm. Add the realms
r1andr2.
Adding Collectors to Realms
- Add the two collectors that are installed in each realm. Distributed collectors now have an IP Realm field on their configuration screen set each collector to the appropriate realm configured above.
- Change each collector so that it is in the correct realm.
Adding Devices to Realms
- Now we are ready to add devices to the system. As mentioned above,
adding the same device to the system twice can simulate a
multi-realm setup. Add a device called
A.testmaking sure that when it is added the collector is set to one of the remote collectors, and notlocalhost. - Now rename the device.
- Add the device a second time using your other collector, again not
localhost. - After the device is loaded, select Software and follow the network link on one of the interfaces. Notice that the network has been created underneath the realm created earlier. This configuration is at the heart of multi-realm, as networks are discovered they are created within each realm. Monitoring is now happening on each representation of the device from the different collectors in different overlapping realms.
As another test try searching by IP from the top-level search. Two devices will be returned -- one within each realm.
Notes
- If an event contains the unique name of a device then it is straight-forward to assign it to the proper device. If only the IP address is sent the event will be assigned by looking up the IP within the context of the realm.
- If a device is moved between realms it must be remodeled so that its IPs are placed in the proper location.
- The Network Map only supports the display the default realm.